|
National Aerospace Technology Administration
National Aerospace Technology Administration (NATA; ) is the official space agency of North Korea, succeeding the Korean Committee of Space Technology (KCST). It was founded on 1 April 2013. Formerly called the National Aerospace Development Administration (NADA), it changed its name in September 2023 following the 9th Session of the 14th Supreme People's Assembly. The current basis for the activities of NATA is the Law on Space Development, passed in 2014 during the 7th session of the 12th Supreme People's Assembly. The act sets out the North Korean principles of the development of space capabilities as it relates to the principles of the North Korean Juche ideology and independence, as well as the aim of solving scientific and technological problems of space exploration to improve its economy, science, and technology. The law also regulates the position of NATA and the principles of notification, security, research, and possibly compensation in relation to satellite launches. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yu Chol-u
Yu Chol-u (born 8 August 1959) is the current Director of the North Korean National Aerospace Development Administration. See also *Politics of North Korea The politics of North Korea (officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea or DPRK) takes place within the framework of the official state philosophy, Kimilsungism-Kimjongilism. ''Juche'', which is a part of Kimilsungism-Kimjongilism, i ... References Space program of North Korea Living people 1959 births Place of birth missing (living people) 21st-century North Korean people {{NorthKorea-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convention On International Liability For Damage Caused By Space Objects
The Convention on International Liability for Damage Caused by Space Objects, also known as the Space Liability Convention, is a treaty from 1972 that expands on the liability rules created in the Outer Space Treaty of 1967. In 1978, the crash of the nuclear-powered Soviet satellite Kosmos 954 in Canadian territory led to the only claim filed under the convention. Status The Liability Convention was concluded and opened for signature on 29 March 1972. It entered into force on 1 September 1972. As of 1 January 2021, 98 States have ratified the Liability Convention, 19 have signed but not ratified and four international intergovernmental organizations (the European Space Agency, the European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites, the Intersputnik International Organization of Space Communications, and the European Telecommunications Satellite Organization) have declared their acceptance of the rights and obligations provided for in the Agreement. Key pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
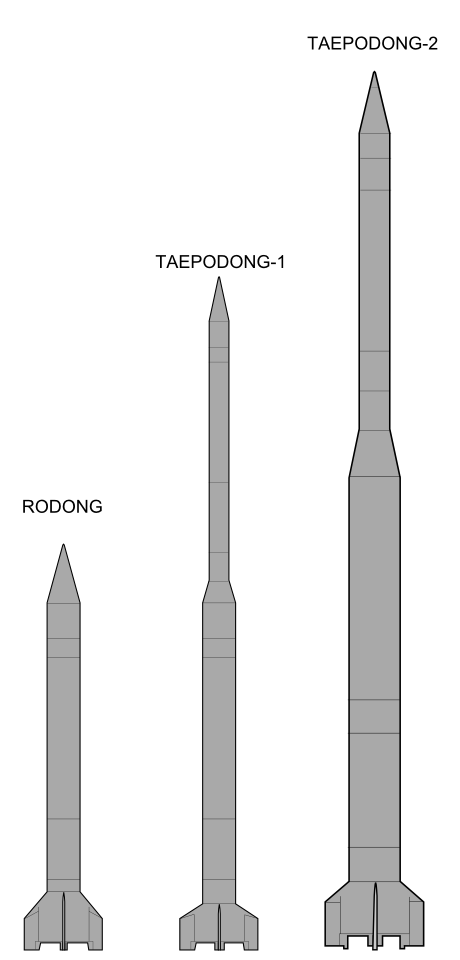
2006 North Korean Missile Test
Two rounds of North Korean missile tests were conducted on July 5, 2006. The Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK or North Korea) reportedly fired at least seven separate missiles. These included one long-range Taepodong-2 missile and short-range Scud derived missiles including the enlarged Nodong missile. The Taepodong-2 was estimated by United States intelligence agencies as having a potential range reaching as far as Alaska, although this missile failed after about 42 seconds of flight.. Accessed July 31, 2009.ArchivedAugust 5, 2009. North Korea made its first public acknowledgement of the tests on July 6, through its foreign ministry, describing them as "successful" and part of "regular military drills to strengthen self-defense", insisting that it had the legal right to do so. The country warned of "stronger physical actions" if it were put under pressure by the international community. On July 8, CNN reported that the U.S. had deployed the USS ''Mustin'', a guided ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unha
The Unha or Eunha ( ko, 은하, 銀河, "Galaxy") is a North Korean expendable launch system, expendable launch vehicle, carrier rocket, which partially utilizes the same delivery system as the Taepodong-2 orbital launch system. History North Korea's first orbital space launch attempt occurred on August 31, 1998, and was unsuccessful. This launch attempt was performed by a Paektusan (rocket), Paektusan-1 rocket, which used a solid motor third stage, a Scud missile, Scud-missile-based second stage, and a Rodong-1, Nodong-1 based first stage. Nodong-1 was a North Korean-developed stage thought to be a scale-up of the old Soviet Scud missile. The Paektusan-1 stood tall, was in diameter, and weighed about 21 tonnes. Vehicle description The Unha's first stage consists of four clustered Rodong-1, Nodong motors, which themselves are enlarged Scud motors. The second stage was initially thought to be based on the SS-N-6, although it, too, is now believed to be based on Scud technol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonghae Satellite Launching Ground
The Tonghae Satellite Launching Ground, also known as Musudan-ri (), is a rocket launching site in North Korea. Location It lies in southern Hwadae County, North Hamgyong Province, near Musu Dan, the cape marking the northern end of the East Korea Bay. The area was formerly known as Taep'o-dong (대포동) during the period when Korea was occupied by Japan, and the Taepodong rockets take their name from this. This single loose-surface road is susceptible to seasonal flooding. The site is 45 km northeast of port city of Kimchaek and 45 kilometers (28 miles) from the town of Kilju (길주읍). There is a small wharf located at the fishing village of Tongha-dong but can only accommodate vessels smaller than 40 meters in length. History By the early 80s, North Korea needed a flight-test facility for its program to reverse-engineer and produce copies of the Scud-B which it acquired from the Soviet Union in the late 60s. Previously, North Korea used a facility at Hwajin-ri (華 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paektusan (rocket)
Taepodong-1 ( ko, 대포동-1) was a three-stage technology demonstrator developed by North Korea, a development step toward an intermediate-range ballistic missile. The missile was derived originally from the Scud rocket and was tested once in 1998 as a space launch vehicle. As a space launch vehicle, it was sometimes called the Paektusan 1. History On August 31, 1998, North Korea announced that they had used this rocket to launch their first satellite Kwangmyŏngsŏng-1 from a pad on the Musudan-ri peninsula. However, the satellite failed to achieve orbit; outside observers conjecture that the additional third stage either failed to fire or malfunctioned. This is contrary to official statements of the North Korean state media, which stated that the satellite achieved orbit about 5 minutes after launch. On this single launch, the main two-stage booster flew for 1,646 km without any significant problems. The rocket was launched eastward, passing over Japan at an altitude ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kwangmyŏngsŏng-1
Kwangmyŏngsŏng-1 or Gwangmyeongseong-1 ( ko, 광명성 1호, Hanja: , meaning Bright Star 1) was a satellite allegedly launched by North Korea on 31 August 1998. While the North Korean government claimed that the launch was successful, no objects were ever tracked in orbit from the launch, and outside North Korea it is considered to have been a failure. It was the first satellite to be launched as part of the Kwangmyŏngsŏng program, and the first satellite that North Korea attempted to launch. It was launched from Musudan-ri using a Paektusan rocket, at 03:07 GMT on 31 August 1998, a few days before the 50th anniversary of North Korea's independence from Japan. On 4 September, the Korean Central News Agency announced that the satellite had successfully been placed into low Earth orbit. The China National Space Administration was involved in the development of Kwangmyŏngsŏng-1, which had a 72-faced polyhedral shape, similar to Dong Fang Hong I, the first Chinese satellit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercontinental Ballistic Missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more thermonuclear warheads). Conventional, chemical, and biological weapons can also be delivered with varying effectiveness, but have never been deployed on ICBMs. Most modern designs support multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles (MIRVs), allowing a single missile to carry several warheads, each of which can strike a different target. Russia, the United States, China, France, India, the United Kingdom, and North Korea are the only countries known to have operational ICBMs. Early ICBMs had limited precision, which made them suitable for use only against the largest targets, such as cities. They were seen as a "safe" basing option, one that would keep the deterrent force close to home where it would be difficult to attack. Attacks against military targets (especially hardened ones) still demanded th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hwasong-17
The Hwasong-17 () is a North Korean two-stage ICBM, first unveiled on 10 October 2020, the 75th anniversary of the founding of the Workers' Party of Korea (WPK) parade. This missile is the latest iteration of North Korea's intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) program. Japan has estimated its operational range at 15,000 km or more. Unlike its predecessors, the Hwasong-17 may be capable of carrying multiple warheads. North Korea claimed the first Hwasong-17 was successfully launched on 24 March 2022. Western analysts instead believe the 24 March launch was an earlier missile design, and a later test that took place on 18 November 2022 was in fact the first successful test launch. Description The Hwasong-17 is assumed to be a two-stage, liquid fuelled road-mobile ICBM carried by a 22-wheeled transporter erector launcher (TEL) vehicle. The missile itself is judged from images to be 26 m long with a diameter of 2.7 m. The exact capabilities of the missile are as yet unconfirme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simorgh (rocket)
Simorgh ( fa, ماهوارهبر سیمرغ, ''Phoenix''), also called Safir-2, is an Iranian expendable launch vehicle under development. It is the successor of the Safir, Iran's first space launch vehicle. Its mission is to carry heavier satellites into higher orbit than Safir. The project was unveiled by Iranian President Mahmoud Ahmadinejad on 3 February 2010, as part of celebrations of the first anniversary of the launch of Omid, the first indigenously launched Iranian satellite, and was launched for the first time on 19 April 2016. Design Simorgh is a two-stage liquid-fueled rocket developed from the Safir rocket. It is be able to place a payload into a circular low Earth orbit (LEO). It is also the first Iranian rocket that can place multiple payloads into orbit (e.g., one main payload and several secondary cubesats). In comparison, the Safir was only able to place a 50 kg payload into a 250x375 km elliptic orbit. The Simorgh rocket is long, and has a launch mass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business Insider
''Insider'', previously named ''Business Insider'' (''BI''), is an American financial and business news website founded in 2007. Since 2015, a majority stake in ''Business Insider''s parent company Insider Inc. has been owned by the German publishing house Axel Springer. It operates several international editions, including one in the United Kingdom. ''Insider'' publishes original reporting and aggregates material from other outlets. , it maintained a liberal policy on the use of anonymous sources. It has also published native advertising and granted sponsors editorial control of its content. The outlet has been nominated for several awards, but is criticized for using factually incorrect clickbait headlines to attract viewership. In 2015, Axel Springer SE acquired 88 percent of the stake in Insider Inc. for $343 million (€306 million), implying a total valuation of $442 million. In February 2021, the brand was renamed simply ''Insider''. History ''Busi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CNET
''CNET'' (short for "Computer Network") is an American media website that publishes reviews, news, articles, blogs, podcasts, and videos on technology and consumer electronics globally. ''CNET'' originally produced content for radio and television in addition to its website and now uses new media distribution methods through its Internet television network, CNET Video, and its podcast and blog networks. Founded in 1994 by Halsey Minor and Shelby Bonnie, it was the flagship brand of CNET Networks and became a brand of CBS Interactive through that unit's acquisition of CNET Networks in 2008. It has been owned by Red Ventures since October 30, 2020. Other than English, ''CNETs region- and language-specific editions include Chinese, French, German, Japanese, Korean, and Spanish. History Origins After leaving PepsiCo, Halsey Minor and Shelby Bonnie launched ''CNET'' in 1994, after website Yahoo! was launched. With help from Fox Network co-founder Kevin Wendle and forme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |