|
Navfor
Operation Atalanta, formally European Union Naval Force (EU NAVFOR) Somalia, is a current counter-piracy military operation at sea off the Horn of Africa and in the Western Indian Ocean, that is the first naval operation conducted by the European Union (EU). The operational headquarters is currently located at the Spanish Operation Headquarters (ESOHQ) at Naval Station Rota (NAVSTA Rota) in Spain, having moved from London as a result of the British withdrawal from the EU. It is part of a larger global action by the EU to prevent and combat acts of piracy in the Indian Ocean, and it is the first EU naval operation to be launched. It cooperates with the multinational Combined Task Force 151 of the US-led Combined Maritime Forces (CMF) and NATO's anti-piracy Operation Ocean Shield. The mission was launched in December 2008 with a focus on protecting Somalia-bound vessels and shipments belonging to the WFP and AMISOM, as well as select other vulnerable shipments. In addition, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piracy In Somalia
Piracy off the coast of Somalia occurs in the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channel and Somali Sea, in Somali territorial waters and other surrounding areas and has a long and troubled history with different perspectives from different communities. It was initially a threat to international fishing vessels, expanding to international shipping since the Consolidation of states within Somalia (1998–2006), consolidation of states phase of the Somali Civil War around 2000. Somali waters have high fisheries production potential, but the sustainability of those fisheries is compromised by the presence of foreign fishing vessels, many of them fishing illegally. The Somali domestic fishing sector is small and poorly developed, whereas foreign vessels have fished in Somali waters for at least seven decades. Some foreign vessels and their crew have been viewed by Somali artisanal fishers as a threat to their traditional livelihoods. Many foreign vessels directly compete for fish, reducing fis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
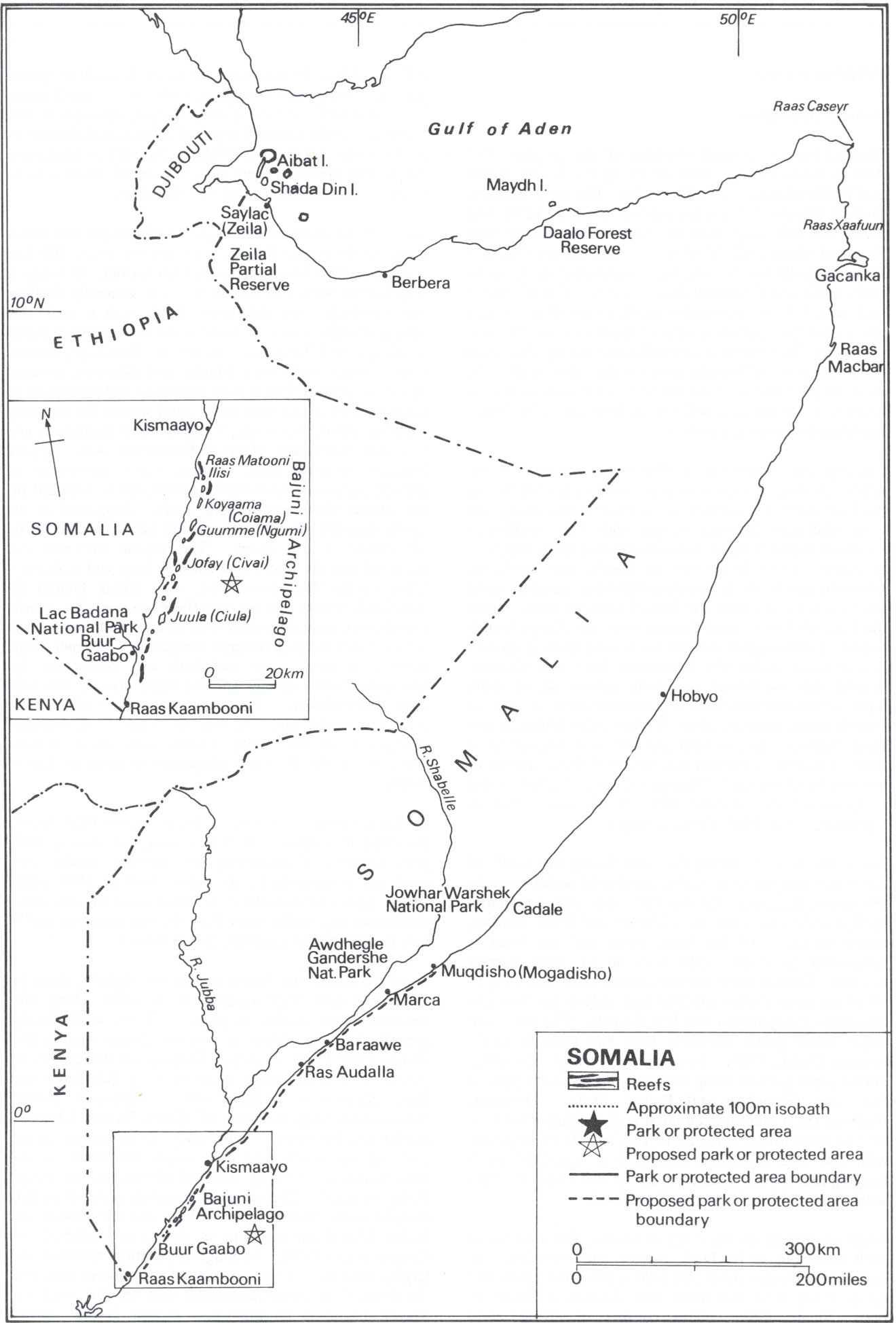
Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constitution, (; ), is a country in the Horn of Africa. The country is bordered by Ethiopia to the west, Djibouti to the northwest, the Gulf of Aden to the north, the Indian Ocean to the east, and Kenya to the southwest. Somalia has the longest coastline on Africa's mainland. Its terrain consists mainly of plateaus, plains, and highlands. Hot conditions prevail year-round, with periodic monsoon winds and irregular rainfall. Somalia has an estimated population of around million, of which over 2 million live in the capital and largest city Mogadishu, and has been described as Africa's most culturally homogeneous country. Around 85% of its residents are ethnic Somalis, who have historically inhabited the country's north. Ethnic minorities are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1816
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1816 was unanimously adopted on 2 June 2008. Resolution Condemning all acts of piracy and armed robbery against vessels off the coast of Somalia, the Security Council this afternoon authorized a series of decisive measures to combat those crimes. By the terms of resolution 1816 (2008), which was unanimously adopted today, the Council decided that the States cooperating with the country’s transitional Government would be allowed, for a period of six months, to enter the territorial waters of Somalia and use “all necessary means” to repress acts of piracy and armed robbery at sea, in a manner consistent with relevant provisions of international law. The text was adopted with consent of Somalia, which lacks the capacity to interdict pirates or patrol and secure its territorial waters, following a surge in attacks on ships in the waters off the country’s coast, including hijackings of vessels operated by the World Food Programme and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nations Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the Organs of the United Nations, six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international security, international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the United Nations General Assembly, General Assembly, and approving any changes to the UN Charter. Its powers include establishing peacekeeping operations, enacting international sanctions, and authorizing military action. The UNSC is the only UN body with the authority to issue binding United Nations Security Council resolution, resolutions on member states. Like the UN as a whole, the Security Council was created after World War II to address the failings of the League of Nations in maintaining world peace. It held its first session on 17 January 1946 but was largely paralyzed in the following decades by the Cold War between the United States and the Soviet Union (and their allies). Nevertheless, it authorized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maritime Patrol Aircraft
A maritime patrol aircraft (MPA), also known as a patrol aircraft, maritime reconnaissance aircraft, or by the older American term patrol bomber, is a fixed-wing aircraft designed to operate for long durations over water in maritime patrol roles — in particular anti-submarine warfare (ASW), anti-ship warfare (AShW), and search and rescue (SAR). Among other maritime surveillance resources, such as satellites, ships, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and helicopters, the MPA is an important asset. To perform ASW operations, MPAs typically carry air-deployable sonar buoys as well as torpedoes and are usually capable of extended flight at low altitudes. History First World War The first aircraft that would now be identified as maritime patrol aircraft were flown by the Royal Naval Air Service and the French Aéronautique Maritime during the First World War, primarily on anti-submarine patrols. France, Italy and Austria-Hungary used large numbers of smaller patrol aircraft for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lockheed P-3 Orion
The Lockheed P-3 Orion is a four-engined, turboprop anti-submarine and maritime surveillance aircraft developed for the United States Navy and introduced in the 1960s. Lockheed based it on the L-188 Electra commercial airliner. The aircraft is easily distinguished from the Electra by its distinctive tail stinger or "MAD" boom, used for the (MAD) of submarines. Over the years, the aircraft has seen numerous design developments, most notably in its electronics packages. Nume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brest, France
Brest (; ) is a port city in the Finistère department, Brittany. Located in a sheltered bay not far from the western tip of the peninsula, and the western extremity of metropolitan France, Brest is an important harbour and the second French military port after Toulon. The city is located on the western edge of continental France. With 142,722 inhabitants in a 2007 census, Brest forms Western Brittany's largest metropolitan area (with a population of 300,300 in total), ranking third behind only Nantes and Rennes in the whole of historic Brittany, and the 19th most populous city in France; moreover, Brest provides services to the one million inhabitants of Western Brittany. Although Brest is by far the largest city in Finistère, the ''préfecture'' (regional capital) of the department is the much smaller Quimper. During the Middle Ages, the history of Brest was the history of its castle. Then Richelieu made it a military harbour in 1631. Brest grew around its arsenal unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Directorate-General For Maritime Affairs And Fisheries
The Directorate-General for Maritime Affairs and Fisheries (DG MARE) is a Directorate-General of the European Commission, responsible for the policy area of fisheries, the Law of the Sea and Maritime Affairs of the European Union. The current director-general is Charlina Vitcheva. Mission The mission of DG MARE is “To steer, in close relationship with stakeholders at regional and European level, the development and implementation of the Integrated Maritime Policy and to manage the Common Fisheries Policy with a view to promote the sustainable development of maritime activities as well as the sustainable exploitation of fisheries resources within and beyond Community waters” Structure The DG MARE encompasses 6 Directorates, all headquartered in Brussels: * A: Policy development and coordination * B: External Policy and Markets * C: Atlantic, outermost regions and Arctic * D: Mediterranean and Black Sea * E: Baltic Sea, Black Sea and landlocked member states * F: Resources ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piracy
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and other valuable goods. Those who conduct acts of piracy are called pirates, vessels used for piracy are pirate ships. The earliest documented instances of piracy were in the 14th century BC, when the Sea Peoples, a group of ocean raiders, attacked the ships of the Aegean and Mediterranean civilisations. Narrow channels which funnel shipping into predictable routes have long created opportunities for piracy, as well as for privateering and commerce raiding. Historic examples include the waters of Gibraltar, the Strait of Malacca, Madagascar, the Gulf of Aden, and the English Channel, whose geographic structures facilitated pirate attacks. The term ''piracy'' generally refers to maritime piracy, although the term has been generalized to refer to acts committed on land, in the air, on computer networks, and (in scie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Union Mission In Somalia
The African Union Mission in Somalia (AMISOM) was a regional peacekeeping mission operated by the African Union with the approval of the United Nations Security Council. It was mandated to support transitional governmental structures, implement a national security plan, train the Somali security forces, and to assist in creating a secure environment for the delivery of humanitarian aid. As part of its duties, AMISOM supported the Federal Government of Somalia's forces in their battle against Al-Shabaab militants. AMISOM was created by the African Union's Peace and Security Council on 19 January 2007 with an initial six-month mandate. On 21 February 2007 the United Nations Security Council approved the mission's mandate. Subsequent six-monthly renewals of AMISOM's mandate by the African Union Peace and Security Council have also been authorized by the United Nations Security Council. The duration of AMISOM's mandate had been extended in each period that it has been up for r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of The European Union
The Council of the European Union, often referred to in the treaties and other official documents simply as the Council, and informally known as the Council of Ministers, is the third of the seven Institutions of the European Union (EU) as listed in the Treaty on European Union. It is one of two legislative bodies and together with the European Parliament serves to amend and approve or veto the proposals of the European Commission, which holds the right of initiative. The Council of the European Union and the European Council are the only EU institutions that are explicitly intergovernmental, that is, forums whose attendees express and represent the position of their Member State's executive, be they ambassadors, ministers or heads of state/government. The Council meets in 10 different configurations of national ministers (one per state). The precise membership of these configurations varies according to the topic under consideration; for example, when discussing agri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


