|
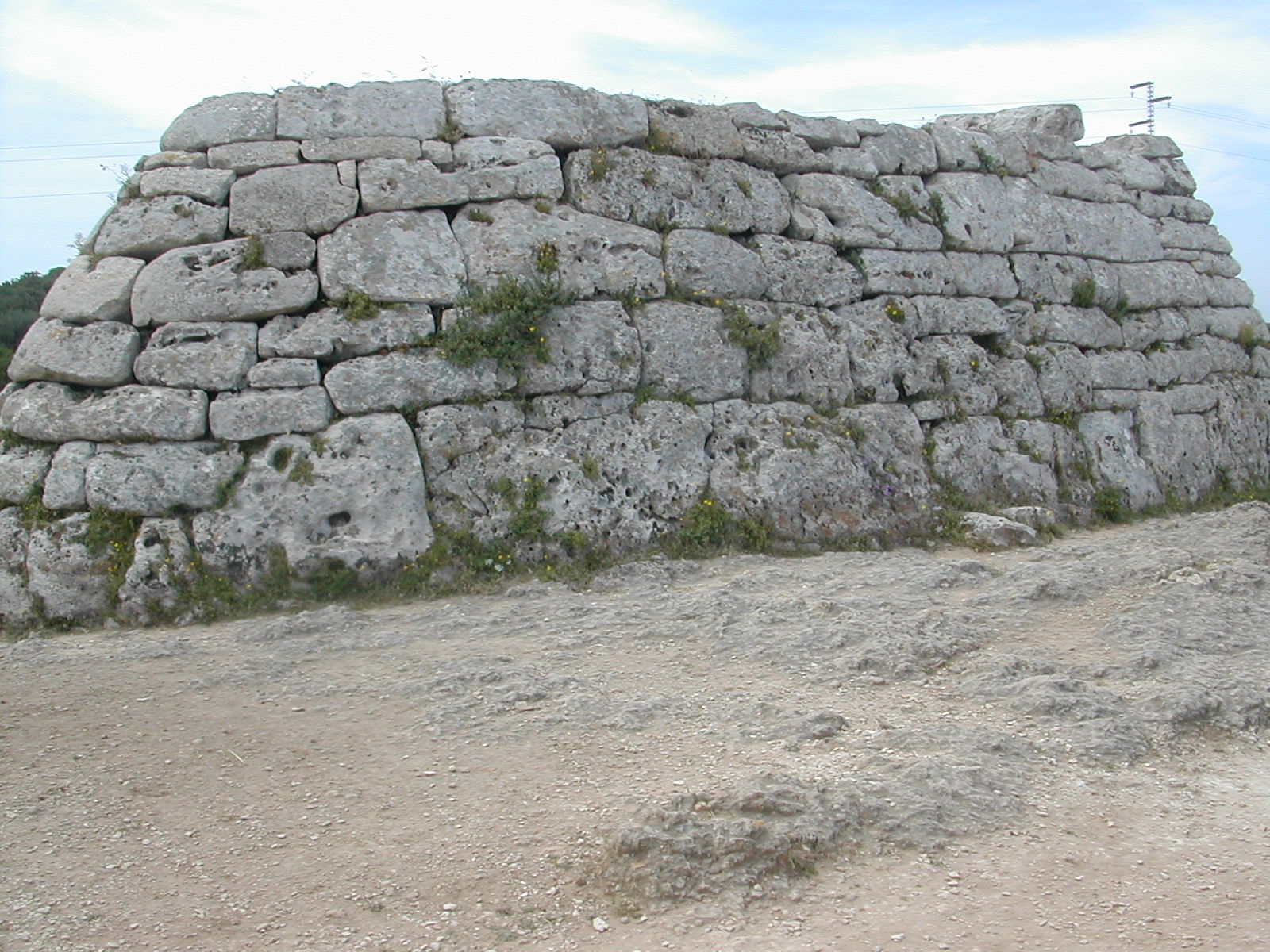
Naveta
{{No footnotes, date=April 2022 A naveta is a form of megalithic chamber tomb unique to the Balearic island of Menorca. They date to the early Bronze Age. They have two vertical and two corbelled walls giving them the form of an upturned boat, from which the navetas take their name. The largest example is the Naveta d'Es Tudons which is around 4m high, 14m long and 6.4m wide. The first author who wrote about these structures was Juan Ramis in his book '' Celtic antiquities on the island of Menorca'', which was edited in 1818, it being the first book in the Spanish language entirely devoted to prehistory Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use .... External links *José Simón Gornés HacheroContinuidad y cambio en las prácticas funerarias del bronce final y primera eda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naveta D'Es Tudons
The Naveta d'Es Tudons, or Naveta of Es Tudons (in Menorquí, ''naveta'', or ''naueta'', a diminutive form of ''nau'', means ''nave'', and ''Es Tudons'', lit. ''the woodpigeons'', is the name of the place), is the most remarkable megalithic chamber tomb in the Balearic island of Menorca, Spain. It is located in the Western part of the island, on the Ciutadella de Menorca-Mahón road, approximately 3 miles out from Ciutadella, and 200 m south of the road. It stands on slightly rising ground in a sloping valley. Currently the Naveta d'Es Tudons is open to the public for visits (except for its interior as a measure of protection). It is one of the main tourist attractions of Menorca. History In Menorca and Majorca there are several dozen habitational and funerary naveta complexes, some of which similarly comprise two storeys. Navetas (''navetes'' in Menorquí) are chronologically pre-Talaiotic (i.e. prior to the Talaiotic age) constructions. Navetas were described in the early 19th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naveta Tudons
{{No footnotes, date=April 2022 A naveta is a form of megalithic chamber tomb unique to the Balearic island of Menorca. They date to the early Bronze Age. They have two vertical and two corbelled walls giving them the form of an upturned boat, from which the navetas take their name. The largest example is the Naveta d'Es Tudons which is around 4m high, 14m long and 6.4m wide. The first author who wrote about these structures was Juan Ramis in his book '' Celtic antiquities on the island of Menorca'', which was edited in 1818, it being the first book in the Spanish language entirely devoted to prehistory Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use .... External links *José Simón Gornés HacheroContinuidad y cambio en las prácticas funerarias del bronce final y primera edad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menorca
Menorca or Minorca (from la, Insula Minor, , smaller island, later ''Minorica'') is one of the Balearic Islands located in the Mediterranean Sea belonging to Spain. Its name derives from its size, contrasting it with nearby Majorca. Its capital is Mahón ( ca, Maó), situated on the island's eastern end, although Menorca is not a province and forms a political union with the other islands in the archipelago. Ciutadella and Mahon are the main ports and largest towns. The port of Mahon is the second biggest natural port in the world. Menorca has a population of approximately 93,397 (at 1 January 2019). It is located 39°47' to 40°00'N, 3°52' to 4°24'E. Its highest point, called El Toro (from Catalan "''turó''" meaning ''hill''), is above sea level. History The island is known for its collection of megalithic stone monuments: ''navetes'', ''taules'' and '' talaiots'', which indicate very early prehistoric human activity. Some of the earliest culture on Menorca was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megalithic
A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. There are over 35,000 in Europe alone, located widely from Sweden to the Mediterranean sea. The word was first used in 1849 by the British antiquarian Algernon Herbert in reference to Stonehenge and derives from the Ancient Greek words " mega" for great and "lithos" for stone. Most extant megaliths were erected between the Neolithic period (although earlier Mesolithic examples are known) through the Chalcolithic period and into the Bronze Age. At that time, the beliefs that developed were dynamism and animism, because Indonesia experienced the megalithic age or the great stone age in 2100 to 4000 BC. So that humans ancient tribe worship certain objects that are considered to have supernatural powers. Some relics of the megalithic era are menhirs (stone monuments) and dolmens (stone tables). Types and definitions While "megalith" i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chamber Tomb
A chamber tomb is a tomb for burial used in many different cultures. In the case of individual burials, the chamber is thought to signify a higher status for the interred than a simple grave. Built from rock or sometimes wood, the chambers could also serve as places for storage of the dead from one family or social group and were often used over long periods for multiple burials. Most the chamber tombs were constructed from large stones or megaliths and covered by cairns, barrows or earth. Some chamber tombs are rock-cut monuments or wooden-chambered tombs covered with earth barrows. Grave goods are a common characteristic of chamber tomb burials. In Neolithic and Bronze Age Europe, stone-built examples of these burials are known by the generic term of megalithic tombs. Chamber tombs are often distinguished by the layout of their chambers and entrances or the shape and material of the structure that covered them, either an earth barrow or stone cairn. A wide variety ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balearic Islands
The Balearic Islands ( ca, Illes Balears ; es, Islas Baleares or ) are an archipelago in the western Mediterranean Sea, near the eastern coast of the Iberian Peninsula. The archipelago forms a Provinces of Spain, province and Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Spain, with Palma de Mallorca being its capital and largest city. Formerly part of the Kingdom of Majorca, Kingdom of Mallorca, the islands were made a province in the 19th century provincial division, which in 1983 received a Statute of Autonomy of the Balearic Islands, Statute of Autonomy. In its later reform of 2007, the Statute designates the Balearic Islands as one of the ''nationalities and regions of Spain, nationalities'' of Spain. The official Languages of Spain, languages of the Balearic Islands are Catalan language, Catalan and Spanish language, Spanish. The archipelago islands are further grouped in western Pityusic Islands, Pytiuses (the largest being Ibiza and Formentera), and east ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second principal period of the three-age system proposed in 1836 by Christian Jürgensen Thomsen for classifying and studying ancient societies and history. An ancient civilization is deemed to be part of the Bronze Age because it either produced bronze by smelting its own copper and alloying it with tin, arsenic, or other metals, or traded other items for bronze from production areas elsewhere. Bronze is harder and more durable than the other metals available at the time, allowing Bronze Age civilizations to gain a technological advantage. While terrestrial iron is naturally abundant, the higher temperature required for smelting, , in addition to the greater difficulty of working with the metal, placed it out of reach of common use until th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan Ramis
Juan Ramis y Ramis (27 April 1746 – 12 February 1819) was a lawyer, writer and historian from Menorca, Balearic Islands. Biography Ramis y Ramis was born and died in Mahón. He was the son of Bartolomé Ramis y Serra and Caternia Ramis y Calafat, and was the eldest of eight siblings: Pere (1748-1816), who was a distinguished lawyer and translator; Bartolomé (1751-1837), doctor; José (1766-1821), priest; Antonio (1771-1840), who took over the historiographic work of Juan; Ramon; Marianna, married to Nicolau Orfila (a lawyer from Ferreries and member of Societat Maonesa); and Joana. Since his early days he was instructed in Latin grammar, arithmetic and some modern languages. In 1762 he was sent to Palma de Mallorca to study rhetoric and philosophy in the University of Letters of Mallorca, where he was promoted to Bachelor of Philosophy on 5 March 1765 and appointed Master and Doctor in Liberal Arts four days later, with the distinction ''nemine discrepante''. He continued ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celtic Antiquities On The Island Of Menorca
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to: Language and ethnicity *pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia **Celts (modern) *Celtic languages **Proto-Celtic language *Celtic music *Celtic nations Sports Football clubs * Celtic F.C., a Scottish professional football club based in Glasgow ** Celtic F.C. Women *Bangor Celtic F.C., Northern Irish, defunct * Belfast Celtic F.C., Northern Irish, defunct * Blantyre Celtic F.C., Scottish, defunct * Bloemfontein Celtic F.C., South African *Castlebar Celtic F.C., Irish *Celtic F.C. (Jersey City), United States, defunct *Celtic FC America, from Houston, Texas * Celtic Nation F.C., English, defunct *Cleator Moor Celtic F.C., English * Cork Celtic F.C., Irish, defunct * Cwmbran Celtic F.C., Welsh * Derry Celtic F.C., Irish, defunct *Donegal Celtic F.C., Northern Irish * Dungiven Celtic F.C., Northern Irish, defunct *Farsley Celtic F.C., English * Leicester Celtic A.F.C., Irish * Lurgan Celtic F.C., Northe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistory
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burial Monuments And Structures
Burial, also known as interment or inhumation, is a method of final disposition whereby a dead body is placed into the ground, sometimes with objects. This is usually accomplished by excavating a pit or trench, placing the deceased and objects in it, and covering it over. A funeral is a ceremony that accompanies the final disposition. Humans have been burying their dead since shortly after the origin of the species. Burial is often seen as indicating respect for the dead. It has been used to prevent the odor of decay, to give family members closure and prevent them from witnessing the decomposition of their loved ones, and in many cultures it has been seen as a necessary step for the deceased to enter the afterlife or to give back to the cycle of life. Methods of burial may be heavily ritualized and can include natural burial (sometimes called "green burial"); embalming or mummification; and the use of containers for the dead, such as shrouds, coffins, grave liners, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |