|
National Minimum Wage Regulations 1999
The National Minimum Wage Regulations 1999SI 1999/584 were passed as a statutory instrument under the National Minimum Wage Act 1998 to specify various detailed points about how to calculate whether someone is being paid the minimum wage, who gets it, and how to enforce it. Contents Regulations 3 to 6 define four different types of work that people do. *r 3, time work *r 4, salaried work *r 5, output work *r 6, unmeasured work *r 7, travelling definition *r 8 (and Part IV) wage includes incentive pay, bonuses and tips paid through the payroll *r 9 (and Part IV) wage excludes benefits in kind (with exception of accommodation), overtime and shift premia *r 10, definition of ‘pay reference period’ as one month, or a shorter period if that is how a worker is paid. *r 12, excluded are au pairs and family members in family business *r 15(1) ‘time work includes time when a worker is available at or near a place of work, other than his home, for the purpose of doing time work, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Minimum Wage Act 1998
The National Minimum Wage Act 1998 creates a minimum wage across the United Kingdom.. E McGaughey, ''A Casebook on Labour Law'' (Hart 2019) ch 6(1) From 1 April 2022 this was £9.50 for people age 23 and over, £9.18 for 21- to 22-year-olds, £6.83 for 18- to 20-year-olds, £4.81 for people under 18 and apprentices. (See Current and past rates.) It was a flagship policy of the Labour Party in the UK during their successful 1997 general election campaign. The national minimum wage (NMW) took effect on 1 April 1999. On 1 April 2016, an amendment to the act attempted an obligatory " National Living Wage" for workers over 25 (now extended to workers aged 23 and over), which was implemented at a significantly higher minimum wage rate of £7.20 (now increased to £9.50 as of 1 April 2022). This was expected to rise to at least £9 per hour by 2020, but in reality by that year it had only reached £8.72 per hour. Background No national minimum wage existed prior to 1998, although the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tax Credits
A tax credit is a tax incentive which allows certain taxpayers to subtract the amount of the credit they have accrued from the total they owe the state. It may also be a credit granted in recognition of taxes already paid or a form of state "discount" applied in certain cases. Another way to think of a tax credit is as a rebate. Refundable vs. non-refundable A refundable tax credit is one which, if the credit exceeds the taxes due, the government pays back to the taxpayer the difference. In other words, it makes possible a negative tax liability. For example, if a taxpayer has an initial tax liability of $100 and applies a $300 tax credit, then the taxpayer ends with a liability of –$200 and the government refunds to the taxpayer that $200. With a non-refundable tax credit, if the credit exceeds the taxes due then the taxpayer pays nothing but does not receive the difference. In this case, the taxpayer from the example would end with a tax liability of $0 (i.e. they could mak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
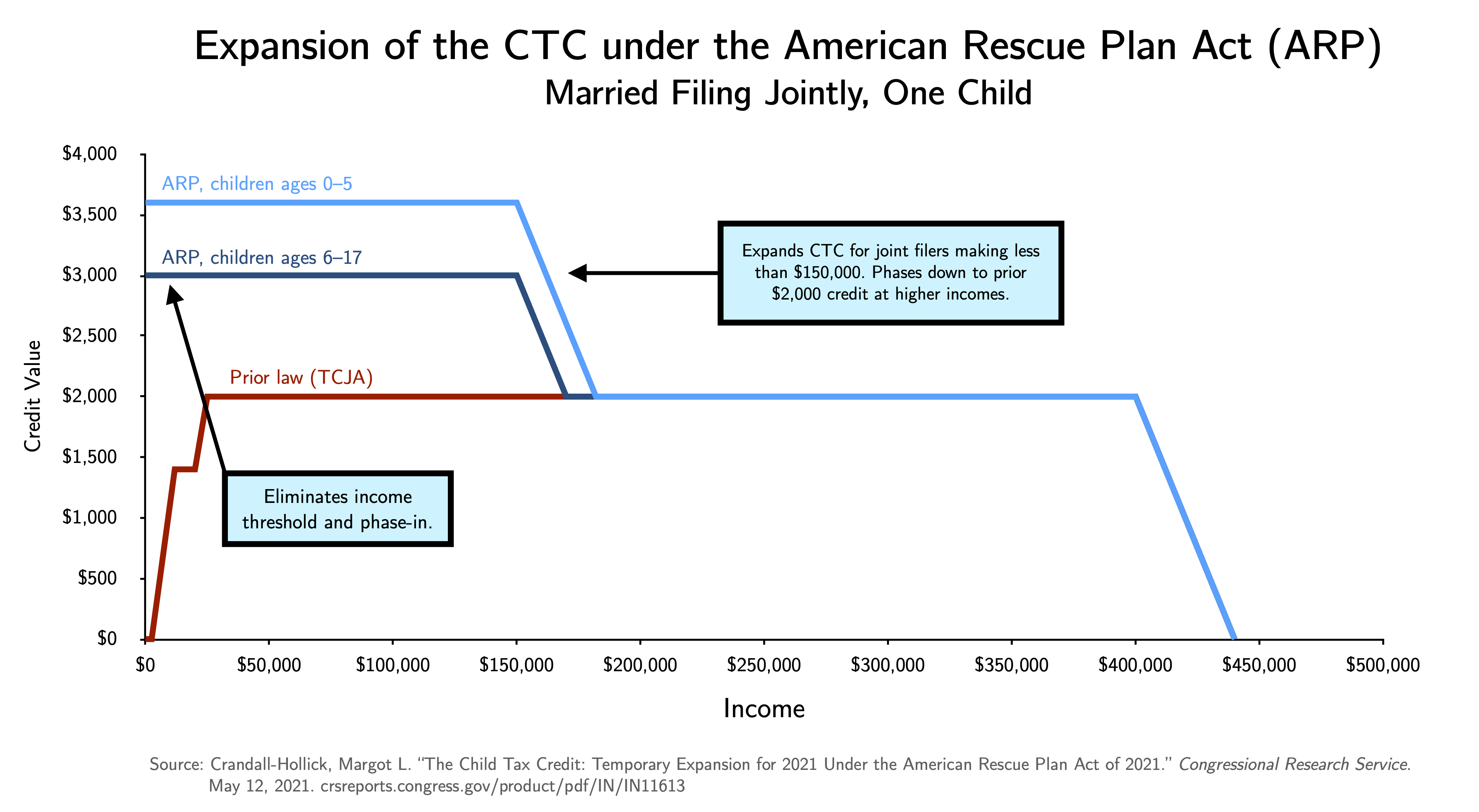
Child Tax Credit
A child tax credit (CTC) is a tax credit for parents with dependent children given by various countries. The credit is often linked to the number of dependent children a taxpayer has and sometimes the taxpayer's income level. For example, in the United States, only families making less than $400,000 per year may claim the full CTC. Similarly, in the United Kingdom, the tax credit is only available for families making less than £42,000 per year. Germany Germany has a programme called the which, despite technically being a tax exemption and not a tax credit, functions similarly. The child allowance is an allowance in German tax law, in which a certain amount of money is tax-free in the taxation of parents. In the income tax fee paid, child benefit and tax savings through the child tax credit are compared against each other, and the parents pay whichever results in the lesser amount of tax. United Kingdom In the United Kingdom, a family with children and an income below about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Working Tax Credit
Working Tax Credit (WTC) is a state benefit in the United Kingdom made to people who work and have a low income. It was introduced in April 2003 and is a means-tested benefit. Despite their name, tax credits are not to be confused with tax credits linked to a person's tax bill, because they are used to top-up wages. Unlike most other benefits, it is paid by HM Revenue and Customs (HMRC). WTC can be claimed by working individuals, childless couples and working families with dependent children. In addition, people may also be entitled to Child Tax Credit (CTC) if they are responsible for any children. WTC and CTC are assessed jointly and families remain eligible for CTC even if where no adult is working or they have too much income to receive WTC. In 2010 the coalition government announced that the Working Tax Credit would, by 2017, be integrated into and replaced by the new Universal Credit. However implementation of this has been repeatedly delayed and will not be finished ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wage Regulation
Wage regulation refers to attempts by a government to regulate wages paid to citizens. Minimum wage Minimum wage regulation attempts to set an hourly, or other periodic monetary standard for pay at work. A recent example was the U.K. National Minimum Wage Act 1998. Germany is currently debating whether to introduce its own. Collective bargaining Collective agreements between trade unions and employers can regulate wages of workers according to the needs of the business. Arbitration Arbitration involves makes collective agreements between trade unions and employers legally binding and mediated through a state appointed judge or magistrate. Economic labour theory An economic analysis of the law holds very simply that any intervention in a contract between two parties creates an inefficient labour market. Wages kept artificially high, by imposing any administrative or monetary costs on employers distorts the labour market equilibrium. For a national economy in a globalised world ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom Labour Law
United Kingdom labour law regulates the relations between workers, employers and trade unions. People at work in the UK can rely upon a minimum charter of employment rights, which are found in Acts of Parliament, Regulations, common law and equity. This includes the right to a minimum wage of £9.50 for over-23-year-olds from April 2022 under the National Minimum Wage Act 1998. The Working Time Regulations 1998 give the right to 28 days paid holidays, breaks from work, and attempt to limit long working hours. The Employment Rights Act 1996 gives the right to leave for child care, and the right to request flexible working patterns. The Pensions Act 2008 gives the right to be automatically enrolled in a basic occupational pension, whose funds must be protected according to the Pensions Act 1995. Workers must be able to vote for trustees of their occupational pensions under the Pensions Act 2004. In some enterprises, such as universities, staff can vote for the directors of the orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statutory Instruments Of The United Kingdom
A statute is a formal written enactment of a legislative authority that governs the legal entities of a city, state, or country by way of consent. Typically, statutes command or prohibit something, or declare policy. Statutes are rules made by legislative bodies; they are distinguished from case law or precedent, which is decided by courts, and regulations issued by government agencies. Publication and organization In virtually all countries, newly enacted statutes are published and distributed so that everyone can look up the statutory law. This can be done in the form of a government gazette which may include other kinds of legal notices released by the government, or in the form of a series of books whose content is limited to legislative acts. In either form, statutes are traditionally published in chronological order based on date of enactment. A universal problem encountered by lawmakers throughout human history is how to organize published statutes. Such publications h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1999 In British Law
File:1999 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The funeral procession of King Hussein of Jordan in Amman; the 1999 İzmit earthquake kills over 17,000 people in Turkey; the Columbine High School massacre, one of the first major school shootings in the United States; the Year 2000 problem ("Y2K"), perceived as a major concern in the lead-up to the year 2000; the Millennium Dome opens in London; online music downloading platform Napster is launched, soon a source of online piracy; NASA loses both the Mars Climate Orbiter and the Mars Polar Lander; a destroyed T-55 tank near Prizren during the Kosovo War., 300x300px, thumb rect 0 0 200 200 Death and state funeral of King Hussein rect 200 0 400 200 1999 İzmit earthquake rect 400 0 600 200 Columbine High School massacre rect 0 200 300 400 Kosovo War rect 300 200 600 400 Year 2000 problem rect 0 400 200 600 Mars Climate Orbiter rect 200 400 400 600 Napster rect 400 400 600 600 Millennium Dome 1999 was designated as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |