|
Nathan, Queensland
Nathan is a suburb in the City of Brisbane, Queensland, Australia. In the , it had a population of 1,085. Geography Nathan is home to Toohey Forest Conservation Park, Griffith University's Nathan campus and the Queensland Sport and Athletics Centre which hosted the opening ceremony of the 1982 Commonwealth Games. The Queensland Academy of Sport currently uses the facilities located at the stadium. The Mount Gravatt Cemetery is part of Nathan. Nathan remains sparsely populated, with much of the park and university campus being filled with eucalypt forest, grass trees, banksia and leptospermum. Local fauna include tawny frogmouths, powerful owl, hoary wattled bats, sugar gliders, greater gliders, squirrel gliders, flying foxes and possums. Surrounding suburbs include MacGregor, Robertson, Salisbury, Coopers Plains, Tarragindi, Holland Park Holland Park is an area of Kensington, on the western edge of Central London, that contains a street and public park of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queensland Sport And Athletics Centre
) , nickname = Sunshine State , image_map = Queensland in Australia.svg , map_caption = Location of Queensland in Australia , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Australia , established_title = Before federation , established_date = Colony of Queensland , established_title2 = Separation from New South Wales , established_date2 = 6 June 1859 , established_title3 = Federation , established_date3 = 1 January 1901 , named_for = Queen Victoria , demonym = , capital = Brisbane , largest_city = capital , coordinates = , admin_center_type = Administration , admin_center = 77 local government areas , leader_title1 = Monarch , leader_name1 = Charles III , leader_title2 = Governor , leader_name2 = Jeannette Young , leader_title3 = Premier , leader_name3 = Annastacia Palaszczuk ( ALP) , legislature = Parliament of Queensland , judiciary = Supreme Court of Queensland , national_representation = Parliament of Australia , national_representat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Griffith University
Griffith University is a public research university in South East Queensland on the east coast of Australia. Formally founded in 1971, Griffith opened its doors in 1975, introducing Australia's first degrees in environmental science and Asian studies. The university is named after Sir Samuel Walker Griffith, who was twice Premier of Queensland and the first Chief Justice of the High Court of Australia. Sir Samuel Griffith played a major role in the Federation of Australia and was the principal author of the Australian constitution. Opening at Nathan as a single campus of 451 students, the University now has five campuses spanning three cities, the largest of which are the Gold Coast campus at Southport and the Nathan campus in Brisbane. The Mount Gravatt and South Bank campuses are also located in Brisbane, while the Logan campus is at Meadowbrook. Griffith has about 50,000 students and offers a full suite of undergraduate, postgraduate and research degrees in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megabat
Megabats constitute the family Pteropodidae of the order Chiroptera ( bats). They are also called fruit bats, Old World fruit bats, or—especially the genera '' Acerodon'' and '' Pteropus''— flying foxes. They are the only member of the superfamily Pteropodoidea, which is one of two superfamilies in the suborder Yinpterochiroptera. Internal divisions of Pteropodidae have varied since subfamilies were first proposed in 1917. From three subfamilies in the 1917 classification, six are now recognized, along with various tribes. As of 2018, 197 species of megabat had been described. The leading theory of the evolution of megabats has been determined primarily by genetic data, as the fossil record for this family is the most fragmented of all bats. They likely evolved in Australasia, with the common ancestor of all living pteropodids existing approximately 31 million years ago. Many of their lineages probably originated in Melanesia, then dispersed over time to mainland Asi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squirrel Gliders
The squirrel glider (''Petaurus norfolcensis'') is a nocturnal gliding possum. The squirrel glider is one of the wrist-winged gliders of the genus ''Petaurus''. Habitat This species' home range extends from Bordertown near the South Australian/Victorian Border through south-eastern Australia to northern Queensland. This species was thought to be extinct in South Australia since 1939 until a genetic test confirmed their inhabitance in this area. The squirrel glider lives in south-eastern Australia in the dry sclerophyll forest and woodlands. In Queensland, however, they occupy a wetter eucalypt forest. The glider will make a den in the hollow tree and line it with leaves. Here it will sleep and usually lives in groups of one male, 2 females, and offspring. Appearance Like most of the wrist-winged gliders, the squirrel glider is endemic to Australia. It is about twice the size of the related sugar glider (''P. breviceps''). Its body is 18–23 cm long and its tail measu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Gliders
The greater gliders are three species of large gliding marsupials in the genus ''Petauroides'', all of which are found in eastern Australia. Until 2020 they were considered to be one species, '' Petauroides volans''. In 2020 morphological and genetic differences, obtained using diversity arrays technology, showed there were three species subsumed under this one name. The two new species were named ''Petauroides armillatus'' and '' Petauroides minor''. These species are not closely related to the ''Petaurus'' group of gliding marsupials but instead to the lemur-like ringtail possum, ''Hemibelideus lemuroides'', with which it shares the subfamily Hemibelideinae. The greater gliders are nocturnal and are solitary herbivores feeding almost exclusively on ''Eucalyptus'' leaves and buds. Like their relative, the lemur-like ringtail, the southern greater glider is found in two forms: a sooty brown form and a grey-to-white form. The central greater glider is instead silvery brown, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
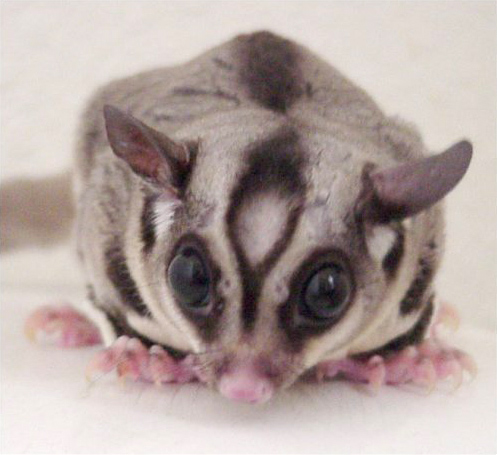
Sugar Gliders
The sugar glider (''Petaurus breviceps'') is a small, omnivorous, arboreal, and nocturnal gliding possum belonging to the marsupial infraclass. The common name refers to its predilection for sugary foods such as sap and nectar and its ability to glide through the air, much like a flying squirrel. They have very similar habits and appearance to the flying squirrel, despite not being closely related—an example of convergent evolution. The scientific name, ''Petaurus breviceps'', translates from Latin as "short-headed rope-dancer", a reference to their canopy acrobatics. The sugar glider is characterised by its pair of gliding membranes, known as patagia, which extend from its forelegs to its hindlegs. Gliding serves as an efficient means of reaching food and evading predators. The animal is covered in soft, pale grey to light brown fur which is countershaded, being lighter in colour on its underside. The sugar glider is native to a small portion of southeastern Austral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoary Wattled Bat
The hoary wattled bat (''Chalinolobus nigrogriseus'') is a species of vesper bat found in northern Australia and Papua New Guinea. Two subspecies are currently recognised: * ''C. n. nigrogriseus'' ( Gould, 1852) * ''C. n. rogersi'' (Thomas Thomas may refer to: People * List of people with given name Thomas * Thomas (name) * Thomas (surname) * Saint Thomas (other) * Thomas Aquinas (1225–1274) Italian Dominican friar, philosopher, and Doctor of the Church * Thomas the ..., 1909) References Taxa named by John Gould Chalinolobus Mammals described in 1852 Bats of Australia Bats of Oceania Mammals of Papua New Guinea Mammals of Western New Guinea Mammals of the Northern Territory Mammals of Western Australia Mammals of New South Wales Mammals of Queensland Taxonomy articles created by Polbot Bats of New Guinea {{WesternAustralia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Powerful Owl
The powerful owl (''Ninox strenua''), a species of owl native to south-eastern and eastern Australia, is the largest owl on the continent. It is found in coastal areas and in the Great Dividing Range, rarely more than inland. The IUCNRed List of Threatened Species also refers to this species as the powerful boobook. An apex predator in its narrow distribution, powerful owls are often opportunists, like most predators, but generally are dedicated to hunting arboreal mammals, in particular small to medium-sized marsupials. Such prey can comprise about three-quarters of their diet. Generally, this species lives in primary forests with tall, native trees, but can show some habitat flexibility when not nesting. The powerful owl is a typically territorial raptorial bird that maintains a large home range and has long intervals between egg-laying and hatching of clutches. Also, like many types of raptorial birds, they must survive a long stretch to independence in young owls after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tawny Frogmouths
The tawny frogmouth (''Podargus strigoides'') is a species of frogmouth native to the Australian mainland and Tasmania and found throughout. It is a big-headed, stocky bird, often mistaken for an owl, due to its nocturnal habits and similar colouring, and sometimes, at least archaically, referred to as ''mopoke'' or ''mopawk'', a name also used for the Australian boobook, the call of which is often confused with that of the tawny frogmouth. Names Its name in reconstructed Proto-Pama–Nyungan is ''*tawa'' or ''*tawu''.Alpher, Barry. 2004. Pama-Nyungan: Phonological Reconstruction and Status as a Phylo-Genetic Group. In Claire Bowern and Harold Koch (eds.), ''Australian Languages: Classification and the Comparative Method'', 93–126, 387–574. Amsterdam: John Benjamins. Taxonomy The tawny frogmouth was first described in 1801 by the English naturalist John Latham. Its specific epithet is derived from Latin ''strix'' 'owl' and ''oides'' 'form'. Tawny frogmouths belong to the fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptospermum
''Leptospermum'' is a genus of shrubs and small trees in the myrtle family Myrtaceae commonly known as tea trees, although this name is sometimes also used for some species of ''Melaleuca''. Most species are endemic to Australia, with the greatest diversity in the south of the continent, but some are native to other parts of the world, including New Zealand and Southeast Asia. Leptospermums all have five conspicuous petals and five groups of stamens which alternate with the petals. There is a single style in the centre of the flower and the fruit is a woody capsule. The first formal description of a leptospermum was published in 1776 by the German botanists Johann Reinhold Forster and his son Johann Georg Adam Forster, but an unambiguous definition of individual species in the genus was not achieved until 1979. Leptospermums grow in a wide range of habitats but are most commonly found in moist, low-nutrient soils. They have important uses in horticulture, in the production o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banksia
''Banksia'' is a genus of around 170 species in the plant family Proteaceae. These Australian wildflowers and popular garden plants are easily recognised by their characteristic flower spikes, and fruiting "cones" and heads. ''Banksias'' range in size from prostrate woody shrubs to trees up to 30 metres (100 ft) tall. They are found in a wide variety of landscapes: sclerophyll forest, (occasionally) rainforest, shrubland, and some more arid landscapes, though not in Australia's deserts. Heavy producers of nectar, ''banksias'' are a vital part of the food chain in the Australian bush. They are an important food source for nectarivorous animals, including birds, bats, rats, possums, stingless bees and a host of invertebrates. Further, they are of economic importance to Australia's nursery and cut flower industries. However, these plants are threatened by a number of processes including land clearing, frequent burning and disease, and a number of species are rare and endan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eucalypt
Eucalypt is a descriptive name for woody plants with capsule fruiting bodies belonging to seven closely related genera (of the tribe Eucalypteae) found across Australasia: ''Eucalyptus'', '' Corymbia'', '' Angophora'', '' Stockwellia'', '' Allosyncarpia'', '' Eucalyptopsis'' and ''Arillastrum''. Taxonomy For an example of changing historical perspectives, in 1991, largely genetic evidence indicated that some prominent ''Eucalyptus'' species were actually more closely related to ''Angophora'' than to other eucalypts; they were accordingly split off into the new genus ''Corymbia''. Although separate, all of these genera and their species are allied and it remains the standard to refer to the members of all seven genera ''Angophora'', ''Corymbia'', ''Eucalyptus'', ''Stockwellia'', ''Allosyncarpia'', ''Eucalyptopsis'' and ''Arillastrum'' as "eucalypts" or as the eucalypt group. The extant genera ''Stockwellia'', ''Allosyncarpia'', ''Eucalyptopsis'' and ''Arillastrum'' comprise s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |