|
National Anthem Of Switzerland
The "Swiss Psalm" (german: Schweizerpsalm, italic=no / "Trittst im Morgenrot daher..."; french: Cantique suisse, italic=no, ; it, Salmo svizzero, italic=no, ; rm, Psalm Svizzer, italic=no, ) is the national anthem of Switzerland. It was composed in 1841, by Alberich Zwyssig (1808–1854). Since then, it has been frequently sung at patriotic events. The Federal Council declined, however, on numerous occasions to accept the psalm as the official anthem. This was because the council wanted the people to express their say on what they wanted as a national anthem. From 1961 to 1981, it provisionally replaced "" ("When You Call, My Country"; French ""; Italian "", Romansh ""), the anthem by Johann Rudolf Wyss (1743–1818) that was set to the melody of " God Save the King". On 1 April 1981, the Swiss Psalm was declared the official Swiss national anthem. In 2014, the organized a public competition and unofficial vote to change the lyrics of the national anthem. History The Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel, St. Gallen a.o.). , coordinates = , largest_city = Zürich , official_languages = , englishmotto = "One for all, all for one" , religion_year = 2020 , religion_ref = , religion = , demonym = , german: Schweizer/Schweizerin, french: Suisse/Suissesse, it, svizzero/svizzera or , rm, Svizzer/Svizra , government_type = Federalism, Federal assembly-independent Directorial system, directorial republic with elements of a direct democracy , leader_title1 = Federal Council (Switzerland), Federal Council , leader_name1 = , leader_title2 = , leader_name2 = Walter Thurnherr , legislature = Fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Symbols Of Switzerland
National symbols of Switzerland are the symbols used to represent Switzerland. As of 2020 the Swiss legislature has made three Swiss national symbols official, a flag, coat of arms and anthem, but various other symbols are used as well to represent the Swiss people. Official national symbols Unofficial national symbols {, class="wikitable" ! !Symbol !Image !Notes and source , - , National motto , One for all, all for one (Unus pro omnibus, omnes pro uno) , , Traditional and widespread, but not yet official. It has been recognized and used by various Swiss presidents. German: ''Einer für alle, alle für einen''; French: ''Un pour tous, tous pour un''; Italian: ''Uno per tutti, tutti per uno''; Romansh: ''In per tuts, tuts per in''. , - , National personification , Helvetia , , Unofficial, but shown on the national currency and stamps. , - , National flower , Edelweiss (Leontopodium nivale) , , Widely accepted as the Swiss national flower. Has been used on money, rank ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss Music
Switzerland has long had a distinct cultural identity, despite its diversity of German, French, Italian, Romansh and other ethnicities. Religious and folk music dominated the country until the 17th century, with growth in production of other kinds of music occurring slowly. Folk music Due to a lack of detailed records, little is known about Swiss folk music prior to the 19th century. Some 16th-century lute tablatures have been reconstructed into authentic instrumental arrangements; however, the first major source of information comes from 19th-century collections of folk songs, and work done by musicologist Hanny Christen. One of the oldest varieties of folk music was the Swiss song Kühreihen, an agricultural Alpine song in the Lydian mode. Traditional instruments included alphorn, hammered dulcimer, fife, hurdy-gurdy, castanets, rebec, bagpipe, cittern and shawm. At the beginning of the 19th century, Swiss folk music was largely performed by ensembles made of itinerant music ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Anthems
Most nation states have an anthem, defined as "a song, as of praise, devotion, or patriotism"; most anthems are either marches or hymns in style. A song or hymn can become a national anthem under the state's constitution, by a law enacted by its legislature, or simply by tradition. A royal anthem is a patriotic song similar to a national anthem, but it specifically praises or prays for a monarch or royal dynasty. Such anthems are usually performed at public appearances by the monarch or during other events of royal importance. Some states use their royal anthem as the national anthem, such as the state anthem of Jordan. There are multiple claimants to the position of oldest national anthem. Among the national anthems, the first to be composed was the Dutch national anthem, the "Wilhelmus", which was written between 1568 and 1572. This has both Dutch and English language versions and is unusual in being an acrostic in both languages. The Japanese anthem, "Kimigayo", employs the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Of Switzerland
The four national languages of Switzerland are German, French, Italian, and Romansh. German, French, and Italian maintain equal status as official languages at the national level within the Federal Administration of the Swiss Confederation, while Romansh is used in dealings with people who speak it. Latin is occasionally used in some formal contexts, particularly to denote the country (''Confederatio Helvetica)''. In 2020, 62.3% of the population of Switzerland were native speakers of German (either Swiss German or Standard German) at home; 22.8% French (mostly Swiss French, but including some Franco-Provençal dialects); 8% Italian (mostly Swiss Italian, but including Lombard); and 0.5% Romansh. The German region (''Deutschschweiz'') is roughly in the east, north, and centre; the French part (''la Romandie'') in the west; and the Italian area (''Svizzera italiana'') in the south. There remains a small Romansh-speaking native population in Grisons in the east. The canton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Constitution Of Switzerland
The Federal Constitution of the Swiss Confederation (SR 10; german: Bundesverfassung der Schweizerischen Eidgenossenschaft (BV); french: Constitution fédérale de la Confédération suisse (Cst.); it, Costituzione federale della Confederazione Svizzera (Cost.); rm, ) of 18 April 1999 (SR 101) is the third and current federal constitution of Switzerland. It establishes the ''Swiss Confederation'' as a federal republic of 26 cantons (states). The document contains a catalogue of individual and popular rights (including the right to call for popular referendums on federal laws and constitutional amendments), delineates the responsibilities of the cantons and the Confederation and establishes the federal authorities of government. The Constitution was adopted by a referendum on 18 April 1999, in which a majority of the people and the Cantons voted in favour. It replaced the prior federal constitution of 1874, which it was intended to bring up to date without changing its s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preamble And Title 1 Of The Swiss Federal Constitution
The preamble and the first title of the Swiss Federal Constitution of 18 April 1999 determine the general outlines of Switzerland as a democratic federal republic of 26 cantons governed by the rule of law. Preamble The preamble to the Constitution states, in full: By opening with a solemn invocation of God, the preamble is in line with all preceding Swiss constitutional documents, back to the Federal Charter of 1291, except for the constitutions adopted under French sway in the time of the Helvetic Republic. Apart from continuing tradition, the '' invocatio dei'' is understood to be a reference to transcendental values underlying society, putting into perspective any claims to authority by the State – a merely human creation. The preamble was authored by journalist Daniel S. Miéville, and inspired in part by a 1977 draft by writer Adolf Muschg. It is a symbolic summation of the will to and purpose of statehood, a declaration of intent by the popular Sovereign, an int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
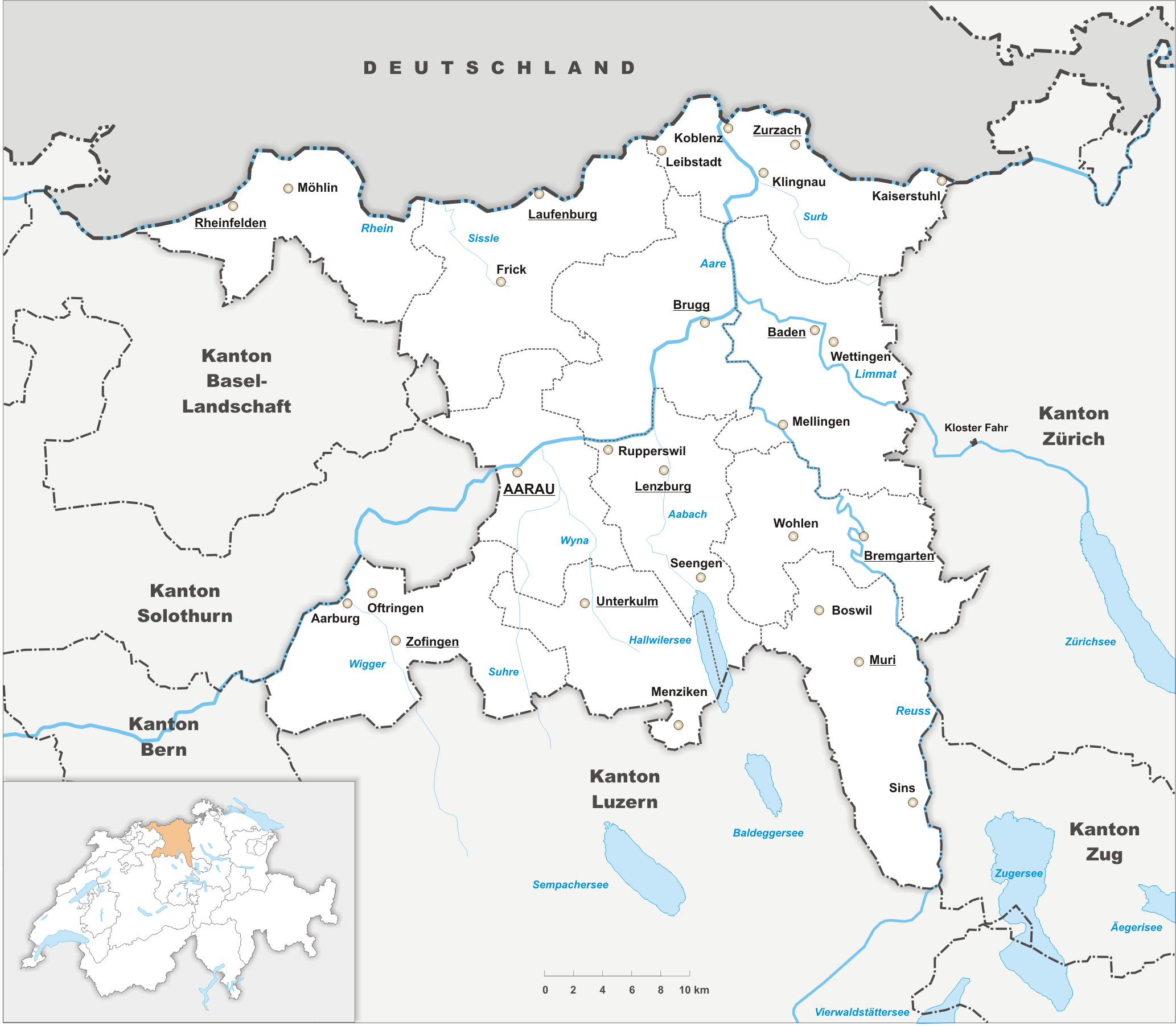
Argovia
Aargau, more formally the Canton of Aargau (german: Kanton Aargau; rm, Chantun Argovia; french: Canton d'Argovie; it, Canton Argovia), is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of eleven districts and its capital is Aarau. Aargau is one of the most northerly cantons of Switzerland. It is situated by the lower course of the Aare River, which is why the canton is called ''Aar- gau'' (meaning "Aare province"). It is one of the most densely populated regions of Switzerland. History Early history The area of Aargau and the surrounding areas were controlled by the Helvetians, a member of the Celts, as far back as 200 BC. It was eventually occupied by the Romans and then by the 6th century, the Franks. The Romans built a major settlement called Vindonissa, near the present location of Brugg. Medieval Aargau The reconstructed Old High German name of Aargau is ''Argowe'', first unambiguously attested (in the spelling ''Argue'') in 795. The term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henri-Frédéric Amiel
Henri Frédéric Amiel (; 27 September 1821 – 11 May 1881) was a Swiss moral philosopher, poet, and critic. Biography Born in Geneva in 1821, Amiel was descended from a Huguenot family that moved to Switzerland following the revocation of the Edict of Nantes. After losing his parents at an early age, Amiel travelled widely, became intimate with the intellectual leaders of Europe, and made a special study of German philosophy in Berlin. In 1849 he was appointed professor of aesthetics at the academy of Geneva, and in 1854 became professor of moral philosophy. These appointments, conferred by the democratic party, deprived him of the support of the aristocratic party, whose patronage dominated all the culture of the city. This isolation inspired the one book by which Amiel is still known, the ''Journal Intime'' ("Private Journal"), which, published after his death, obtained a European reputation. It was translated into English by British writer Mary Augusta Ward at the suggesti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss Italian
The Italian language in Switzerland or Swiss Italian ( it, italiano svizzero) is the variety of the Italian language taught in the Italian-speaking area of Switzerland. Italian is spoken natively by about 700,000 people in the canton of Ticino, in the southern part of Graubünden (Canton Grigioni) and in the rest of the country. Characteristics The presence of calques from French and German means that there are some differences in vocabulary between the standard registers of the Italian language used in Italy and Switzerland. An example would be the words for driving licence: in Italy, it is called a ''patente di guida'' but in Swiss Italian, it becomes ''licenza di condurre'', from the French ''permis de conduire''. Another example is the interurban bus: in Italy it would be ''autobus'' or ''corriera'' but in Switzerland, it is the '' Autopostale'' or ''posta'' since nearly all interurban lines are run by a subsidiary of the Swiss Post. Another notable difference is the us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian Phonology
The phonology of Italian describes the sound system—the phonology and phonetics—of Standard Italian and its geographical variants. Consonants Notes: * Between two vowels, or between a vowel and an approximant () or a liquid (), consonants can be both singleton or geminated. Geminated consonants shorten the preceding vowel (or block phonetic lengthening) and the first geminated element is unreleased. For example, compare ('fate') with ('fact'). However, , , , , are always geminated intervocalically. Similarly, nasals, liquids, and sibilants are pronounced slightly longer in medial consonant clusters. * , , and are the only consonants that cannot be geminated. * are laminal denti-alveolar , commonly called "dental" for simplicity. * are pre-velar before . * have two variants: ** Dentalized laminal alveolar (commonly called "dental" for simplicity), pronounced with the blade of the tongue very close to the upper front teeth, with the tip of the tongue resti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)