|
National Immunisation Program Schedule
The Australian National Immunisation Program Schedule sets out the immunisations Australians are given at different stages in their life. The program aims to reduce the number of preventable disease cases in Australia by increasing national immunisation coverage. The program starts for an Australian when they are born. Vaccinations are given at birth, then again when the baby is 2 months, 4 months, 6 months, 12 months and 18 months. The immunisation schedule continues when the child is 4 years old, and then into adolescent years. The program is not compulsory and parents have the choice if they want their child vaccinated. Background The National Immunisation Program was first introduced in Australia in 1997. The program was set up by the Commonwealth, state and territory governments. The most recent update to the National Immunisation Program was effective since 1 April 2019. This was an update from the 2007 schedule, one change including the introduction of meningococcal AC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunization
Immunization, or immunisation, is the process by which an individual's immune system becomes fortified against an infectious agent (known as the immunogen). When this system is exposed to molecules that are foreign to the body, called ''non-self'', it will orchestrate an immune response, and it will also develop the ability to quickly respond to a subsequent encounter because of immunological memory. This is a function of the adaptive immune system. Therefore, by exposing a human, or an animal, to an immunogen in a controlled way, its body can learn to protect itself: this is called active immunization. The most important elements of the immune system that are improved by immunization are the T cells, B cells, and the antibodies B cells produce. Memory B cells and memory T cells are responsible for a swift response to a second encounter with a foreign molecule. Passive immunization is direct introduction of these elements into the body, instead of production of these elements b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by area in Oceania and the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, sixth-largest country. Australia is the oldest, flattest, and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils. It is a Megadiverse countries, megadiverse country, and its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes and climates, with Deserts of Australia, deserts in the centre, tropical Forests of Australia, rainforests in the north-east, and List of mountains in Australia, mountain ranges in the south-east. The ancestors of Aboriginal Australians began arriving from south east Asia approximately Early human migrations#Nearby Oceania, 65,000 years ago, during the Last Glacial Period, last i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Commonwealth
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by area in Oceania and the world's sixth-largest country. Australia is the oldest, flattest, and driest inhabited continent, with the least fertile soils. It is a megadiverse country, and its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes and climates, with deserts in the centre, tropical rainforests in the north-east, and mountain ranges in the south-east. The ancestors of Aboriginal Australians began arriving from south east Asia approximately 65,000 years ago, during the last ice age.religious_traditions_in_the_world._Australia's_history_of_Australia.html" "title="The_Dreaming.html" ;"title="Aboriginal_Art.html" "title="he Story of Australia's People, Volume 1: The Rise and Fall of Ancient Australia, Penguin Books Australia Ltd., Vic., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meningococcal Disease
Meningococcal disease describes infections caused by the bacterium ''Neisseria meningitidis'' (also termed meningococcus). It has a high mortality rate if untreated but is vaccine-preventable. While best known as a cause of meningitis, it can also result in sepsis, which is an even more damaging and dangerous condition. Meningitis and meningococcemia are major causes of illness, death, and disability in both developed and under-developed countries. There are approximately 2,600 cases of bacterial meningitis per year in the United States, and on average 333,000 cases in developing countries. The case fatality rate ranges between 10 and 20 percent. The incidence of endemic meningococcal disease during the last 13 years ranges from 1 to 5 per 100,000 in developed countries, and from 10 to 25 per 100,000 in developing countries. During epidemics the incidence of meningococcal disease approaches 100 per 100,000. Meningococcal vaccines have sharply reduced the incidence of the diseas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Needle Injection Stock Footage
Needle may refer to: Crafting * Crochet needle, a tool for making loops in thread or yarn * Knitting needle, a tool for knitting, not as sharp as a sewing needle * Sewing needle, a long slender tool with a pointed tip * Trussing needle, a long slender tool, sometimes with a flattened point, to tie poultry for cooking * Upholstery needle, a tool for upholstery, generally thick and curved Science and technology Botany * Needle (botany), of conifers Medicine * Hypodermic needle, a hollow needle commonly used with a syringe to inject fluid into or extract fluid from the body * Surgical needle, several types of needles used for surgical suture * Tuohy needle, a needle used to administer epidural catheters Technology * Acupuncture needle, in alternative medicine * Gramophone needle, used for playing records * Indicator needle, of a measuring instrument * Needle valve Places * Needle Rocks, Tasmania, Australia * Needle (stack), a sea stack on the island of Hoy, Orkney, Scotland * Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
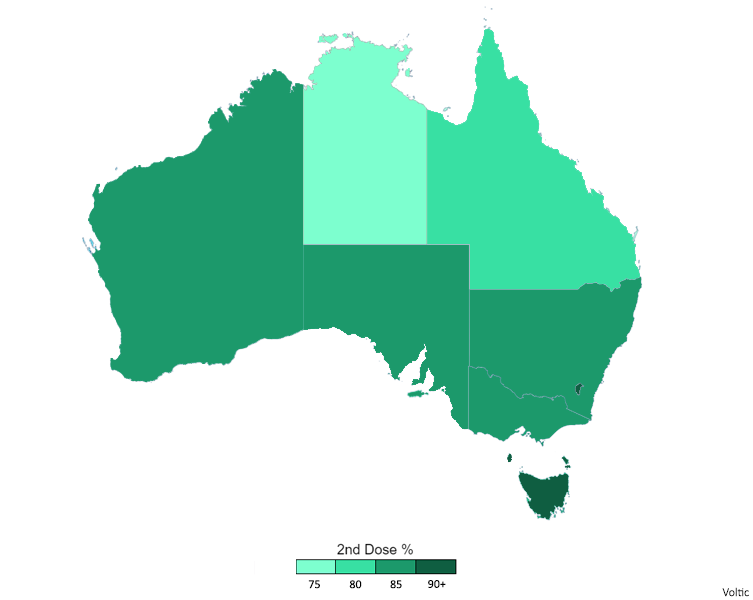
COVID-19 Vaccination In Australia
The general COVID-19 vaccination in Australia program began on 22 February 2021 in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, with the goal of vaccinating all willing people in Australia before 2022. Front-line workers and aged care staff and residents had priority for being inoculated, before a gradual phased release to less-vulnerable and lower-risk population groups throughout 2021. The Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) approved four vaccines for Australian use in 2021: the Pfizer–BioNTech vaccine on 25 January, the Oxford–AstraZeneca vaccine on 16 February, Janssen vaccine on 25 June and the Moderna vaccine on 9 August. Although approved for use, the Janssen vaccine was not included in the Australian vaccination program . As of 3 August 2022, Australia had administered 62,492,656 vaccine doses across the country.(The data on this site changes daily)( The data on this site changes daily.)( The data on this site changes daily) The country's vaccination rollout initia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Technical Advisory Group On Immunisation
The Australian Technical Advisory Group on Immunisation (ATAGI) is a technical advisory group of the Australian Government. As part of the Department of Health, ATAGI provides advice to the Minister of Health on the immunisation program of Australia and related matters, including the strength of evidence pertaining to existing, new, and emerging vaccines. Roles ATAGI's role * The main role of ATAGI is to provide advice on the administration of vaccinations related to the National Immunisation Program (NIP) to the Minister of Health * Advisory on the ongoing immunisation research or the most needed areas * furnish industry supports with pre-accommodation guidance for likely entries to the Pharmaceutical Benefits Advisory Committee (PBAC) on immunisation viability and use in Australia. ATAGI guidance should be looked for before support making an accommodation to the PBAC * Discussion with pertinent associations to create the Australian Immunisation Handbook * Discussion with si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |