|
Natural Apophyseal Glides
Natural apophyseal glides (NAGS) refers to a spinal physical therapy treatment technique developed by Brian Mulligan.Brian R. Mulligan (2004). ''Manual therapy: NAGS, SNAGS, MWMS etc.'' (5th Ed). Plane View Services Ltd. Technique NAGS involves a mid to end-range facet joint mobilisation applied anterocranially along the plane of treatment within the desired joint, combined with a small amount of manual traction. The purpose of this treatment is to increase movement within the spine, and decrease symptomatic pain. Sustained natural apophyseal glides Sustained natural apophyseal glides (SNAGS) are a separate technique involving a combination of a sustained facet glide with active motion, which is then followed by overpressure. Clinical evidence A 2010 study concluded that whilst both NAGS and SNAGS showed signs of effectiveness, SNAGS demonstrated greater statistically significant efficacy over NAGS in reducing pain and disability in subjects with chronic neck pain. Another stu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is one of the allied health professions. It is provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through physical examination, diagnosis, management, prognosis, patient education, physical intervention, rehabilitation, disease prevention, and health promotion. Physical therapists are known as physiotherapists in many countries. In addition to clinical practice, other aspects of physical therapist practice include research, education, consultation, and health administration. Physical therapy is provided as a primary care treatment or alongside, or in conjunction with, other medical services. In some jurisdictions, such as the United Kingdom, physical therapists have the authority to prescribe medication. Overview Physical therapy addresses the illnesses or injuries that limit a person's abilities to move and perform functional activities in their daily lives. PTs use an individual's history and physic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
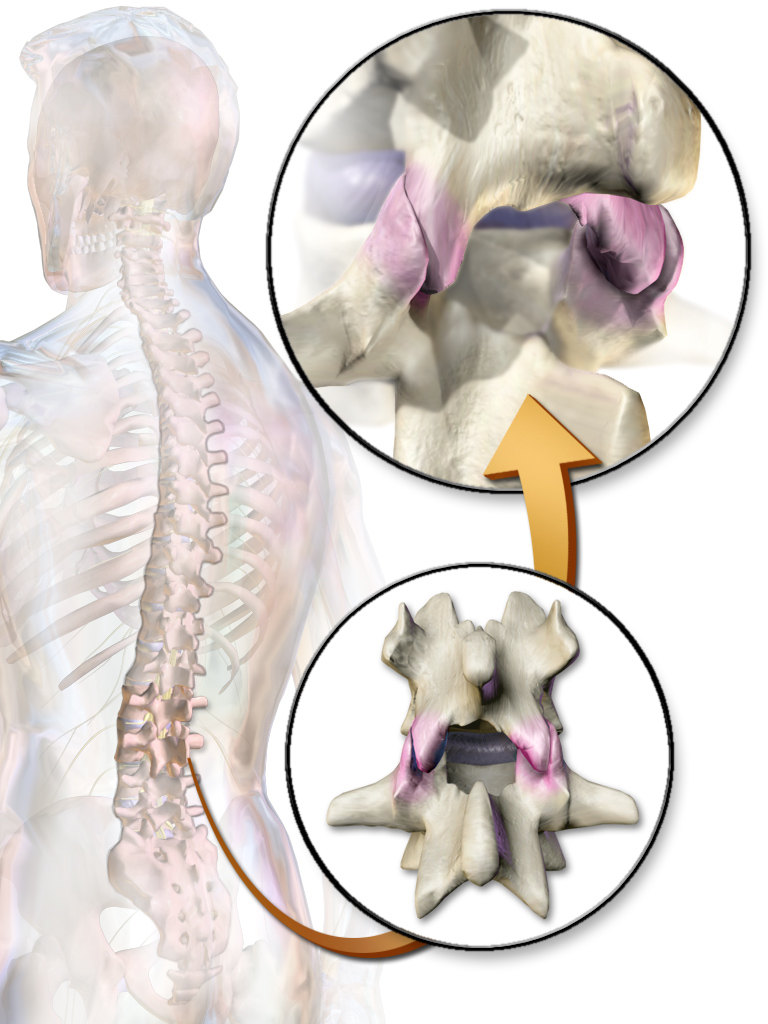
Facet Joint
The facet joints (or zygapophysial joints, zygapophyseal, apophyseal, or Z-joints) are a set of synovial, plane joints between the articular processes of two adjacent vertebrae. There are two facet joints in each spinal motion segment and each facet joint is innervated by the recurrent meningeal nerves. Innervation Innervation to the facet joints vary between segments of the spinal, but they are generally innervated by medial branch nerves that come off the dorsal rami. It is thought that these nerves are for primary sensory input, though there is some evidence that they have some motor input local musculature. Within the cervical spine, most joints are innervated by the medial branch nerve (a branch of the dorsal rami) from the same levels. In other words, the facet joint between C4 and C5 vertebral segments is innervated by the C4 and C5 medial branch nerves. However, there are two exceptions: # The facet joint between C2 and C3 is innervated by the third occipital nerv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neck Pain
Neck pain, also known as cervicalgia, is a common problem, with two-thirds of the population having neck pain at some point in their lives. Neck pain, although felt in the neck, can be caused by numerous other spinal problems. Neck pain may arise due to muscular tightness in both the neck and upper back, or pinching of the nerves emanating from the cervical vertebrae. Joint disruption in the neck creates pain, as does joint disruption in the upper back. The head is supported by the lower neck and upper back, and it is these areas that commonly cause neck pain. The top three joints in the neck allow for most movement of the neck and head. The lower joints in the neck and those of the upper back create a supportive structure for the head to sit on. If this support system is affected adversely, then the muscles in the area will tighten, leading to neck pain. Neck pain affects about 5% of the global population as of 2010. Differential diagnosis Neck pain may come from any of the str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Spondylosis
Spondylosis is the degeneration of the vertebral column from any cause. In the more narrow sense it refers to spinal osteoarthritis, the age-related wear and tear of the spinal column, which is the most common cause of spondylosis. The degenerative process in osteoarthritis chiefly affects the vertebral bodies, the neural foramina and the facet joints (facet syndrome). If severe, it may cause pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots with subsequent sensory or motor disturbances, such as pain, paresthesia, imbalance, and muscle weakness in the limbs. When the space between two adjacent vertebrae narrows, compression of a nerve root emerging from the spinal cord may result in radiculopathy (sensory and motor disturbances, such as severe pain in the neck, shoulder, arm, back, or leg, accompanied by muscle weakness). Less commonly, direct pressure on the spinal cord (typically in the cervical spine) may result in myelopathy, characterized by global weakness, gait dysfunction, l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiculopathy
Radiculopathy, also commonly referred to as pinched nerve, refers to a set of conditions in which one or more nerves are affected and do not work properly (a neuropathy). Radiculopathy can result in pain (radicular pain), weakness, altered sensation (paresthesia) or difficulty controlling specific muscles. Pinched nerves arise when surrounding bone or tissue, such as cartilage, muscles or tendons, put pressure on the nerve and disrupt its function. In a radiculopathy, the problem occurs at or near the root of the nerve, shortly after its exit from the spinal cord. However, the pain or other symptoms often radiate to the part of the body served by that nerve. For example, a nerve root impingement in the neck can produce pain and weakness in the forearm. Likewise, an impingement in the lower back or lumbar-sacral spine can be manifested with symptoms in the foot. The radicular pain that results from a radiculopathy should not be confused with referred pain, which is different bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervicogenic Headache
Cervicogenic headache is a type of headache characterized by chronic hemicranial pain referred to the head from either the cervical spine or soft tissues within the neck. The main symptoms of cervicogenic headaches include pain originating in the neck that can travel to the head or face, headaches that get worse with neck movement, and limited ability to move the neck. Diagnostic imaging can display lesions of the cervical spine or soft tissue of the neck that can be indicative of a cervicogenic headache. When being evaluated for cervicogenic headaches, it is important to rule out a history of migraines and traumatic brain injuries. Studies show that combining interventions such as moist heat applied to the area of pain, spinal and cervical manipulations, and neck massages all help reduce or relieve symptoms. Neck exercises are also beneficial. Specifically, craniocervical flexion, or forward bending of the neck, against light resistance helps increase muscular stability of the he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low Back Pain
Low back pain (LBP) or lumbago is a common disorder involving the muscles, nerves, and bones of the back, in between the lower edge of the ribs and the lower fold of the buttocks. Pain can vary from a dull constant ache to a sudden sharp feeling. Low back pain may be classified by duration as acute (pain lasting less than 6 weeks), sub-chronic (6 to 12 weeks), or chronic (more than 12 weeks). The condition may be further classified by the underlying cause as either mechanical, non-mechanical, or referred pain. The symptoms of low back pain usually improve within a few weeks from the time they start, with 40–90% of people recovered by six weeks. In most episodes of low back pain, a specific underlying cause is not identified or even looked for, with the pain believed to be due to mechanical problems such as muscle or joint strain. If the pain does not go away with conservative treatment or if it is accompanied by "red flags" such as unexplained weight loss, fever, or signific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passive Accessory Intervertebral Movements
Passive accessory intervertebral movements (PAIVM) refers to a spinal physical therapy assessment and treatment technique developed by Geoff Maitland. The purpose of PAIVM is to assess the amount and quality of movement at various intervertebral levels, and to treat pain and stiffness of the cervical and lumbar spine.Geoffrey Douglas Maitland, Elly Hengeveld, Kevin Banks, Kay English, (2005). ''Maitland's Vertebral Manipulation, Volume 1.'' Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann. . Technique During assessment, the aim of PAIVM is to reproduce patient symptoms, and assess the endfeel of cervical movement, quality of resistance, behaviour of pain throughout the range of movement, and observe any muscle spasm. A posterior to anterior force of varying strength is applied by the therapist either centrally onto the spinous process, or unilaterally on either the left or right articular pillar. As a treatment technique, pain is treated by oscillations of small amplitude short of resistance, whilst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passive Physiological Intervertebral Movements
Passive physiological intervertebral movements (PPIVM) refers to a spinal physical therapy assessment and treatment technique developed by Geoff Maitland used to assess intervertebral movement at a single joint, and to mobilise neck stiffness.Geoffrey Douglas Maitland, Elly Hengeveld, Kevin Banks, Kay English, (2005). ''Maitland's Vertebral Manipulation, Volume 1.'' Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann. . Technique PPIVM is used as an assessment technique to assist with identifying the location, nature, severity and irritability of vertebral symptoms. They can be used to test for cervical or lumbar joint hypermobility or instability, or whether a joint is locked. PPIVM assessments test the movement available at a specific spinal level through the application of a passive physiological movement. Cervical PPIVMs can be performed in cervical lateral flexion or rotation, with the therapist restricting movement beyond a certain cervical level by blocking with the hand; this allows the identi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |