|
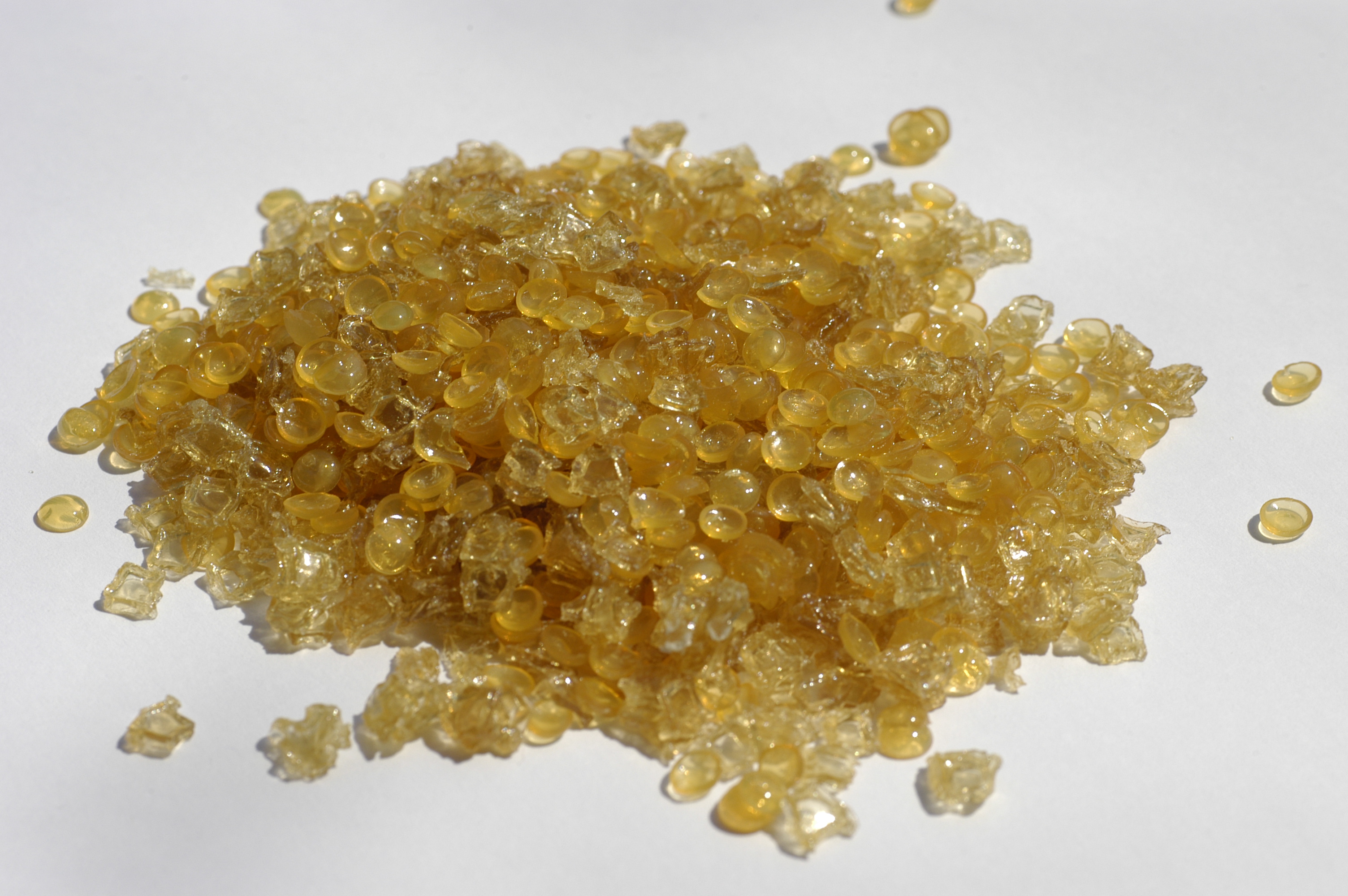
Neatsfoot Oil
Neatsfoot oil is a yellow oil rendered and purified from the shin bones and feet (but not the hooves) of cattle. "Neat" in the oil's name comes from an Old English word for cattle. Neatsfoot oil is used as a conditioning, softening and preservative agent for leather. In the 18th century, it was also used medicinally as a topical application for dry scaly skin conditions. In spite of its name, "prime neatsfoot oil" (or "neatsfoot oil compound") is a blend of actual neatsfoot oil and non-animal oils, generally mineral or other petroleum-based oils. Characteristics Fat from warm-blooded animals normally has a high melting point, becoming hard when cool, but neatsfoot oil remains liquid at room temperature. This is because the relatively slender legs and feet of animals such as cattle are adapted to tolerate and maintain much lower temperatures than that of the body core, using countercurrent heat exchange in the legs between warm arterial and cooler venous blood. Other bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neatsfoot Oil
Neatsfoot oil is a yellow oil rendered and purified from the shin bones and feet (but not the hooves) of cattle. "Neat" in the oil's name comes from an Old English word for cattle. Neatsfoot oil is used as a conditioning, softening and preservative agent for leather. In the 18th century, it was also used medicinally as a topical application for dry scaly skin conditions. In spite of its name, "prime neatsfoot oil" (or "neatsfoot oil compound") is a blend of actual neatsfoot oil and non-animal oils, generally mineral or other petroleum-based oils. Characteristics Fat from warm-blooded animals normally has a high melting point, becoming hard when cool, but neatsfoot oil remains liquid at room temperature. This is because the relatively slender legs and feet of animals such as cattle are adapted to tolerate and maintain much lower temperatures than that of the body core, using countercurrent heat exchange in the legs between warm arterial and cooler venous blood. Other bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soya Oil
Soybean oil (British English: soyabean oil) is a vegetable oil extracted from the seeds of the soybean (''Glycine max''). It is one of the most widely consumed cooking oils and the second most consumed vegetable oil. As a drying oil, processed soybean oil is also used as a base for printing inks (soy ink) and oil paints. History Chinese records dating prior to 2000 BCE mention use of cultivated soybeans to produce edible soy oil. Ancient Chinese literature reveals that soybeans were extensively cultivated and highly valued as a use for the soybean oil production process before written records were kept. Production To produce soybean oil, the soybeans are cracked, adjusted for moisture content, heated to between 60 and 88 °C (140–190 °F), rolled into flakes, and solvent-extracted with hexanes. The oil is then refined, blended for different applications, and sometimes Hydrogenation, hydrogenated. Soybean oils, both liquid and partially hydrogenated are sold as "v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mink Oil
Mink are dark-colored, semiaquatic, carnivorous mammals of the genera '' Neogale'' and '' Mustela'' and part of the family Mustelidae, which also includes weasels, otters, and ferrets. There are two extant species referred to as "mink": the American mink and the European mink. The extinct sea mink was related to the American mink but was much larger. The American mink's fur has been highly prized for use in clothing. Their treatment on fur farms has been a focus of animal rights and animal welfare activism. American mink have established populations in Europe (including Great Britain and Denmark) and South America. Some people believe this happened after the animals were released from mink farms by animal rights activists, or otherwise escaped from captivity. In the UK, under the Wildlife and Countryside Act 1981, it is illegal to release mink into the wild. In some countries, any live mink caught in traps must be humanely killed. American mink are believed by some t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoof Glue
Hoof glue is a form of animal glue made by boiling down the hooves of ungulates into partially hydrolyzed keratin. It is not to be confused with hide glue. History Hoof glue applications include stiffening bow strings, adhering fabric to wood, stiffening fabric, and sealing glass window frames and ceramic containers. Hoof glue is still used today in cabinetry and other fine woodworking projects where the joints must be capable of disassembly. Formulation The general process is to take the hooves of ungulates and break them into small chunks and then boil them in water until all the hoof material has been liquefied. An acid is then added to create a thick gel. The resultant product is then cooled and allowed to harden. Once melted, it is necessary to heat the glue substance until it is the required consistency – thin hoof glue can be used to stiffen fabrics; thicker glue is used in cabinetry. Usage The storable form of hoof glue is a hard block of resin-like material. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dippel's Oil
Dippel's oil (sometimes referred to as bone oil) is a nitrogenous by-product of the destructive distillation of bones. A dark, viscous, tar-like liquid with an unpleasant smell, it is named after its inventor, Johann Konrad Dippel. The oil consists mostly of aliphatic chains, with nitrogen functionalities and includes species such as pyrroles, pyridines and nitriles, as well as other nitrogenous compounds. Dippel's oil had a number of uses which are now mostly obsolete. Its primary use was as an animal and insect repellent. It saw limited use as a chemical warfare harassing agent during the desert campaign of World War II. The oil was used to render wells undrinkable and thus deny their use to the enemy. By not being lethal, the oil was claimed to not be in breach of the Geneva Protocol. See also * Neatsfoot oil, another bone-derived oil * Bone char Bone char ( lat, carbo animalis) is a porous, black, granular material produced by charring animal bones. Its composition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Glue
Animal glue is an adhesive that is created by prolonged boiling of animal connective tissue in a process called rendering. In addition to being used as an adhesive it is used for coating and sizing, in decorative composition ornaments, and as a clarifying agent. These protein colloid glues are formed through hydrolysis of the collagen from skins, bones, tendons, and other tissues, similar to gelatin. The word ''collagen'' itself derives from Greek (), meaning 'glue'. These proteins form a molecular bond with the glued object. Conventionally, keratin glues, while made from animal parts like horns and hooves, are not considered animal glues as they are not collagen glues. Stereotypically, the animal in question is a horse, and horses that are put down are often said to have been "sent to the glue factory". However, other animals are also used, including cattle, rabbits and fish. History Early uses Animal glue has existed since ancient times, although its usage was no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerosene
Kerosene, paraffin, or lamp oil is a combustible hydrocarbon liquid which is derived from petroleum. It is widely used as a fuel in aviation as well as households. Its name derives from el, κηρός (''keros'') meaning " wax", and was registered as a trademark by Canadian geologist and inventor Abraham Gesner in 1854 before evolving into a generic trademark. It is sometimes spelled kerosine in scientific and industrial usage. The term kerosene is common in much of Argentina, Australia, Canada, India, New Zealand, Nigeria, and the United States, while the term paraffin (or a closely related variant) is used in Chile, eastern Africa, South Africa, Norway, and in the United Kingdom. The term lamp oil, or the equivalent in the local languages, is common in the majority of Asia and the Southeastern United States. Liquid paraffin (called mineral oil in the US) is a more viscous and highly refined product which is used as a laxative. Paraffin wax is a waxy solid extracted from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cutting Fluid
Cutting fluid is a type of coolant and lubricant designed specifically for metalworking processes, such as machining and stamping. There are various kinds of cutting fluids, which include oils, oil-water emulsions, pastes, gels, aerosols (mists), and air or other gases. Cutting fluids are made from petroleum distillates, animal fats, plant oils, water and air, or other raw ingredients. Depending on context and on which type of cutting fluid is being considered, it may be referred to as cutting fluid, cutting oil, cutting compound, coolant, or lubricant. Most metalworking and machining processes can benefit from the use of cutting fluid, depending on workpiece material. Common exceptions to this are cast iron and brass, which may be machined dry (though this is not true of all brasses, and any machining of brass will likely benefit from the presence of a cutting fluid). The properties that are sought after in a good cutting fluid are the ability to: * Keep the workpiece at a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horse Harness
Horse harness is a device that connects a horse to a vehicle or another type of load. There are two main categories of horse harness: (1) the "breaststrap" or "breastcollar" design, and (2) the collar and hames design. For light work, such as horse show competition where light carts are used, a harness needs only a breastcollar. It can only be used for lighter hauling, since it places the weight of the load on the sternum of the horse and the nearby windpipe. This is not the heaviest skeletal area; also heavy loads can constrict the windpipe and reduce a horse's air supply. By contrast, the collar and harness places the weight of the load onto the horse's shoulders, and without any restriction on the air supply. For heavy hauling, the harness must include a horse collar to allow the animal to use its full weight and strength. Harness components designed for other animals (such as the yoke used with oxen) are not suitable for horses and will not allow the horse to work effi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saddle
The saddle is a supportive structure for a rider of an animal, fastened to an animal's back by a girth. The most common type is equestrian. However, specialized saddles have been created for oxen, camels and other animals. It is not known precisely when riders first began to use some sort of padding or protection, but a blanket attached by some form of surcingle or girth was probably the first "saddle", followed later by more elaborate padded designs. The solid saddle tree was a later invention, and though early stirrup designs predated the invention of the solid tree, the paired stirrup, which attached to the tree, was the last element of the saddle to reach the basic form that is still used today. Today, modern saddles come in a wide variety of styles, each designed for a specific equestrianism discipline, and require careful fit to both the rider and the horse. Proper saddle care can extend the useful life of a saddle, often for decades. The saddle was a crucial step ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horse Tack
Tack is equipment or accessories equipped on horses and other equines in the course of their use as domesticated animals. This equipment includes such items as saddles, stirrups, bridles, halters, reins, bits, and harnesses. Equipping a horse is often referred to as tacking up, and involves putting the tack equipment on the horse. A room to store such equipment, usually near or in a stable, is a tack room. Saddles Saddles are seats for the rider, fastened to the horse's back by means of a '' girth'' (English-style riding), known as a ''cinch'' in the Western US, a wide strap that goes around the horse at a point about four inches behind the forelegs. Some western saddles will also have a second strap known as a ''flank'' or ''back cinch'' that fastens at the rear of the saddle and goes around the widest part of the horse's belly.Price, Steven D. (ed.) ''The Whole Horse Catalog: Revised and Updated'' New York:Fireside 1998 p. 167-178 It is important that the saddle be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
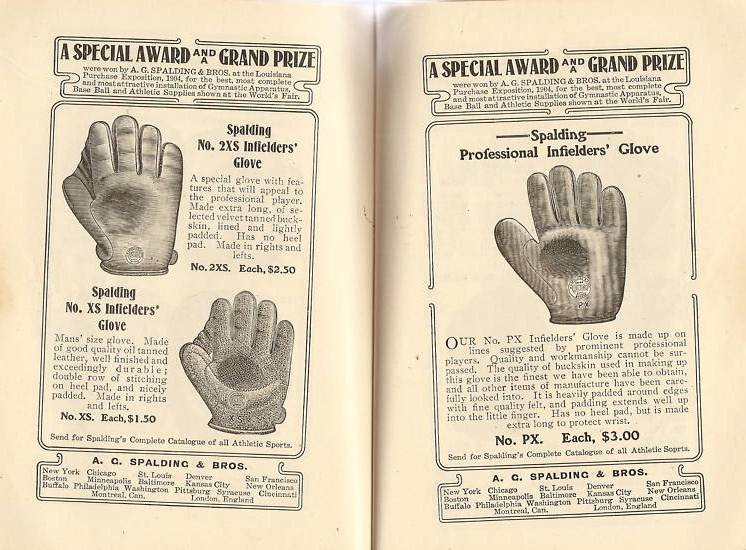
Baseball Glove
A baseball glove or mitt is a large glove (traditionally made of leather, today other options do exist) worn by baseball players of the defending team, which assists players in catching and fielding balls hit by a batter or thrown by a teammate. By convention, the glove is described by the handedness of the intended wearer, rather than the hand on which the glove is worn: a glove that fits on the left hand—used by a right-handed thrower—is called a ''right-handed'' (RH) or "right-hand throw" (RHT) glove. Conversely, a left-handed glove (LH or LHT) is worn on the right hand, allowing the player to throw the ball with the left hand. History Early baseball was a game played without gloves. During the slow transition to gloves, a player who continued to play without one was called a ''barehanded catcher;'' this did not refer to the position of catcher, but rather to the practice of catching with bare hands. The earliest glove was not webbed and not particularly well suited for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)