|
Near-death
A near-death experience (NDE) is a profound personal experience associated with death or impending death which researchers claim share similar characteristics. When positive, such experiences may encompass a variety of sensations including detachment from the body, feelings of levitation, total serenity, security, warmth, the experience of absolute dissolution, and the presence of a light. When negative, such experiences may include sensations of anguish, distress, a void, devastation, and vast emptiness. People often report seeing hellish places and things like their own rendition of "the devil." Explanations for NDEs vary from scientific to religious. Neuroscience research hypothesizes that an NDE is a subjective phenomenon resulting from "disturbed bodily multisensory integration" that occurs during life-threatening events. Some transcendental and religious beliefs about an afterlife include descriptions similar to NDEs. In the U.S., an estimated 9 million people have repo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruce Greyson
Charles Bruce Greyson (born October 1946) is Professor Emeritus of Psychiatry and Neurobehavioral Sciences at the University of Virginia. He is author of '' After: A Doctor Explores What Near-Death Experiences Reveal about Life and Beyond'' (2021), co-author of ''Irreducible Mind'' (2007) and co-editor of ''The Handbook of Near-Death Experiences'' (2009). Greyson has written many journal articles, and has given media interviews, on the subject of near death experiences. Academic appointments Greyson is Chester F. Carlson Professor Emeritus of Psychiatry and Neurobehavioral Sciences, and the former director of The Division of Perceptual Studies (DOPS), formerly the Division of Personality Studies, at the University of Virginia. He is also a Professor of Psychiatric Medicine in the Department of Psychiatric Medicine, Division of Outpatient Psychiatry, at the University of Virginia. Research work Greyson is a researcher in the field of near-death studies and has been called the fathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Out-of-body Experience
An out-of-body experience (OBE or sometimes OOBE) is a phenomenon in which a person perceives the world from a location outside their physical body. An OBE is a form of autoscopy (literally "seeing self"), although this term is more commonly used to refer to the pathological condition of seeing a second self, or doppelgänger. The term ''out-of-body experience'' was introduced in 1943 by G. N. M. Tyrrell in his book ''Apparitions'', and was adopted by researchers such as Celia Green, and Robert Monroe, as an alternative to belief-centric labels such as " astral projection" or "spirit walking". OBEs can be induced by traumatic brain injuries, sensory deprivation, near-death experiences, dissociative and psychedelic drugs, dehydration, sleep disorders, dreaming, and electrical stimulation of the brain, among other causes. It can also be deliberately induced by some. One in ten people has an OBE once, or more commonly, several times in their life. Psychologists and neuroscienti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Out-of-body Experiences
An out-of-body experience (OBE or sometimes OOBE) is a phenomenon in which a person perceives the world from a location outside their physical body. An OBE is a form of autoscopy (literally "seeing self"), although this term is more commonly used to refer to the pathological condition of seeing a second self, or doppelgänger. The term ''out-of-body experience'' was introduced in 1943 by G. N. M. Tyrrell in his book ''Apparitions'', and was adopted by researchers such as Celia Green, and Robert Monroe, as an alternative to belief-centric labels such as "astral projection" or "spirit walking". OBEs can be induced by traumatic brain injuries, sensory deprivation, near-death experiences, dissociative and psychedelic drugs, dehydration, sleep disorders, dreaming, and electrical stimulation of the brain, among other causes. It can also be deliberately induced by some. One in ten people has an OBE once, or more commonly, several times in their life. Psychologists and neuroscientists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raymond Moody
Raymond A. Moody Jr. (born June 30, 1944) is an American philosopher, psychiatrist, physician and author, most widely known for his books about afterlife and near-death experiences (NDE), a term that he coined in 1975 in his best-selling book '' Life After Life''. His research purports to explore what happens when a person dies. He has widely published his views on what he terms near-death-experience psychology. Early life and education Moody was born in Porterdale, Georgia, the son of an agnostic surgeon. He earned a BA (1966), an M.A. (1967) and a PhD (1969) in philosophy from the University of Virginia. He also obtained a PhD in psychology from the University of West Georgia, then known as West Georgia College, where he later became a professor in the topic. In 1976, he received an M.D. from the Medical College of Georgia. Career Early career After obtaining his M.D., Moody worked as a forensic psychiatrist in a maximum-security Georgia state hospital. In 1998, Moody was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afterlife
The afterlife (also referred to as life after death) is a purported existence in which the essential part of an individual's identity or their stream of consciousness continues to live after the death of their physical body. The surviving essential aspect varies between belief systems; it may be some partial element, or the entire soul or spirit of an individual, which carries with it and may confer personal identity or, on the contrary, nirvana. Belief in an afterlife is in contrast to the belief in oblivion after death. In some views, this continued existence takes place in a spiritual realm, while in others, the individual may be reborn into this world and begin the life cycle over again, likely with no memory of what they have done in the past. In this latter view, such rebirths and deaths may take place over and over again continuously until the individual gains entry to a spiritual realm or otherworld. Major views on the afterlife derive from religion, esotericism an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
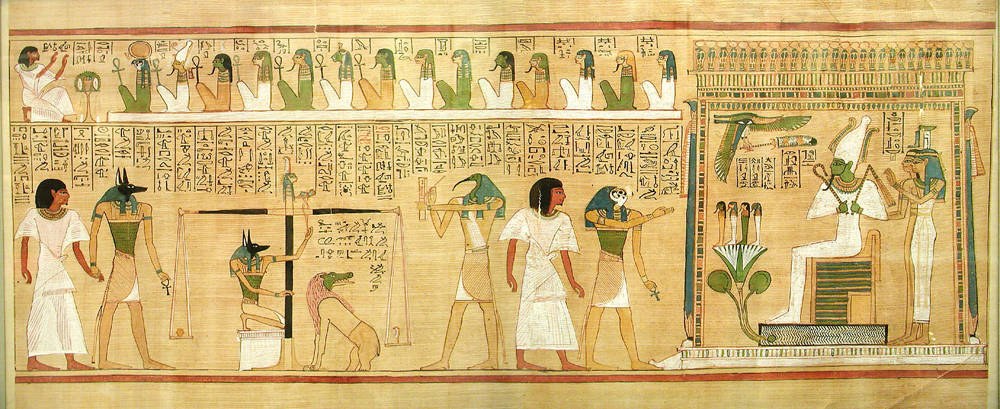
Life Review
The term life review, or flashback before death, refers to a phenomenon widely reported as occurring during near-death experiences, in which a person rapidly sees much or the totality of their life history. Life review is often described by people claiming to have experienced this phenomenon as "''having their life flash before their eyes''". The phenomenon also refers to a widely-used trope in fiction, film, and television where a recap montage of a character's life is shown in a sequence before that character's death. Research and phenomenology CommentatorsHagan, John C. "Near-Death Experiences. I Hope You Are Comfortable With Them By Now!" ''Missouri Medicine'', 112:2 March/April 2015Long, Jeffrey. "Near-Death Experiences. Evidence for Their Reality". ''Missouri Medicine'', 111:5, September/October 2014 note that near-death experiencers undergo a life review in which the meaning of their life is presented to them, but also how their life affected other people, as well as an aw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elisabeth Kübler-Ross
Elisabeth Kübler-Ross (July 8, 1926 – August 24, 2004) was a Swiss-American psychiatrist, a pioneer in near-death studies, and author of the internationally best-selling book, '' On Death and Dying'' (1969), where she first discussed her theory of the five stages of grief, also known as the " Kübler-Ross model". Kübler-Ross was a 2007 inductee into the National Women's Hall of Fame, was named by ''Time'' as one of the "100 Most Important Thinkers" of the 20th century and was the recipient of nineteen honorary degrees. By July 1982, Kübler-Ross taught 125,000 students in death and dying courses in colleges, seminaries, medical schools, hospitals, and social-work institutions. In 1970, she delivered an Ingersoll Lecture at Harvard University on the theme ''On Death and Dying''. Early life and education Elisabeth Kübler was born on July 8, 1926, in Zürich, Switzerland, into a Protestant Christian Family. She was one of a set of triplets, two of whom were identical. Her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.Tylor, Edward. (1871). Primitive Culture. Vol 1. New York: J.P. Putnam's Son Culture is often originated from or attributed to a specific region or location. Humans acquire culture through the learning processes of enculturation and socialization, which is shown by the diversity of cultures across societies. A cultural norm codifies acceptable conduct in society; it serves as a guideline for behavior, dress, language, and demeanor in a situation, which serves as a template for expectations in a social group. Accepting only a monoculture in a social group can bear risks, just as a single species can wither in the face of environmental change, for lack of functional responses to the change. Thus in military culture, valor is counted a typica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychiatrist
A psychiatrist is a physician who specializes in psychiatry, the branch of medicine devoted to the diagnosis, prevention, study, and treatment of mental disorders. Psychiatrists are physicians and evaluate patients to determine whether their symptoms are the result of a physical illness, a combination of physical and mental ailments or strictly mental issues. Sometimes a psychiatrist works within a multi-disciplinary team, which may comprise Clinical psychology, clinical psychologists, Social work, social workers, Occupational therapist, occupational therapists, and Nursing, nursing staff. Psychiatrists have broad training in a Biopsychosocial model, biopsychosocial approach to the assessment and management of mental illness. As part of the clinical assessment process, psychiatrists may employ a mental status examination; a physical examination; brain imaging such as a computerized tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or positron emission tomography scan; and blood testing. P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophy
Philosophy (from , ) is the systematized study of general and fundamental questions, such as those about existence, reason, knowledge, values, mind, and language. Such questions are often posed as problems to be studied or resolved. Some sources claim the term was coined by Pythagoras ( BCE), although this theory is disputed by some. Philosophical methods include questioning, critical discussion, rational argument, and systematic presentation. in . Historically, ''philosophy'' encompassed all bodies of knowledge and a practitioner was known as a ''philosopher''."The English word "philosophy" is first attested to , meaning "knowledge, body of knowledge." "natural philosophy," which began as a discipline in ancient India and Ancient Greece, encompasses astronomy, medicine, and physics. For example, Newton's 1687 ''Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy'' later became classified as a book of physics. In the 19th century, the growth of modern research universiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research
Research is "creativity, creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge". It involves the collection, organization and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness to controlling sources of bias and error. These activities are characterized by accounting and controlling for biases. A research project may be an expansion on past work in the field. To test the validity of instruments, procedures, or experiments, research may replicate elements of prior projects or the project as a whole. The primary purposes of basic research (as opposed to applied research) are documentation, Discovery (observation), discovery, interpretation (philosophy), interpretation, and the research and development (R&D) of methods and systems for the advancement of human knowledge. Approaches to research depend on epistemology, epistemologies, which vary considerably both within and between humanities and sciences. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John C
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died c. AD 30), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (lived c. AD 30), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope Jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |