|
Neffs Cave (Utah)
Neffs Cave (or Neffs Canyon Cave) is a cave in Neffs Canyon on the north side of Mount Olympus, Utah, in the United States. It is one of the deepest caves in the United States but is seldom entered despite its depth and its proximity to Salt Lake City. The United States Forest Service has closed the cave to the public for many years due to safety hazards. In 1977, Neffs Canyon Cave was designated as a National Natural Landmark by the National Park Service. Discovery and exploration Neffs Cave was discovered in 1949 by two teenage brothers, John and Jamie Lyon, who were hiking in Neffs Canyon. They returned to the cave several times to explore its depths but lacked the proper equipment to reach the bottom. In one of their last visits, John Lyon and a group of friends became trapped at the bottom of a steep slope of crumbly shale and had to be extracted by a rescue party, headed by his brother Jamie Lyon. After the rescue, word about the cave began to spread. A party of inexperien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt Lake County
Salt Lake County is located in the U.S. state of Utah. As of the 2020 United States Census, the population was 1,185,238, making it the most populous county in Utah. Its county seat and largest city is Salt Lake City, the state capital. The county was created in 1850. Salt Lake County is the 37th most populated county in the United States and is one of four counties in the Rocky Mountains to make it into the top 100. (Others being Denver County and El Paso County, Colorado and Clark County, Nevada.) Salt Lake County is the only county of the first class in Utah - under the Utah Code (Title 17, Chapter 50, Part 5) is a county with a population of 700,000 or greater. Salt Lake County occupies the Salt Lake Valley, as well as parts of the surrounding mountains, the Oquirrh Mountains to the west and the Wasatch Range to the east (essentially the entire Jordan River watershed north of the Traverse Mountains). In addition, the northwestern section of the county includes part of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fault (geology)
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep. A ''fault plane'' is the plane that represents the fracture surface of a fault. A ''fault trace'' or ''fault line'' is a place where the fault can be seen or mapped on the surface. A fault trace is also the line commonly plotted on geologic maps to represent a fault. A ''fault zone'' is a cluster of parallel faults. However, the term is also used for the zone of crushed rock along a single fault. Prolonged motion along closely spaced faults can blur the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caves Of Utah
A cave or cavern is a natural void in the ground, specifically a space large enough for a human to enter. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. The word ''cave'' can refer to smaller openings such as sea caves, rock shelters, and grottos, that extend a relatively short distance into the rock and they are called ''exogene'' caves. Caves which extend further underground than the opening is wide are called ''endogene'' caves. Speleology is the science of exploration and study of all aspects of caves and the cave environment. Visiting or exploring caves for recreation may be called ''caving'', ''potholing'', or ''spelunking''. Formation types The formation and development of caves is known as ''speleogenesis''; it can occur over the course of millions of years. Caves can range widely in size, and are formed by various geological processes. These may involve a combination of chemical processes, erosion by water, tectonic forces, microorgani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Caves
This is a list of caves of the world that have articles or that are properly cited. They are sorted by continent and then country. Caves which are in overseas territories on a different continent than the home country are sorted by the territory's continent and name. Africa File:Cango Caves, Western Cape (6253225986).jpg, The Cango caves in western cape. File:African cave paintings.jpg, African cave paintings. File:Lithic Industries at Blombos Cave, Southern Cape, South Africa (c. 105 – 90 Ka).jpg, Lithic Industries at Blombos Cave, Southern Cape, South Africa. File:Wonder Caves Praying Mary.JPG, Wonder Caves Praying Mary. Algeria * Aïn Taïba * Anou Achra Lemoun * Anou Boussouil * Anou Ifflis * Anou Timedouine * Gueldaman caves * Ghar Boumâaza * Grotte de Cervantes * Kef Al Kaous * Rivière De La Tafna Botswana * Gcwihaba * Rhino Cave Cameroon * Gouffre de Mbilibekon * Grottes de Linté * Grotte de Loung * Grotte de Mfouda * Grotte Fovu [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grotto
A grotto is a natural or artificial cave used by humans in both modern times and antiquity, and historically or prehistorically. Naturally occurring grottoes are often small caves near water that are usually flooded or often flooded at high tide. Sometimes, artificial grottoes are used as garden features. The '' Grotta Azzurra'' at Capri and the grotto at Tiberius' Villa Jovis in the Bay of Naples are examples of popular natural seashore grottoes. Whether in tidal water or high up in hills, grottoes are generally made up of limestone geology, where the acidity of standing water has dissolved the carbonates in the rock matrix as it passes through what were originally small fissures. Etymology The word ''grotto'' comes from Italian ''grotta'', Vulgar Latin ''grupta'', and Latin ''crypta'' ("a crypt"). It is also related by a historical accident to the word ''grotesque''. In the late 15th century, Romans accidentally unearthed Nero's ''Domus Aurea'' on the Palatine Hill, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caving
Caving – also known as spelunking in the United States and Canada and potholing in the United Kingdom and Ireland – is the recreational pastime of exploring wild cave systems (as distinguished from show caves). In contrast, speleology is the scientific study of caves and the cave environment.Caving in New Zealand (from Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand, Accessed 2012-11.) The challenges involved in caving vary according to the cave being visited; in addition to the total absence of light beyond the entrance, negotiating pitches, squeezes, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cave Research Foundation
The Cave Research Foundation (CRF) is an American private, non-profit group dedicated to the exploration, research, and conservation of caves. The group arose in the early 1950s from the exploration efforts at Floyd Collins Crystal Cave, now within Mammoth Cave National Park. Its stated goals were: to promote exploration and documentation of caves and karst areas, initiate and support cave and karst research, aid in cave conservation and protection, and to assist with the interpretation of caves and karst to the public. Growth CRF officially incorporated in 1957 under the laws of the Commonwealth of Kentucky. The Guadalupe Cave Survey, explorers at Carlsbad Caverns National Park, New Mexico, became part of CRF in 1971. In 1976, cave survey at Sequoia National Park/Kings Canyon National Park, California, and Buffalo National River, Arkansas, became CRF projects. Additional cave projects in Cumberland Gap National Historic Park, Kentucky; Lava Beds National Monument, California; and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cave Conservancies
A cave conservancy is a specialized land trust that primarily manages caves or karst features in the United States. Organizations that serve as cave management consultants to cave owners are usually considered cave conservancies. Almost all cave conservancies are non-profit organizations, but their management methodologies may be diverse. Cave conservancies often provide other services such as being advocates for responsible cave ownership and management, promoting the protection of caves, and advancing research to enhance and discover the values of caves. History Cave management before 1963 Historically, caves have been managed many different ways, from benign neglect to commercialization or other forms of exploitation with widely varying results. Some people saw commercial potential in caves and the development and profit provided the incentive for ownership and a form of conservation. The 19th century public interest in caves as natural curiosities may have led to the increas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
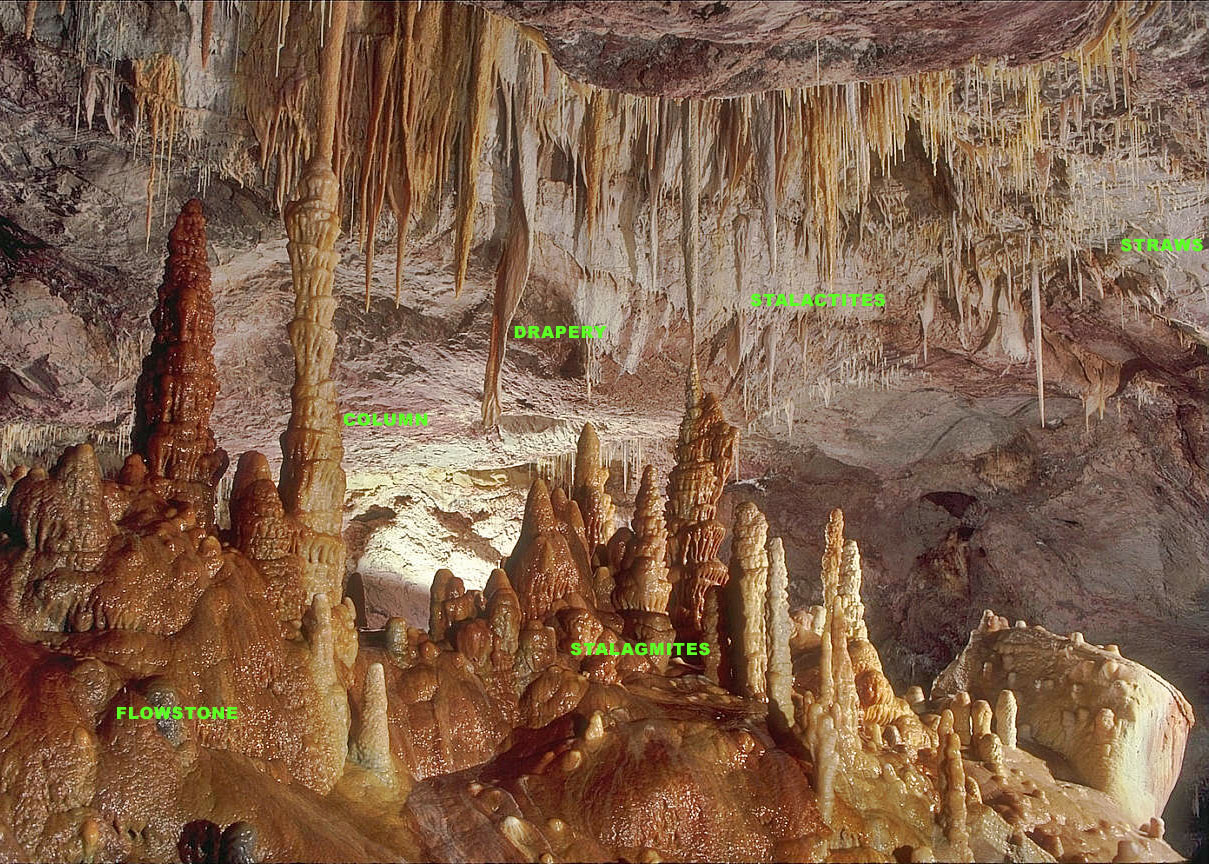
Stalactite
A stalactite (, ; from the Greek 'stalaktos' ('dripping') via ''stalassein'' ('to drip') is a mineral formation that hangs from the ceiling of caves, hot springs, or man-made structures such as bridges and mines. Any material that is soluble and that can be deposited as a colloid, or is in suspension, or is capable of being melted, may form a stalactite. Stalactites may be composed of lava, minerals, mud, peat, pitch, sand, sinter, and amberat (crystallized urine of pack rats). A stalactite is not necessarily a speleothem, though speleothems are the most common form of stalactite because of the abundance of limestone caves. The corresponding formation on the floor of the cave is known as a stalagmite. Mnemonics have been developed for which word refers to which type of formation; one is that ''stalactite'' has a C for "ceiling", and ''stalagmite'' has a G for "ground". Another example is that ''stalactites'' "hang on ''T''ight" and ''stalagmites'' "''M''ight grow up" � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flowstone
Flowstones are sheetlike deposits of calcite or other carbonate minerals, formed where water flows down the walls or along the floors of a cave. They are typically found in "solution caves", in limestone, where they are the most common speleothem. However, they may form in any type of cave where water enters that has picked up dissolved minerals. Flowstones are formed via the degassing of vadose percolation waters. Flowstone may also form on manmade structures as a result of calcium hydroxide being leached from concrete, lime or mortar. These secondary deposits created outside the cave environment, which mimic the shapes and forms of speleothems, are classified as "calthemites" and are associated with concrete degradation.Smith, G.K., (2016). “Calcite Straw Stalactites Growing From Concrete Structures”, Cave and Karst Science, Vol.43, No.1, P.4-10, (April 2016), British Cave Research Association, ISSN 1356-191X. Formation Flowing films of water that move along floors or do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speleothem
A speleothem (; ) is a geological formation by mineral deposits that accumulate over time in natural caves. Speleothems most commonly form in calcareous caves due to carbonate dissolution reactions. They can take a variety of forms, depending on their depositional history and environment. Their chemical composition, gradual growth, and preservation in caves make them useful paleoclimatic proxies. Chemical and physical characteristics More than 300 variations of cave mineral deposits have been identified. The vast majority of speleothems are calcareous, composed of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) minerals (calcite or aragonite). Less commonly, speleothems are made of calcium sulfate (gypsum or mirabilite) or opal. Speleothems of pure calcium carbonate or calcium sulfate are translucent and colorless. The presence of iron oxide or copper provides a reddish brown color. The presence of manganese oxide can create darker colors such as black or dark brown. Speleothems can also be brown d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinkhole
A sinkhole is a depression or hole in the ground caused by some form of collapse of the surface layer. The term is sometimes used to refer to doline, enclosed depressions that are locally also known as ''vrtače'' and shakeholes, and to openings where surface water enters into underground passages known as ''ponor'', swallow hole or swallet. A ''cenote'' is a type of sinkhole that exposes groundwater underneath. A ''sink'' or ''stream sink'' are more general terms for sites that drain surface water, possibly by infiltration into sediment or crumbled rock. Most sinkholes are caused by karst processes – the chemical dissolution of carbonate rocks, collapse or suffosion processes. Sinkholes are usually circular and vary in size from tens to hundreds of meters both in diameter and depth, and vary in form from soil-lined bowls to bedrock-edged chasms. Sinkholes may form gradually or suddenly, and are found worldwide. Formation Natural processes Sinkholes may capture surf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)