|
Negeri Sembilan Malay Language
Negeri Sembilan Malay (; also known as or ) is an Austronesian language spoken mainly in the Malaysian state of Negeri Sembilan and in northern Malacca in Alor Gajah. The language is spoken by the descendants of Minangkabau settlers from Sumatra, who have migrated to Negeri Sembilan since as early as the 14th century. It is often considered a variant or dialect of the Minangkabau language; lexical and phonological studies, however, indicate that it is more closely related to Standard Malay than it is to Minangkabau. History The Minangkabau people began migrating from the Sumatra highlands to the Malay Peninsula in the 14th century. Migration skyrocketed from the 15th century to the 16th century. At that time, trade activity through the Strait of Malacca increased and many migrants were granted protection by the Malacca Sultanate. From the ports of Malacca, groups and groups of Minangkabau settlers started venturing inland. This was the first migration wave of Minangkabau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two regions: Peninsular Malaysia and Borneo's East Malaysia. Peninsular Malaysia shares a land and maritime Malaysia–Thailand border, border with Thailand and Maritime boundary, maritime borders with Singapore, Vietnam, and Indonesia. East Malaysia shares land and maritime borders with Brunei and Indonesia, and a maritime border with the Philippines and Vietnam. Kuala Lumpur is the national capital, the country's largest city, and the seat of the Parliament of Malaysia, legislative branch of the Government of Malaysia, federal government. The nearby Planned community#Planned capitals, planned capital of Putrajaya is the administrative capital, which represents the seat of both the Government of Malaysia#Executive, executive branch (the Cabine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mukim
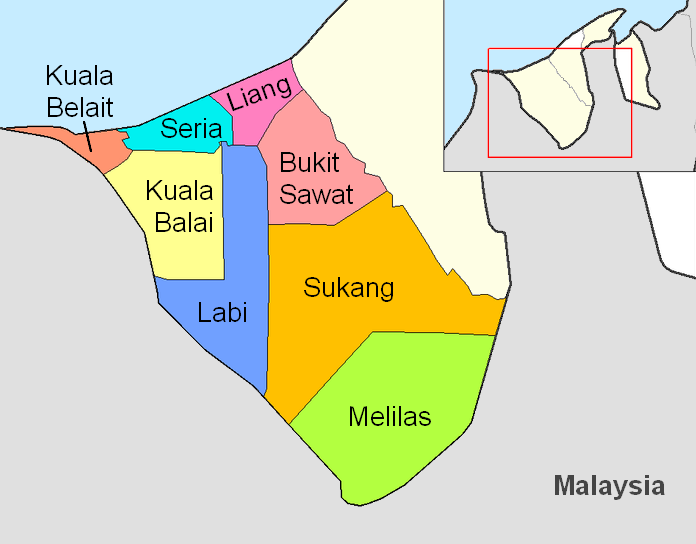
A mukim is a type of administrative division used in Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia and Singapore. The word ''mukim'' is a loanword in English. However, it was also originally a loanword in Malay from the Arabic word: (meaning ''resident''). The closest English translation for mukim is township. Usage Brunei In Brunei, a mukim is the immediate subdivision of a district (). The equivalent English word for 'mukim' is 'township'. There are 38 mukims in Brunei. Each mukim is an administrative area made up of several (Malay for "village"). A mukim is headed by a (Malay for "headman"), which is an elected office. The number of mukims in each of the districts in Brunei is as follows: The smallest mukim by area is Mukim Saba in the Brunei-Muara District. The largest mukim by area is Mukim Sukang in the Belait District. The last change in the mukim boundaries was in the late 1990s when Mukim Kumbang Pasang was merged into Mukim Kianggeh and Mukim Berakas was divided into Muki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaysian Language
Malaysian Malay ( ms, Bahasa Melayu Malaysia), also known as Standard Malay (Malay: ''Bahasa Melayu Standard''), ( English translation: Malaysian language), or simply Malay, is a standardized form of the Malay language used in Malaysia (as opposed to the variety used in Indonesia, which is referred to as the "Indonesian" language). Malaysian Malay is standardized from the Johore-Riau dialect of Malay. It is spoken by much of the Malaysian population, although most learn a vernacular form of Malay or another native language first. Malay is a compulsory subject in primary and secondary schools. Status In Malaysia Article 152 of the Federation designates "Malay" as the official language, but the term "Malaysian" or ''bahasa Malaysia'' is used on official contexts from time to time. The choice of name can be politically contentious; in 1999 the Dewan Bahasa dan Pustaka rejected the publication of some short stories as the preface to the publication used the term ''bahasa Mal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adat Perpatih
Adat Perpatih (also known as Lareh Bodi Caniago) are customary laws which originated from the Minangkabau Highlands in Sumatra, Indonesia. It was founded by a Minangkabau leader named Sutan Balun or more famously known as Dato Perpatih Nan Sebatang. In Malaysia, Adat Perpatih is a combination of practices and rules of life for the Minangkabau people and other aborigins such as Semang, Temuan people, the Bersisi and the Jakun people that were mainly farmers at that time. Over time, this custom is practiced by many other ethnics especially in Negeri Sembilan, including part of Malacca in particular of Masjid Tanah, and part of Johor. Custom The system practices democracy in electing chiefs and a king. Only men are eligible to be elected as leaders for their clan or tribe. There is also a female leader known as Ibu Soko. Their culture is matrilineal and patriarchal, with property and land passing down from mother to daughter, while religious and political affairs are the responsibi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamtuan Besar
Yamtuan, also known officially as Yang di-Pertuan Besar and unofficially as Grand Ruler, is the royal title of the ruler of the states and federal territories of Malaysia, Malaysian state of Negeri Sembilan. The Grand Ruler of Negeri Sembilan is elected by a council of ruling chiefs in the state, or the ''Undangs''. This royal practice has been followed since 1773. The Yamtuan Besar is elected from among the four leading princes of Negeri Sembilan (''Putera Yang Empat''); the Undangs themselves cannot stand for election and their choice of a ruler is limited to a male Muslim who is Malay and also a "lawfully begotten descendant of Raja Radin ibni Raja Lenggang", the 4th Yamtuan. This unique form of government later inspired the first Prime Minister of Malaysia, Tunku Abdul Rahman, to implement a form of rotational constitutional monarchy for a newly independent Federation of Malaya (now Malaysia). Thus, the office of Yang di-Pertuan Agong was created. Early history Early history ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pagaruyung Kingdom
Pagaruyung (ڤاڬارويوڠ; also Pagarruyung, Pagar Ruyung and, Malayapura or Malayupura) was the seat of the Minangkabau kings of Western Sumatra, though little is known about it. Modern Pagaruyung is a village in ''Tanjung Emas'' subdistrict, Tanah Datar regency, located near the town of Batusangkar, Indonesia. History Beginnings Adityawarman is believed to have founded the kingdom and presided over the central Sumatra region between 1347 and 1375, most likely to control the local gold trade. The few artefacts recovered from Adityawarman's reign include a number of stones containing inscriptions, and statues. Some of these items were found at ''Bukit Gombak'', a hill near modern Pagarruyung, and it is believed a royal palace was located there. There is a major gap in the historical picture in the Minangkabau highlands between the last date of Adityawarman's inscription in 1375 and Tomé Pires ''Suma Oriental'', written some time between 1513 and 1515. By the 16th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdul Jalil Shah IV Of Johor
Paduka Sri Sultan ‘Abdu’l Jalil IV Ri’ayat Shah Zillu’llah fi al-’Alam bin Dato’ Bendahara Sri Maharaja Tun Habib Abdul Majid (or simply as Sultan Abdul Jalil Shah IV) was the Sultan and Yang di-Pertuan Besar of Johor and Pahang and their dependencies, who reigned from 1699 to 1718. He was the eldest son of Bendahara Tun Habib Abdul Majid who initially succeeded his father as the Bendahara of Johor in 1697. Following the death of Mahmud Shah II without an heir in 1699, Abdul Jalil was proclaimed as the next sultan. Beginning of Bendahara dynasty Upon the death of Ibrahim Shah in 1685, his ten-year-old son, Mahmud Shah II, ascended the throne while state affairs were left to Bendahara Tun Habib Abdul Majid. As he grew up, Mahmud Shah gained a reputation for his caprice, and Johor gradually descended into a state of chaos. This instability was exacerbated in 1697 by the death of Tun Habib. Although the bendahara's son, Tun Abdul Jalil, inherited the position and mainta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Datuk
Datuk (or its variant Dato or Datu) is a Malay title commonly used in Brunei, Indonesia, and Malaysia, as well as a traditional title by Minangkabau people in West Sumatra, Indonesia. The title of the wife of Datuk is Datin. Origin The oldest historical records mentioning about the title ''datuk'' is the 7th century Srivijayan inscriptions such as Telaga Batu from Palembang, Indonesia, to describe lesser kings or vassalized kings. It was called ''dātu'' in Old Malay language to describe regional leader or elder, a kind of chieftain that rules of a collection of ''kampungs'' (villages) called Kedatuan. The Srivijaya empire was described as a network or mandala that consisted of settlements, villages, and ports each ruled by a datu that vowed their loyalty (''persumpahan'') to the central administration of Srivijayan Maharaja. Unlike the indianized title of raja and maharaja, the term datuk was also found in the Philippines as datu, which suggests its common native Austronesi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buginese People
The Bugis people (pronounced ), also known as Buginese, are an ethnicity—the most numerous of the three major linguistic and ethnic groups of South Sulawesi (the others being Makassar and Toraja), in the south-western province of Sulawesi, third-largest island of Indonesia. The Bugis in 1605 converted to Islam from Animism. The main religion embraced by the Bugis is Islam, with a small minority adhering to Christianity or a pre-Islamic indigenous belief called ''Tolotang''. Despite the population numbering only around six million, the Bugis are influential in the politics in modern Indonesia, and historically influential on the Malay peninsula, Sumatra, Borneo, Lesser Sunda Islands and other parts of the archipelago where they have migrated, starting in the late seventeenth century. The third president of Indonesia, B. J. Habibie, and a former vice president of Indonesia, Jusuf Kalla, are Bugis. In Malaysia, the former prime minister Muhyiddin Yassin has Bugis ancestry. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johor Sultanate
The Johor Sultanate ( ms, Kesultanan Johor or ; also called the Sultanate of Johor, Johor-Pahang, or the Johor Empire) was founded by Malaccan Sultan Mahmud Shah's son, Sultan Alauddin Riayat Shah II in 1528. Johor was part of the Malaccan Sultanate before the Portuguese conquered Malacca's capital in 1511. At its height, the sultanate controlled modern-day Johor, Pahang, Terengganu, and territories stretching from the river Klang to the Linggi and Tanjung Tuan, Muar, Batu Pahat, Singapore, Pulau Tinggi and other islands off the east coast of the Malay peninsula, the Karimun islands, the islands of Bintan, Bulang, Lingga and Bunguran, and Bengkalis, Kampar and Siak in Sumatra. During the colonial era, the mainland part was administered by the British, and the insular part by the Dutch, thus breaking up the sultanate into Johor and Riau. In 1946, the British section became part of the Malayan Union. Two years later, it joined the Federation of Malaya and subsequently ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Undang
An Undang is a ruling chief or territorial chief who still play an important role in the state of Negeri Sembilan, Malaysia. The name is believed to be derived from the Malay word ''undang-undang'' meaning "law". The Minangkabau who settled at Negeri Sembilan, in present-day Malaysia at the end of the 17th century ruled by a ''"penghulu"'' or headman who was chosen from the noble families of Sakai and Jakun called Biduanda. These ''"penghulus"'', notably that of Sungai Ujong, Jelebu, Johol and Rembau became powerful enough to exalt themselves above other ''"penghulus"''. These penghulus later acknowledged by the Sultan of the old Johor Empire as a sovereign in their own territory. By the early part of the 18th Century, the leaders of these four territories started calling themselves "Undang". Malaysia's modern day constitution confirms the status of the Undang under Article 71, 160, 181 and Eight Schedule of Federal Constitution as Malay Ruler within the Federation. Undangs are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nagari (settlement)
A nagari is a semi-autonomous Minangkabau people regional administrative unit in West Sumatra, Indonesia. From 1983-1999 the national government attempted to apply the Javanese ''desa'' village system to other ethnic groups throughout Indonesia, and in 1983 the traditional Minangkabau ''nagari'' village units were split into smaller ''jorong'' units, with some disruption to traditional nagari-centred social and cultural institutions. However following restoration of the role of the ''nagari'' in rural Minangkabau society after 1999 residence and employment in a ''nagari'' is still an aspect of social identity, just as residence in the smaller ''jorong'', or membership of a clan. Etymology Nagari comes from the Sanskrit word ' () which means land or realm. History The nagari system already existed before the Dutch colonial times as "autonomous village republics" in Minangkabau society. The nagari comprises five fundamental institutions : it must have a road (berlebuh), bathing p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

.jpg)
