|
Naranga Diffusa
''Naranga diffusa'', the rice green semilooper, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Francis Walker in 1865. It is found in many agricultural based countries such as Bangladesh, India, Sri Lanka, China, Hong Kong, Iran, Japan, the Korean Peninsula, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Thailand, Taiwan and Vietnam. Description Palpi with second joint reaching above vertex of head and smoothly scaled, and third joint minute. Antennae somewhat thickened, annulate and minutely ciliated in male. Thorax and abdomen tuftless. Forewings with stalked veins 7, 8 and 9. Hindwings with veins 3 and 4 from cell or on a short stalk. Adult has creamy coloured wings with two distinctive oblique bars of brown on the forewing. At the time the eggs are laid, they are yellowish, however the eggs develop purple markings when mature. Caterpillars are green or yellow green. There are narrow white lines which run along the body. Biology The caterpillars are considered t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Walker (entomologist)
Francis Walker (31 July 1809 – 5 October 1874) was an English entomologist. He was born in Southgate, London, on 31 July 1809 and died at Wanstead, England on 5 October 1874. He was one of the most prolific authors in entomology, and stirred controversy during his later life as his publications resulted in a huge number of junior synonyms. However, his assiduous work on the collections of the British Museum had great significance. Between June 1848 and late 1873 Walker was contracted by John Edward Gray Director of the British Museum to catalogue their insects (except Coleoptera) that is Orthoptera, Neuroptera, Hemiptera, Diptera, Lepidoptera and Hymenoptera. Walker largely accomplished this and (Edwards, 1870) wrote of the plan and by implication those who implemented it “It is to him raythat the Public owe the admirable helps to the study of natural history which have been afforded by the series of inventories, guides, and nomenclatures, the publication of which beg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echinochloa Colona
''Echinochloa colona'', commonly known as jungle rice, deccan grass, or awnless barnyard grass, is a type of wild grass originating from tropical Asia. It was formerly classified as a species of ''Panicum''. It is the wild ancestor of the cultivated cereal crop ''Echinochloa frumentacea'', sawa millet. Some taxonomists treat the two taxa as one species, in which case the domesticated forms may also be referred to as ''E. colona''. Distribution and habitat The grass occurs throughout tropical Asia and Africa in fields, and along roadsides and waterways. It is considered an invasive weed in the Americas and Australia. In Australia, it has spread to wetlands, and is threatening the habitat of swamp tea trees. In culinary use In India seeds of this grass are used to prepare a food dish called khichadi ''Khichdi'' or ''khichri'' (, , , , Odia: ଖେଚୁଡି) is a dish in South Asian cuisine made of rice and lentils ('' dal'') with numerous variations. Variations in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charops Brachypterum
{{Disambiguation, human name, genus ...
Charops ( Χάρωψ ) or Charopus may refer to: * Charops (mythology), several Greek mythological characters * Charops of Epirus (2nd century BC), two statesmen (grandfather and grandson) * Charops (Decennial archon) (753 BC), Eupatridae who was the first Decennial Archon * ''Charops'' (wasp), a genus of insects in the tribe Campoplegini Charopus may refer to: * ''Charopus'' (beetle), a genus of insects in the subfamily Malachiinae Malachiinae is a subfamily of beetles of the family Melyridae and having a global distribution. Description Malachiinae have peculiar orange structures along the sides of the abdomen, which may be everted and saclike or withdrawn into the body ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charops Bicolor
{{Disambiguation, human name, genus ...
Charops ( Χάρωψ ) or Charopus may refer to: * Charops (mythology), several Greek mythological characters * Charops of Epirus (2nd century BC), two statesmen (grandfather and grandson) * Charops (Decennial archon) (753 BC), Eupatridae who was the first Decennial Archon * ''Charops'' (wasp), a genus of insects in the tribe Campoplegini Charopus may refer to: * ''Charopus'' (beetle), a genus of insects in the subfamily Malachiinae Malachiinae is a subfamily of beetles of the family Melyridae and having a global distribution. Description Malachiinae have peculiar orange structures along the sides of the abdomen, which may be everted and saclike or withdrawn into the body ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachymeria Lasus
''Brachymeria'' is a genus of parasitic wasps in the family Chalcididae. Over 300 species are known worldwide, all of them parasites of insect pupae. Most species are black with limited yellow markings, and like most chalcidid wasps, they have enlarged hind femora. The female typically lays eggs inside the pupae of a lepidopteran using its ovipositor. Although mostly parasitic on Lepidoptera, a few are hyperparasites (parasites of parasitic Hymenoptera and Diptera Flies are insects of the order Diptera, the name being derived from the Greek δι- ''di-'' "two", and πτερόν ''pteron'' "wing". Insects of this order use only a single pair of wings to fly, the hindwings having evolved into advanced ...), or attack other types of insect larvae (such as '' Polistes erythrocephalus)''. The adult parasites emerge typically from the host pupa. Some species have been used in biological control. References Hymenoptera genera Chalcidoidea {{chalcidoidea-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Pest Management
Integrated pest management (IPM), also known as integrated pest control (IPC) is a broad-based approach that integrates both chemical and non-chemical practices for economic control of pests. IPM aims to suppress pest populations below the economic injury level (EIL). The UN's Food and Agriculture Organization defines IPM as "the careful consideration of all available pest control techniques and subsequent integration of appropriate measures that discourage the development of pest populations and keep pesticides and other interventions to levels that are economically justified and reduce or minimize risks to human health and the environment. IPM emphasizes the growth of a healthy crop with the least possible disruption to agro-ecosystems and encourages natural pest control mechanisms." Entomologists and ecologists have urged the adoption of IPM pest control since the 1970s. IPM allows for safer pest control. The introduction and spread of invasive species can also be managed wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
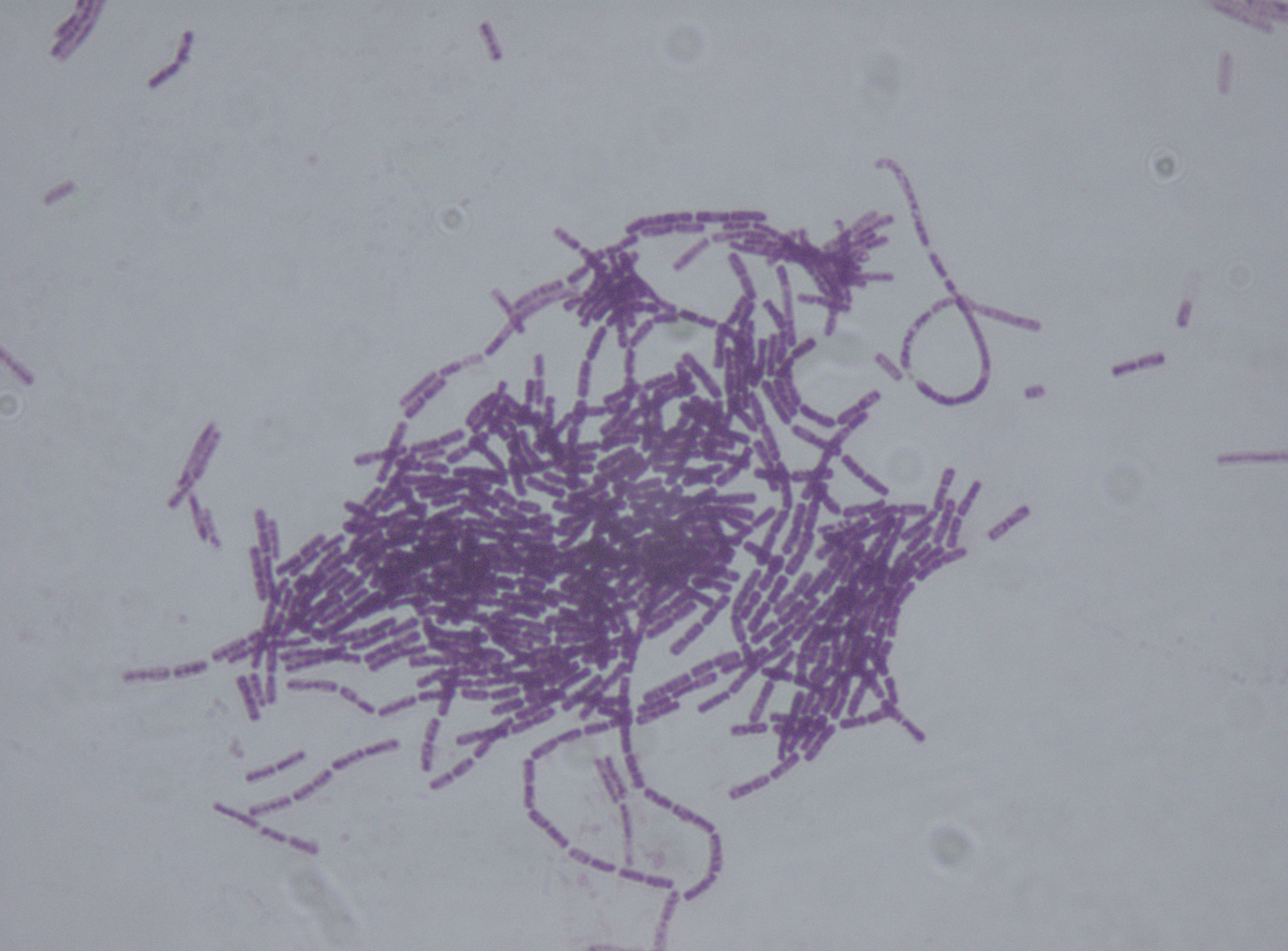
Bacillus Thuringiensis
''Bacillus thuringiensis'' (or Bt) is a gram-positive, soil-dwelling bacterium, the most commonly used biological pesticide worldwide. ''B. thuringiensis'' also occurs naturally in the gut of caterpillars of various types of moths and butterflies, as well on leaf surfaces, aquatic environments, animal feces, insect-rich environments, and flour mills and grain-storage facilities. It has also been observed to parasitize other moths such as ''Cadra calidella''—in laboratory experiments working with ''C. calidella'', many of the moths were diseased due to this parasite. During sporulation, many Bt strains produce crystal proteins (proteinaceous inclusions), called delta endotoxins, that have insecticidal action. This has led to their use as insecticides, and more recently to genetically modified crops using Bt genes, such as Bt corn. Many crystal-producing Bt strains, though, do not have insecticidal properties. The subspecies ''israelensis'' is commonly used for control of mosq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sorghum Bicolor
''Sorghum bicolor'', commonly called sorghum () and also known as great millet, broomcorn, guinea corn, durra, imphee, jowar, or milo, is a Poaceae, grass species cultivated for its grain, which is used for food for humans, animal feed, and ethanol production. Sorghum originated in Africa, and is now cultivated widely in tropical and subtropical regions. Sorghum is the world's fifth-most important cereal crop after rice, wheat, maize, and barley, with 59.34 million metric tons of annual global production in 2018. ''S. bicolor'' is typically an annual, but some cultivars are perennial. It grows in clumps that may reach over 4 m high. The grain is small, ranging from 2 to 4 mm in diameter. Sweet sorghums are sorghum cultivars that are primarily grown for forage, syrup production, and ethanol; they are taller than those grown for grain. ''Sorghum bicolor'' is the cultivated species of sorghum; its wild relatives make up the botanical genus ''Sorghum''. History The first archae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paspalum Distichum
''Paspalum distichum'' is a species of grass. Common names include knotgrass, water finger-grass, couch paspalum, eternity grass, gingergrass, and Thompson grass. Its native range is obscure because it has long been present on most continents, and in most areas it is certainly an introduced species. Its native range probably includes parts of the tropical Americas. This is a perennial grass forming clumps and spreading via rhizomes and stolons. It grows decumbent or erect to a maximum height near 60 centimeters. The inflorescence is usually divided into two branches lined with spikelets. ''Paspalum distichum'' is a food source for several avian species, including the long-tailed widowbird The long-tailed widowbird (''Euplectes progne''), also known as the "sakabula", is a species of bird in the family Ploceidae.Mackworth-Praed, C.W., and C.H. Grant. (1960). ''Birds of Eastern and North Eastern Africa''. Longmans, Green and Co LTD. .... References External links Jepson Manu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paspalum Conjugatum
''Paspalum conjugatum'', commonly known as carabao grass or hilo grass, is a tropical to subtropical perennial grass. It is originally from the American tropics, but has been naturalized widely in tropical Southeast Asia and Pacific Islands. It has also spread to Northern Africa and Northern and Eastern Australia. It is also known as sour paspalum, T-grass (after the shape of their panicle), or more confusingly, as "buffalo grass" or "sour grass". Taxonomy ''Paspalum conjugatum'' belongs to the genus ''Paspalum'' (bahiagrasses or crown grasses) in the grass family Poaceae. It was first described in 1772 in by the Swedish botanist Peter Jonas Bergius. Distribution ''Paspalum conjugatum'' is native to the tropics of the Americas. It was introduced to tropical Southeast Asia and the Pacific Islands during the colonial period. It is particularly abundant in the Philippines from where the English common name "carabao grass" originates (named after the carabao, the local water buff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oryza Sativa
''Oryza sativa'', commonly known as Asian rice or indica rice, is the plant species most commonly referred to in English as ''rice''. It is the type of farmed rice whose cultivars are most common globally, and was first domesticated in the Yangtze River basin in China 13,500 to 8,200 years ago. ''Oryza sativa'' belongs to the genus '' Oryza'' of the grass family Poaceae. With a genome consisting of 430 Mbp across 12 chromosomes, it is renowned for being easy to genetically modify and is a model organism for the botany of cereals. Classification ''Oryza sativa'' contains two major subspecies: the sticky, short-grained ''japonica'' or ''sinica'' variety, and the nonsticky, long-grained ' rice variety. ''Japonica'' was domesticated in the Yangtze Valley 9–6,000 years ago, and its varieties can be cultivated in dry fields (it is cultivated mainly submerged in Japan), in temperate East Asia, upland areas of Southeast Asia, and high elevations in South Asia, while ''indica'' w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptochloa Chinensis
''Leptochloa chinensis'', commonly known as red sprangletop, Asian sprangletop, or Chinese sprangletop, is a species of grass in the family Poaceae. It is a serious weed of rice. It is native to regions of Africa, Asia, and Oceania. Places it is found include Japan, South Korea, Southeast Asia, Australia, Papua New Guinea, Eswatini, West Africa, Fiji and Samoa Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, Sāmoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands ( Savai'i and Upolu); two smaller, inhabited islands ( Manono and Apolima); .... It is known to be a pasture grass and is a livestock grazing feed grass specialty, but in some cases it is a common rice weed. The 1889 book 'The Useful Native Plants of Australia’ records that it is "an excellent pasture grass, much relished by stock ; it has tender panicles, and grows from two to three feet high. It is not endemic in Australia but is found in New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_p._p._sl32.jpg)
_from_the_Philippines.jpg)