|
Nectocaris
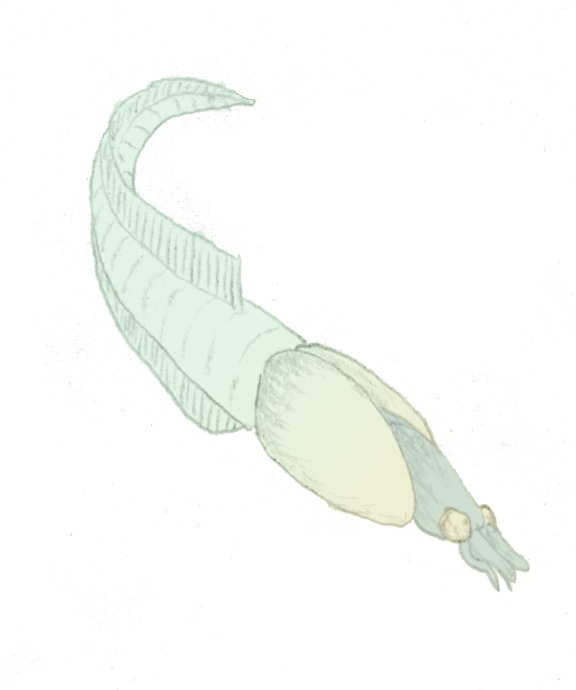
''Nectocaris'' is a genus of squid-like animal of controversial affinities known from the Cambrian period. The initial fossils were described from the Burgess Shale of Canada. Other similar remains possibly referrable to the genus are known from the Emu Bay Shale of Australia and Chengjiang Biota of China. ''Nectocaris'' was a free-swimming, predatory or scavenging organism. This lifestyle is reflected in its binomial name: ''Nectocaris'' means "swimming shrimp" (from the Ancient Greek , ', meaning "swimmer" and , ', "shrimp"; , ', means "wing"). Two morphs are known: a small morph, about an inch long, and a large morph, anatomically identical but around four times longer. Nectocaridids have controversial affinities. Some authors have suggested that they represent the earliest known cephalopods. However, their morphology is strongly dissimilar to confirmed early cephalopods, and thus their affinities to cephalopods and even to molluscs more broadly are rejected by most authors. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nectocaris Pteryx
''Nectocaris'' is a genus of squid-like animal of controversial affinities known from the Cambrian period. The initial fossils were described from the Burgess Shale of Canada. Other similar remains possibly referrable to the genus are known from the Emu Bay Shale of Australia and Chengjiang Biota of China. ''Nectocaris'' was a free-swimming, predatory or scavenging organism. This lifestyle is reflected in its binomial name: ''Nectocaris'' means "swimming shrimp" (from the Ancient Greek , ', meaning "swimmer" and , ', "shrimp"; , ', means "wing"). Two morphs are known: a small morph, about an inch long, and a large morph, anatomically identical but around four times longer. Nectocaridids have controversial affinities. Some authors have suggested that they represent the earliest known cephalopods. However, their morphology is strongly dissimilar to confirmed early cephalopods, and thus their affinities to cephalopods and even to molluscs more broadly are rejected by most authors. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nectocaris
''Nectocaris'' is a genus of squid-like animal of controversial affinities known from the Cambrian period. The initial fossils were described from the Burgess Shale of Canada. Other similar remains possibly referrable to the genus are known from the Emu Bay Shale of Australia and Chengjiang Biota of China. ''Nectocaris'' was a free-swimming, predatory or scavenging organism. This lifestyle is reflected in its binomial name: ''Nectocaris'' means "swimming shrimp" (from the Ancient Greek , ', meaning "swimmer" and , ', "shrimp"; , ', means "wing"). Two morphs are known: a small morph, about an inch long, and a large morph, anatomically identical but around four times longer. Nectocaridids have controversial affinities. Some authors have suggested that they represent the earliest known cephalopods. However, their morphology is strongly dissimilar to confirmed early cephalopods, and thus their affinities to cephalopods and even to molluscs more broadly are rejected by most authors. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalopod
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda (Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head, and a set of arms or tentacles (muscular hydrostats) modified from the primitive molluscan foot. Fishers sometimes call cephalopods "inkfish", referring to their common ability to squirt ink. The study of cephalopods is a branch of malacology known as teuthology. Cephalopods became dominant during the Ordovician period, represented by primitive nautiloids. The class now contains two, only distantly related, extant subclasses: Coleoidea, which includes octopuses, squid, and cuttlefish; and Nautiloidea, represented by ''Nautilus'' and ''Allonautilus''. In the Coleoidea, the molluscan shell has been internalized or is absent, whereas in the Nautiloidea, the external shell remains. About 800 living species of cephalopods have been ident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalopod
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda (Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head, and a set of arms or tentacles (muscular hydrostats) modified from the primitive molluscan foot. Fishers sometimes call cephalopods "inkfish", referring to their common ability to squirt ink. The study of cephalopods is a branch of malacology known as teuthology. Cephalopods became dominant during the Ordovician period, represented by primitive nautiloids. The class now contains two, only distantly related, extant subclasses: Coleoidea, which includes octopuses, squid, and cuttlefish; and Nautiloidea, represented by ''Nautilus'' and ''Allonautilus''. In the Coleoidea, the molluscan shell has been internalized or is absent, whereas in the Nautiloidea, the external shell remains. About 800 living species of cephalopods have been ident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nectocotis
''Nectocotis rusmithi'' is an Ordovician nectocaridid, differing from ''Nectocaris ''Nectocaris'' is a genus of squid-like animal of controversial affinities known from the Cambrian period. The initial fossils were described from the Burgess Shale of Canada. Other similar remains possibly referrable to the genus are known from ...'' in the possession of an internal skeletal element. References Fossil taxa described in 2019 Late Ordovician animals Nectocarididae Ordovician animals of North America {{paleo-cephalopod-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mollusca
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000 additional species. The proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied. Molluscs are the largest marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms. Numerous molluscs also live in freshwater and terrestrial habitats. They are highly diverse, not just in size and anatomical structure, but also in behaviour and habitat. The phylum is typically divided into 7 or 8 taxonomic classes, of which two are entirely extinct. Cephalopod molluscs, such as squid, cuttlefish, and octopuses, are among the most neurologically advanced of all invertebrates—and either the giant squid or the colossal squid is the largest known invertebrate species. The gastropod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chengjiang Biota
The Maotianshan Shales are a series of Early Cambrian deposits in the Chiungchussu Formation, famous for their '' Konservat Lagerstätten'', deposits known for the exceptional preservation of fossilized organisms or traces. The Maotianshan Shales form one of some forty Cambrian fossil locations worldwide exhibiting exquisite preservation of rarely preserved, non-mineralized soft tissue, comparable to the fossils of the Burgess Shale. They take their name from Maotianshan Hill (, Literal meaning: Hat Sky Mountain) in Chengjiang County, Yunnan Province, China. The most famous assemblage of organisms are referred to as the Chengjiang biota for the multiple scattered fossil sites in Chengjiang. The age of the Chengjiang Lagerstätte is locally termed Qiongzhusian, a stage correlated to the late Atdabanian Stage in Siberian sequences of the middle of the Early Cambrian. The shales date to ≤. The shales also contain the slightly younger Guanshan biota from Malong District in Yunnan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coleoidea
Subclass (biology), Subclass Coleoidea, or Dibranchiata, is the grouping of cephalopods containing all the various taxa popularly thought of as "soft-bodied" or "shell-less" (i.e., octopuses, squid and cuttlefish). Unlike its extant sister group, Nautiloidea, whose members have a rigid outer shell for protection, the coleoids have at most an internal cuttlebone, gladius (cephalopod), gladius, or shell that is used for buoyancy or support. Some species have lost their cuttlebone altogether, while in some it has been replaced by a chitinous support structure. A unique trait of the group is the ability to edit their own RNA. The major divisions of Coleoidea are based upon the number of cephalopod limb, arms or tentacles and their structure. The extinct and most primitive form, the Belemnoidea, presumably had ten equally-sized arms in five pairs numbered Dorsum (biology), dorsal to ventral as I, II, III, IV and V. More modern species either modified or lost a pair of arms. The superor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a Segmentation (biology), segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and Arthropod cuticle, cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate. The arthropod body plan consists of segments, each with a pair of appendages. Arthropods are bilaterally symmetrical and their body possesses an exoskeleton, external skeleton. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. Some species have wings. They are an extremely diverse group, with up to 10 million species. The haemocoel, an arthropod's internal cavity, through which its haemolymph – analogue of blood – circulates, accommodates its interior Organ (anatomy), organs; it has an open circulatory system. Like their exteriors, the internal or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counter Slab
A compression fossil is a fossil preserved in sedimentary rock that has undergone physical compression. While it is uncommon to find animals preserved as good compression fossils, it is very common to find plants preserved this way. The reason for this is that physical compression of the rock often leads to distortion of the fossil. The best fossils of leaves are found preserved in fine layers of sediment that have been compressed in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the deposited sediment. Since leaves are basically flat, the resulting distortion is minimal. Plant stems and other three-dimensional plant structures do not preserve as well under compression. Typically, only the basic outline and surface features are preserved in compression fossils; internal anatomy is not preserved. These fossils may be studied while still partially entombed in the sedimentary rock matrix where they are preserved, or once lifted out of the matrix by a peel or transfer technique. Compre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Doolittle Walcott
Charles Doolittle Walcott (March 31, 1850February 9, 1927) was an American paleontologist, administrator of the Smithsonian Institution from 1907 to 1927, and director of the United States Geological Survey.Wonderful Life (book) by Stephen Jay Gould published in 1989, Chapter 4 He is famous for his discovery in 1909 of well-preserved fossils, including some of the oldest soft-part imprints, in the Burgess Shale of British Columbia, Canada. Early life Charles Doolittle Walcott was born on March 31, 1850 in New York Mills, New York. His grandfather, Benjamin S. Walcott, moved from Rhode Island in 1822. His father, also Charles Doolittle Walcott, died when Charles Jr. was only two. Walcott was the youngest of four children. He was interested in nature from an early age, collecting minerals and bird eggs and, eventually, fossils. He attended various schools in the Utica area but left at the age of eighteen without completing high school, the end of his formal education. His intere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chordate
A chordate () is an animal of the phylum Chordata (). All chordates possess, at some point during their larval or adult stages, five synapomorphies, or primary physical characteristics, that distinguish them from all the other taxa. These five synapomorphies include a notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, endostyle or thyroid, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail. The name “chordate” comes from the first of these synapomorphies, the notochord, which plays a significant role in chordate structure and movement. Chordates are also Bilateral symmetry, bilaterally symmetric, have a coelom, possess a circulatory system, and exhibit Metameric, metameric segmentation. In addition to the morphological characteristics used to define chordates, analysis of genome sequences has identified two conserved signature indels (CSIs) in their proteins: cyclophilin-like protein and mitochondrial inner membrane protease ATP23, which are exclusively shared by all vertebrates, tunicates and cep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)




