|
Negative Partisanship
Negative partisanship is the tendency of some voters to form their political opinions primarily in opposition to political parties they dislike. Whereas traditional partisanship involves supporting the policy positions of one's own party, its negative counterpart in turn means opposing those positions of a disliked party. It has been claimed to be the cause of severe polarization in American politics. It has also been studied in the Canadian context, as well as in Australia and New Zealand. Cross-national studies indicate that negative partisanship undermines public satisfaction with democracy, which threatens democratic stability. Traditional partisans, on the other hand, are more likely to support their country's democracy, which promotes democratic stability. United States Alan Abramowitz, a professor of political science at Emory University, likens negative partisanship to a sports rivalry, where members of one side may have internal disagreements but are motivated to a fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Party
A political party is an organization that coordinates candidates to compete in a particular country's elections. It is common for the members of a party to hold similar ideas about politics, and parties may promote specific political ideology, ideological or policy goals. Political parties have become a major part of the politics of almost every country, as modern party organizations developed and spread around the world over the last few centuries. It is extremely rare for a country to have Non-partisan democracy, no political parties. Some countries have Single-party state, only one political party while others have Multi-party system, several. Parties are important in the politics of autocracies as well as democracies, though usually democracies have more political parties than autocracies. Autocracies often have a single party that governs the country, and some political scientists consider competition between two or more parties to be an essential part of democracy. Part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voter Turnout
In political science, voter turnout is the participation rate (often defined as those who cast a ballot) of a given election. This can be the percentage of registered voters, eligible voters, or all voting-age people. According to Stanford University political scientists Adam Bonica and Michael McFaul, there is a consensus among political scientists that "democracies perform better when more people vote." Institutional factors drive the vast majority of differences in turnout rates.Michael McDonald and Samuel Popkin"The Myth of the Vanishing Voter"in American Political Science Review. December 2001. p. 970. For example, simpler parliamentary democracies where voters get shorter ballots, fewer elections, and a multi-party system that makes accountability easier see much higher turnout than the systems of the United States, Japan, and Switzerland. Significance Some parts of society are more likely to vote than others. As turnout approaches 90%, significant differences between vot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
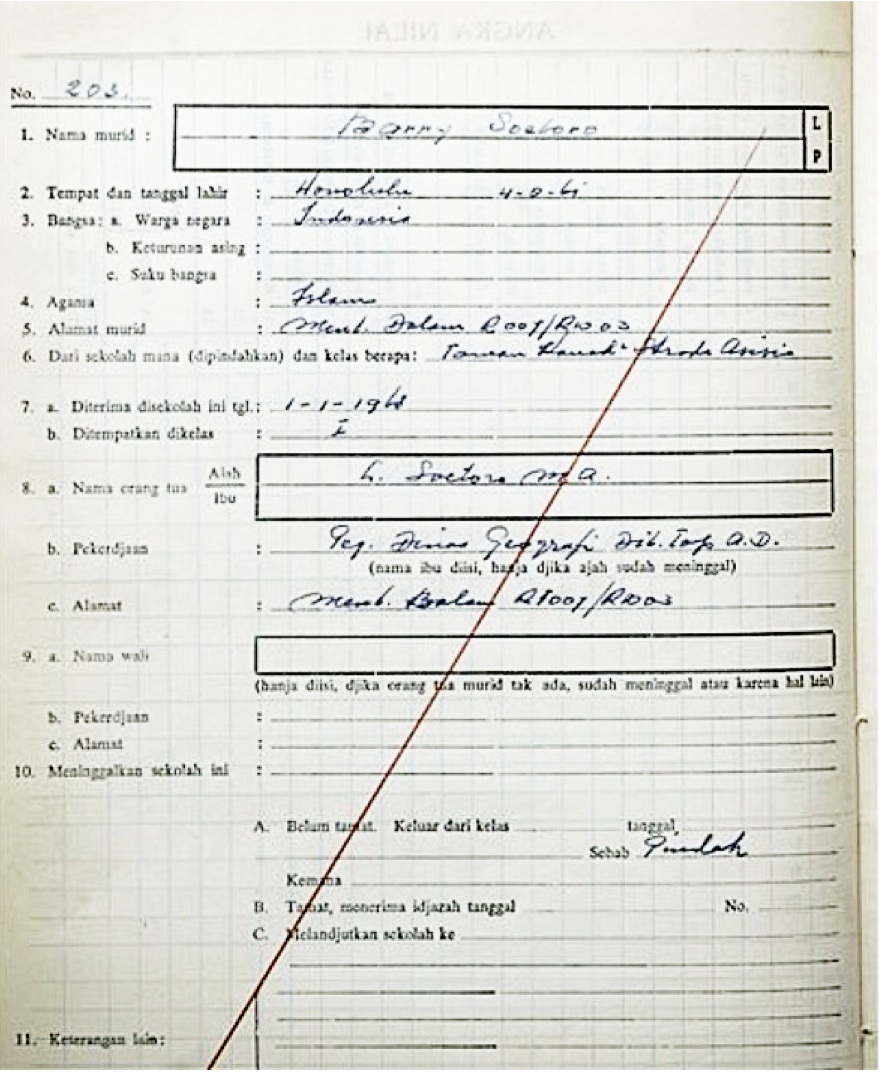
Gary Berntson
Gary Berntson (born 1945) is an emeritus professor at Ohio State University with appointments in the departments of psychology, psychiatry and pediatrics. He is an expert in psychophysiology, neuroscience, biological psychology, and with his colleague John Cacioppo, a founding father of social neuroscience. His research attempts to elucidate the functional organization of brain mechanisms underlying behavioral and affective processes, with a special emphasis on social cognition. Background Berntson studied biology and psychology at the University of Minnesota, and was awarded a Ph.D. (psychobiology and life sciences) in 1971. He then worked as a post-doc fellow with Neal Miller at Rockefeller University in the department of psychology between 1971 and 1973. Since 1973, Berntson is on the faculty at the Ohio State University. Awards and Professional Activities Berntson is a past president of the Society for Psychophysiological Science, and is currently a fellow of that organi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John T
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died c. AD 30), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (lived c. AD 30), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope Joh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left–right Political Spectrum
The left–right political spectrum is a system of classifying political positions characteristic of left-right politics, ideologies and parties with emphasis placed upon issues of social equality and social hierarchy. In addition to positions on the left and on the right, there are centrists or moderates who are not strongly aligned with either end of the spectrum. On this type of political spectrum, left-wing politics and right-wing politics are often presented as opposed, although a particular individual or group may take a left-wing stance on one matter and a right-wing stance on another; and some stances may overlap and be considered either left-wing or right-wing depending on the ideology. In France, where the terms originated, the left has been called "the party of movement" and the right "the party of order". Ambrose Bierce's 1911 Devil's Dictionary characterized the right/left distinction, at the same time wryly noting each side's opinion of the other, by defining a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Ideology
An ideology is a set of beliefs or philosophies attributed to a person or group of persons, especially those held for reasons that are not purely epistemic, in which "practical elements are as prominent as theoretical ones." Formerly applied primarily to economic, political, or religious theories and policies, in a tradition going back to Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels, more recent use the term as mainly condemnatory. The term was coined by Antoine Destutt de Tracy, a French Enlightenment aristocrat and philosopher, who conceived it in 1796 as the "science of ideas" to develop a rational system of ideas to oppose the irrational impulses of the mob. In political science, the term is used in a descriptive sense to refer to political belief systems. Etymology and history The term ''ideology'' originates from French ''idéologie'', itself deriving from combining (; close to the Lockean sense of ''idea'') and '' -logíā'' (). The term ideology, and the system of ideas associ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group Identity
Collective identity is the shared sense of belonging to a group. In sociology In 1989, Alberto Melucci published ''Nomads of the Present'', which introduces his model of collective identity based on studies of the social movements of the 1980s. Melucci based his ideas on the writings by Touraine (1925- ) and Pizzorno (1924-2019), specifically their ideas on social movements and collective action respectively. Alberto Melucci writes: "collective identity is an interactive and shared definition produced by several individuals (or groups at a more complex level) and concerned with the orientation of action and the field of opportunities and constraints in which the action takes place". Unsatisfied with the gap between theories on how collective actions form and how individuals find motivation, Melucci defines an intermediate process, in which individuals recognize that they share certain orientations in common and on that basis decide to act together. He considers collective iden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Université De Montréal
The Université de Montréal (UdeM; ; translates to University of Montreal) is a French-language public research university in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. The university's main campus is located in the Côte-des-Neiges neighborhood of Côte-des-Neiges–Notre-Dame-de-Grâce on Mount Royal near the Outremont Summit (also called Mount Murray), in the borough of Outremont. The institution comprises thirteen faculties, more than sixty departments and two affiliated schools: the Polytechnique Montréal (School of Engineering; formerly the École polytechnique de Montréal) and HEC Montréal (School of Business). It offers more than 650 undergraduate programmes and graduate programmes, including 71 doctoral programmes. The university was founded as a satellite campus of the Université Laval in 1878. It became an independent institution after it was issued a papal charter in 1919 and a provincial charter in 1920. Université de Montréal moved from Montreal's Quartier Latin to its pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the United States. He previously served as a U.S. senator from Illinois from 2005 to 2008 and as an Illinois state senator from 1997 to 2004, and previously worked as a civil rights lawyer before entering politics. Obama was born in Honolulu, Hawaii. After graduating from Columbia University in 1983, he worked as a community organizer in Chicago. In 1988, he enrolled in Harvard Law School, where he was the first black president of the '' Harvard Law Review''. After graduating, he became a civil rights attorney and an academic, teaching constitutional law at the University of Chicago Law School from 1992 to 2004. Turning to elective politics, he represented the 13th district in the Illinois Senate from 1997 until 2004, when he ran for the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Cook Political Report
''The Cook Political Report with Amy Walter'' is an American online newsletter that analyzes elections and campaigns for the U.S. Presidency, the United States Senate, the United States House of Representatives, and U.S. governors' offices. Self-described as independent and nonpartisan, it was founded by political analyst Charlie Cook in 1984. Amy Walter is the editor, publisher, and owner. The Cook Political Report with Amy Walter was previously a hard-copy publication known as The Cook Political Report. The Report moved to an all-online format in 2004. On July 30, 2021, the publication name changed to "The Cook Political Report with Amy Walter," as Walter took full control of the website and Cook decided to focus on writing and speeches. Reports include Charlie Cook's two weekly columns for ''National Journal'' magazine and ''National Journal Daily''. In addition, changes are generally made each week to The Cook Political Report's House, Senate, and Governors At-A-Glance ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Wasserman
David Nathan Wasserman (born September 13, 1984) is an American political analyst known for his coverage of elections to the United States House of Representatives. He has worked as an editor at the nonpartisan election analysis newsletter ''The Cook Political Report with Amy Walter'' since 2007 and is a contributor to NBC News. Wasserman is considered an expert on redistricting in the United States. Early life and education Wasserman grew up in Montgomery Township, New Jersey where he attended Montgomery High School as part of the class of 2002. He attended the University of Virginia, where he studied government. As a student, he worked for ''Sabato's Crystal Ball'', serving as its House Editor for three years. In that role, he correctly predicted that the Democratic Party would gain 29 seats in the 2006 United States House of Representatives elections. Wasserman graduated from the university with distinction in 2006 and was awarded the Emmerich-Wright Prize for his thesis on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |