|
Natural Fiber
Natural fibers or natural fibres (see Spelling differences#-re, -er, spelling differences) are fibers that are produced by geology, geological processes, or from the bodies of plants or animals. They can be used as a component of Composite material, composite materials, where the orientation of fibers impacts the properties. Natural fibers can also be Felted, matted into sheets to make paper or felt. The earliest evidence of humans using fibers is the discovery of wool and dyed flax fibers found in a prehistoric cave in the Georgia (country), Republic of Georgia that date back to 36,000 Before Present, BP. Natural fibers can be used for high-tech applications, such as Composite material, composite parts for automobiles and medical supplies. Compared to composites reinforced with glass fibers, composites with natural fibers have advantages such as lower density, better thermal insulation, and reduced skin irritation. Further, unlike glass fibers, natural fibers can be broken down ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spelling Differences
Despite the various English dialects spoken from country to country and within different regions of the same country, there are only slight regional variations in English orthography, the two most notable variations being British and American spelling. Many of the differences between American and British or Commonwealth English date back to a time before spelling standards were developed. For instance, some spellings seen as "American" today were once commonly used in Britain, and some spellings seen as "British" were once commonly used in the United States. A "British standard" began to emerge following the 1755 publication of Samuel Johnson's '' A Dictionary of the English Language'', and an "American standard" started following the work of Noah Webster and, in particular, his '' An American Dictionary of the English Language'', first published in 1828. Webster's efforts at spelling reform were effective in his native country, resulting in certain well-known pattern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seed Fiber
In botany, a seed is a plant structure containing an embryo and stored nutrients in a protective coat called a ''testa''. More generally, the term "seed" means anything that can be sown, which may include seed and husk or tuber. Seeds are the product of the ripened ovule, after the embryo sac is fertilized by sperm from pollen, forming a zygote. The embryo within a seed develops from the zygote and grows within the mother plant to a certain size before growth is halted. The formation of the seed is the defining part of the process of reproduction in seed plants (spermatophytes). Other plants such as ferns, mosses and liverworts, do not have seeds and use water-dependent means to propagate themselves. Seed plants now dominate biological niches on land, from forests to grasslands both in hot and cold climates. In the flowering plants, the ovary ripens into a fruit which contains the seed and serves to disseminate it. Many structures commonly referred to as "seeds" are actual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
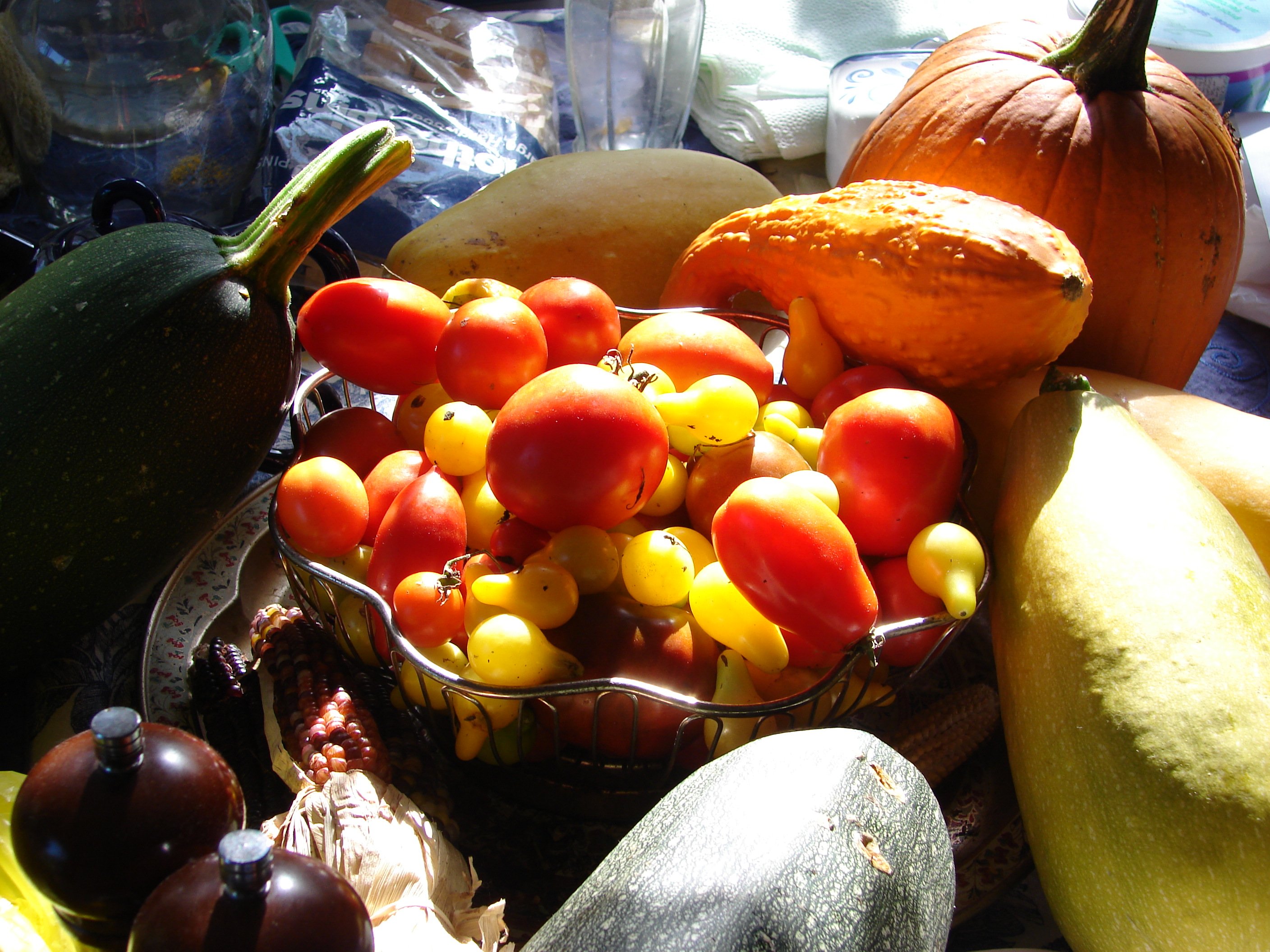
Fruit Fiber
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants (angiosperms) that is formed from the ovary after flowering. Fruits are the means by which angiosperms disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particular have long propagated using the movements of humans and other animals in a symbiotic relationship that is the means for seed dispersal for the one group and nutrition for the other; humans, and many other animals, have become dependent on fruits as a source of food. Consequently, fruits account for a substantial fraction of the world's agricultural output, and some (such as the apple and the pomegranate) have acquired extensive cultural and symbolic meanings. In common language and culinary usage, ''fruit'' normally means the seed-associated fleshy structures (or produce) of plants that typically are sweet (or sour) and edible in the raw state, such as apples, bananas, grapes, lemons, oranges, and strawberries. In botanical usage, the term ''fruit'' also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jute Field Bangladesh (7749587518)
Jute ( ) is a long, rough, shiny bast fibre that can be spun into coarse, strong threads. It is produced from flowering plants in the genus ''Corchorus'', of the mallow family Malvaceae. The primary source of the fiber is '' Corchorus olitorius'', but such fiber is considered inferior to that derived from '' Corchorus capsularis''. Jute fibers, composed primarily of cellulose and lignin, are collected from bast (the phloem of the plant, sometimes called the "skin"). The industrial term for jute fiber is ''raw jute''. The fibers are off-white to brown and range from long. In Bangladesh, jute is called the "golden fiber" for its color and monetary value. The bulk of the jute trade is centered in South Asia, with India and Bangladesh as the primary producers. The majority of jute is used for durable and sustainable packaging, such as burlap sacks. Its production and usage declined as disposable plastic packaging became common, but this trend has begun to reverse as merchants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vine
A vine is any plant with a growth habit of trailing or scandent (that is, climbing) stems, lianas, or runners. The word ''vine'' can also refer to such stems or runners themselves, for instance, when used in wicker work.Jackson; Benjamin; Daydon (1928). ''A Glossary of Botanic Terms with their Derivation and Accent'', 4th ed. London: Gerald Duckworth & Co. In parts of the world, including the British Isles, the term "vine" usually applies exclusively to grapevines, while the term "climber" is used for all climbing plants. Growth forms Certain plants always grow as vines, while a few grow as vines only part of the time. For instance, poison ivy and bittersweet can grow as low shrubs when support is not available, but will become vines when support is available. A vine displays a growth form based on very long stems. This has two purposes. A vine may use rock exposures, other plants, or other supports for growth rather than investing energy in a lot of supportive tissu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
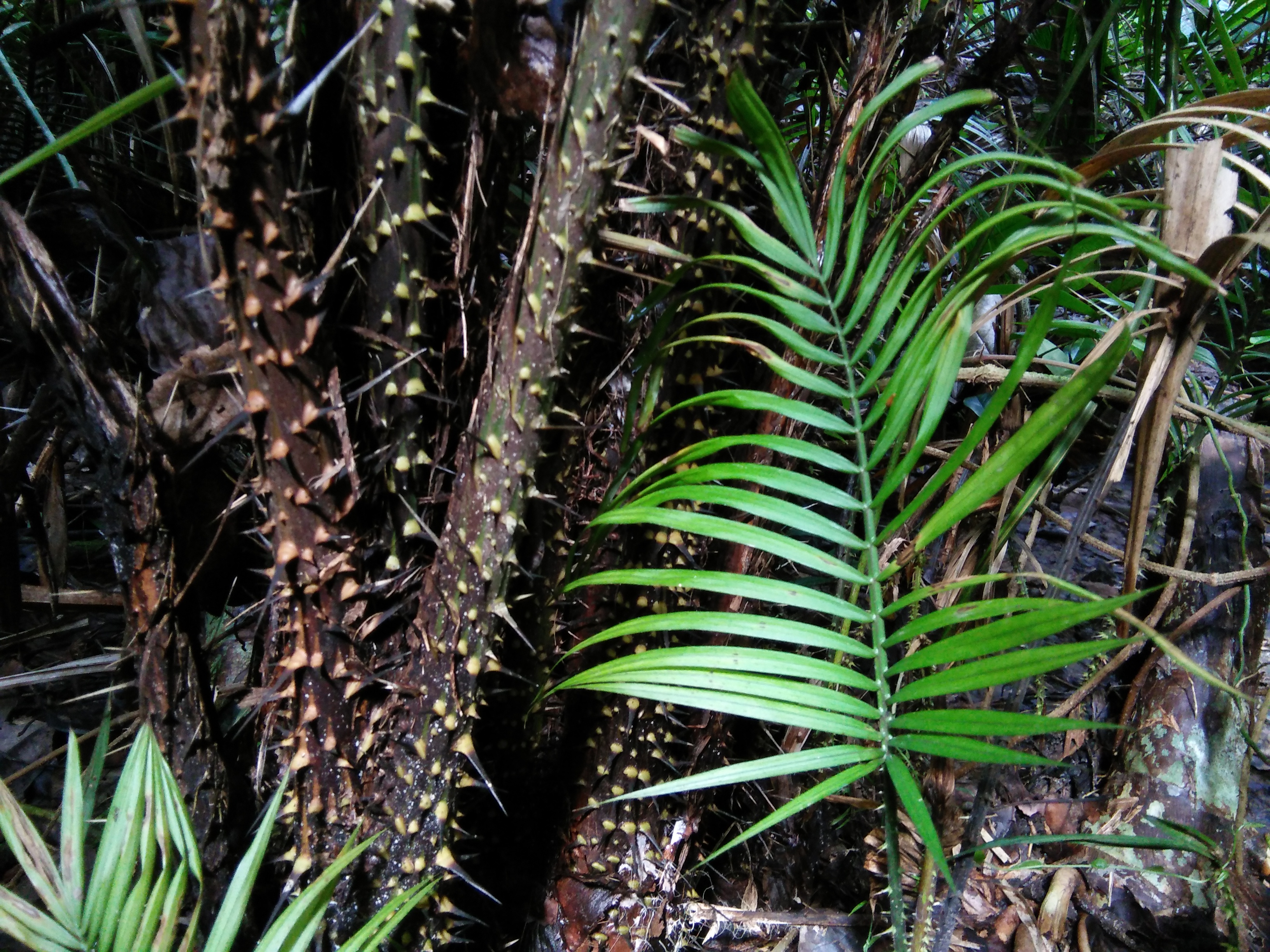
Rattan
Rattan, also spelled ratan (from Malay language, Malay: ''rotan''), is the name for roughly 600 species of Old World climbing palms belonging to subfamily Calamoideae. The greatest diversity of rattan palm species and genera are in the closed-Canopy (biology), canopy Old-growth forest, old-growth tropical forests of Southeast Asia, though they can also be found in other parts of tropical Asia and Africa. Most rattan palms are ecologically considered lianas due to their climbing habits, unlike other palm species. A few species also have tree-like or shrub-like habits. Around 20% of rattan palm species are economically important and are traditionally used in Southeast Asia in producing wickerwork furniture, baskets, Walking stick, canes, woven mats, Rope, cordage, and other handicrafts. Rattan canes are one of the world's most valuable non-timber forest products. Some species of rattan also have edible scaly fruit and heart of palm. Despite increasing attempts in the last 30 y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramie
Ramie (pronounced: , ; from Malay ), ''Boehmeria nivea'', is a flowering plant in the nettle family Urticaceae, native to eastern Asia. It is an herbaceous perennial growing to tall;Ramie: Old Fiber - New Image at the (September 17, 2002). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemp
Hemp, or industrial hemp, is a plant in the botanical class of ''Cannabis sativa'' cultivars grown specifically for industrial and consumable use. It can be used to make a wide range of products. Along with bamboo, hemp is among the fastest growing plants on Earth. It was also one of the first plants to be spun into usable fiber 50,000 years ago. It can be refined into a variety of commercial items, including paper, rope, textiles, clothing, Bioplastic, biodegradable plastics, paint, Thermal insulation, insulation, biofuel, food, and Fodder, animal feed. Although chemotype I cannabis and hemp (types II, III, IV, V) are both ''Cannabis sativa'' and contain the psychoactive component tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), they represent distinct cultivar groups, typically with unique phytochemistry, phytochemical compositions and uses. Hemp typically has lower concentrations of total THC and may have higher concentrations of cannabidiol (CBD), which potentially mitigates the Psychoactive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenaf
Kenaf [etymology: Persian], ''Hibiscus cannabinus'', is a plant in the family Malvaceae also called Deccan hemp and Java jute. ''Hibiscus cannabinus'' is in the genus ''Hibiscus'' and is native to Africa, though its exact origin is unknown. The name also applies to the fibre obtained from this plant. Kenaf is one of the allied fibres of jute and shows similar characteristics. Common names *Europe: **English: Deccan hemp, Java jute, wild stockrose **French language, French: chanvre de Bombay, chanvre du Deccan, chanvre de Guinée, chanvre de Gambo, chanvre de roselle, jute de Java, jute de Siam, kénaf, ketmie à feuilles de chanvre (Belgium), roselle **German language, German: Ambari, Dekkanhanf, Gambohanf, Hanfeibisch, Javajute, Kenaf, Rosellahanf, Roselle, Siamjute **Portuguese language, Portuguese: cânhamo rosella, juta-de-java, juta-do-sião, quenafe **Spanish language, Spanish: cáñamo de la India, cáñamo de gambo, cáñamo Rosella, pavona encendida, yute de Java, yute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jute
Jute ( ) is a long, rough, shiny bast fibre that can be Spinning (textiles), spun into coarse, strong threads. It is produced from flowering plants in the genus ''Corchorus'', of the mallow family Malvaceae. The primary source of the fiber is ''Corchorus olitorius'', but such fiber is considered inferior to that derived from ''Corchorus capsularis''. Jute fibers, composed primarily of cellulose and lignin, are collected from bast (the phloem of the plant, sometimes called the "skin"). The industrial term for jute fiber is ''raw jute''. The fibers are off-white to brown and range from long. In Bangladesh, jute is called the "golden fiber" for its color and monetary value. The bulk of the jute trade is centered in South Asia, with India and Bangladesh as the primary producers. The majority of jute is used for durable and sustainable packaging, such as Gunny sack, burlap sacks. Its production and usage declined as Disposable product, disposable plastic packaging became common, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bast Fiber
Bast fibre (also called phloem fibre or skin fibre) is plant fibre collected from the phloem (the "inner bark", sometimes called "skin") or bast surrounding the stem of certain dicotyledonous plants. Some of the economically important bast fibres are obtained from herbs cultivated in agriculture, for instance flax, hemp, or ramie, but bast fibres from wild plants, such as stinging nettle, and trees such as lime or linden, willow, oak, wisteria, and mulberry have also been used. Bast fibres are soft and flexible, as opposed to leaf fibres from monocotyledonous plants, which are hard and stiff. Since the valuable fibres are located in the phloem, they must often be separated from the woody core, the xylem, and sometimes also from the epidermis. The process for this is retting, and can be performed by micro-organisms either on land (nowadays the most important) or in water, or by chemicals (for instance high pH and chelating agents), or by pectinolytic enzymes. In the phloem, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abacá
Abacá ( ; ), also known as Manila hemp, is a species of banana, ''Musa textilis'', endemic to the Philippines. The plant grows to , and averages about . The plant has great economic importance, being harvested for its fiber extracted from the leaf-stems. The lustrous fiber is traditionally hand-loomed into various indigenous textiles (abaca cloth or medriñaque) in the Philippines. They are still featured prominently as the traditional material of the barong tagalog, the national male attire of the Philippines, as well as in sheer lace-like fabrics called ''nipis'' used in various clothing components. Native abaca textiles also survive into the modern era among various ethnic groups, like the ''t'nalak'' of the T'boli people and the ''dagmay'' of the Bagobo people. Abaca is also used in traditional Philippine millinery, as well as for bags, shawls, and other decorative items. The hatmaking straw made from Manila hemp is called ''tagal'' or ''tagal straw''. The fiber is also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |