|
Neck Dissection
The neck dissection is a surgical procedure for control of neck lymph node metastasis from squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the head and neck. The aim of the procedure is to remove lymph nodes from one side of the neck into which cancer cells may have migrated. Metastasis of squamous cell carcinoma into the lymph nodes of the neck reduce survival and is the most important factor in the spread of the disease. The metastases may originate from SCC of the upper aerodigestive tract, including the oral cavity, tongue, nasopharynx, oropharynx, hypopharynx, and larynx, as well as the thyroid, parotid and posterior scalp. History of neck dissections * 1906 – George W. Crile of the Cleveland Clinic describes the radical neck dissection. The operation encompasses removal of all the lymph nodes on one side of the neck, and includes removal of the spinal accessory nerve (SAN), internal jugular vein (IJV) and sternocleidomastoid muscle (SCM). * 1957 – Hayes Martin describes routine use of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgery
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pathological condition such as a disease or injury, to help improve bodily function, appearance, or to repair unwanted ruptured areas. The act of performing surgery may be called a surgical procedure, operation, or simply "surgery". In this context, the verb "operate" means to perform surgery. The adjective surgical means pertaining to surgery; e.g. surgical instruments or surgical nurse. The person or subject on which the surgery is performed can be a person or an animal. A surgeon is a person who practices surgery and a surgeon's assistant is a person who practices surgical assistance. A surgical team is made up of the surgeon, the surgeon's assistant, an anaesthetist, a circulating nurse and a surgical technologist. Surgery usually spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submental Triangle
The submental triangle (or suprahyoid triangle) is a division of the anterior triangle of the neck. Boundaries It is limited to: * Lateral (away from the midline), formed by the anterior belly of the digastricus * Medial (towards the midline), formed by the midline of the neck between the mandible and the hyoid bone * Inferior (below), formed by the body of the hyoid bone *Floor is formed by the mylohyoideus *Roof is formed by Investing layer of deep cervical fascia Contents It contains one or two lymph glands, the submental lymph nodes The submental glands (or suprahyoid) are situated between the anterior bellies of the digastric muscle and the hyoid bone. Their '' afferents'' drain the central portions of the lower lip and floor of the mouth and the apex of the tongue. Their ... (three or four in number) and Submental veins and commencement of anterior jugular veins. (The contents of the triangle actually lie in the superficial fascia over the roof of submental tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carotid
In anatomy, the left and right common carotid arteries (carotids) ( in Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary '.) are that supply the head and neck with ; they divide in the neck to form the and |
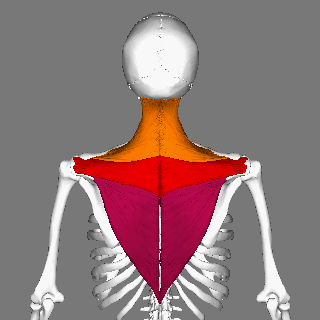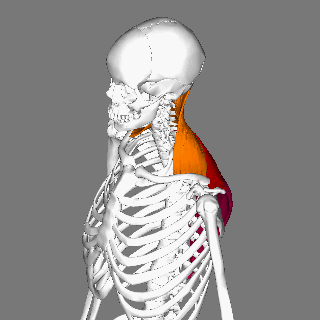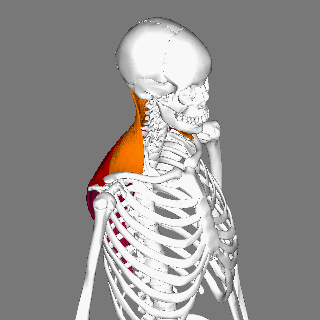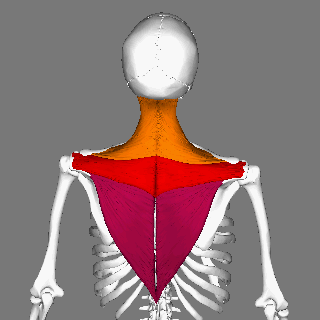
Trapezius
The trapezius is a large paired trapezoid-shaped surface muscle that extends longitudinally from the occipital bone to the lower thoracic vertebrae of the spine and laterally to the spine of the scapula. It moves the scapula and supports the arm. The trapezius has three functional parts: an upper (descending) part which supports the weight of the arm; a middle region (transverse), which retracts the scapula; and a lower (ascending) part which medially rotates and depresses the scapula. Name and history The trapezius muscle resembles a trapezium, also known as a trapezoid, or diamond-shaped quadrilateral. The word "spinotrapezius" refers to the human trapezius, although it is not commonly used in modern texts. In other mammals, it refers to a portion of the analogous muscle. Similarly, the term "tri-axle back plate" was historically used to describe the trapezius muscle. Structure The ''superior'' or ''upper'' (or descending) fibers of the trapezius originate from the sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternum
The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. Shaped roughly like a necktie, it is one of the largest and longest flat bones of the body. Its three regions are the manubrium, the body, and the xiphoid process. The word "sternum" originates from the Ancient Greek στέρνον (stérnon), meaning "chest". Structure The sternum is a narrow, flat bone, forming the middle portion of the front of the chest. The top of the sternum supports the clavicles (collarbones) and its edges join with the costal cartilages of the first two pairs of ribs. The inner surface of the sternum is also the attachment of the sternopericardial ligaments. Its top is also connected to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The sternum consists of three main parts, listed from the top: * Manubrium * Body (gladiolus) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clavicle
The clavicle, or collarbone, is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately 6 inches (15 cm) long that serves as a strut between the shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on the left and one on the right. The clavicle is the only long bone in the body that lies horizontally. Together with the shoulder blade, it makes up the shoulder girdle. It is a palpable bone and, in people who have less fat in this region, the location of the bone is clearly visible. It receives its name from the Latin ''clavicula'' ("little key"), because the bone rotates along its axis like a key when the shoulder is abducted. The clavicle is the most commonly fractured bone. It can easily be fractured by impacts to the shoulder from the force of falling on outstretched arms or by a direct hit. Structure The collarbone is a thin doubly curved long bone that connects the arm to the trunk of the body. Located directly above the first rib, it acts as a strut to k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternohyoid
The sternohyoid muscle is a thin, narrow muscle attaching the hyoid bone to the sternum. It is one of the paired strap muscles of the infrahyoid muscles. It is supplied by the ansa cervicalis. It depresses the hyoid bone. Structure The sternohyoid muscle is one of the paired strap muscles of the infrahyoid muscles. It arises from the posterior border of the medial end of the clavicle, the posterior sternoclavicular ligament, and the upper and posterior part of the manubrium of the sternum. Passing upward and medially, it is inserted by short tendinous fibers into the lower border of the body of the hyoid bone. It runs lateral to the trachea. Nerve supply The sternohyoid muscle is supplied by a branch of the ansa cervicalis. Variations The sternohyoid muscle may be doubled, have accessory slips (Cleidohyoideus) or be completely absent in some people. It sometimes presents a transverse tendinous inscription immediately above its origin. Function The sternohyoid muscle pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cricoid
The cricoid cartilage , or simply cricoid (from the Greek ''krikoeides'' meaning "ring-shaped") or cricoid ring, is the only complete ring of cartilage around the trachea. It forms the back part of the voice box and functions as an attachment site for muscles, cartilages, and ligaments involved in opening and closing the airway and in producing speech. Structure The cricoid cartilage sits just inferior to the thyroid cartilage in the neck, at the level of the C6 vertebra, and is joined to it medially by the median cricothyroid ligament and postero-laterally by the cricothyroid joints. Inferior to it are the rings of cartilage around the trachea (which are not continuous – rather they are C-shaped with a gap posteriorly). The cricoid is joined to the first tracheal ring by the cricotracheal ligament, and this can be felt as a more yielding area between the firm thyroid cartilage and firmer cricoid. It is also anatomically related to the thyroid gland; although the thyr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stylohyoid Muscle
The stylohyoid muscle is a slender muscle, lying anterior and superior of the posterior belly of the digastric muscle. It is one of the suprahyoid muscles. It shares this muscle's innervation by the facial nerve, and functions to draw the hyoid bone backwards and elevate the tongue. Its origin is the styloid process of the temporal bone. It inserts on the body of the hyoid. Structure The stylohyoid muscle originates from the posterior and lateral surface of the styloid process of the temporal bone, near the base. Passing inferior and anterior, it inserts into the body of the hyoid bone, at its junction with the greater cornu, and just superior to the omohyoid muscle. It belongs to the group of suprahyoid muscles. It is perforated, near its insertion, by the intermediate tendon of the digastric muscle. The stylohyoid muscle has vascular supply from the lingual artery, a branch of the external carotid artery. Nerve supply A branch of the facial nerve The facial n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, these two parts are the neurocranium and the viscerocranium ( facial skeleton) that includes the mandible as its largest bone. The skull forms the anterior-most portion of the skeleton and is a product of cephalisation—housing the brain, and several sensory structures such as the eyes, ears, nose, and mouth. In humans these sensory structures are part of the facial skeleton. Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision, and fixing the position of the ears to enable sound localisation of the direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, such as horned ungulates (mammals with hooves), the skull also has a defensive function by providing the mount (on the front ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stylohyoid
The stylohyoid muscle is a slender muscle, lying anterior and superior of the posterior belly of the digastric muscle. It is one of the suprahyoid muscles. It shares this muscle's innervation by the facial nerve, and functions to draw the hyoid bone backwards and elevate the tongue. Its origin is the styloid process of the temporal bone. It inserts on the body of the hyoid. Structure The stylohyoid muscle originates from the posterior and lateral surface of the styloid process of the temporal bone, near the base. Passing inferior and anterior, it inserts into the body of the hyoid bone, at its junction with the greater cornu, and just superior to the omohyoid muscle. It belongs to the group of suprahyoid muscles. It is perforated, near its insertion, by the intermediate tendon of the digastric muscle. The stylohyoid muscle has vascular supply from the lingual artery, a branch of the external carotid artery. Nerve supply A branch of the facial nerve (CN VII) innervates the st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
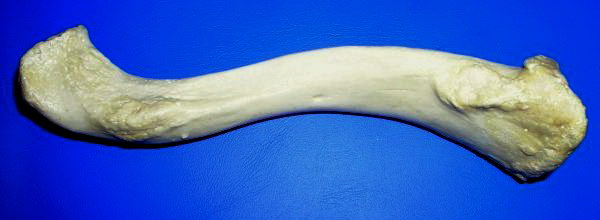
Mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower tooth, teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone of the skull (discounting the ossicles of the middle ear). It is connected to the temporal bones by the temporomandibular joints. The bone is formed prenatal development, in the fetus from a fusion of the left and right mandibular prominences, and the point where these sides join, the mandibular symphysis, is still visible as a faint ridge in the midline. Like other symphyses in the body, this is a midline articulation where the bones are joined by fibrocartilage, but this articulation fuses together in early childhood.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, p. 59 The word "mandible" derives from the Latin word ''mandibula'', "jawbone" (literally "one used for chewing"), from ''wikt:mandere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)