|
Narainapur
Narainapur is a town in Banke District in the Bheri Zone of south-western Nepal. At the time of the 1991 Nepal census it had a population of 3,870 and had 692 houses in the town. Government The purpose of Village Development Committees like Narainapur is to organise village people structurally at a local level and creating a partnership between the community and the public sector for improved service delivery system. A VDC has a status as an autonomous institution and authority for interacting with the more centralised institutions of governance in Nepal. In doing so, the VDC gives village people an element of control and responsibility in development, and also ensures proper utilization and distribution of state funds and a greater interaction between government officials, NGOs and agencies. The village development committees within a given area will discuss education, water supply, basic health, sanitation and income and will also monitor and record progress which is displayed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
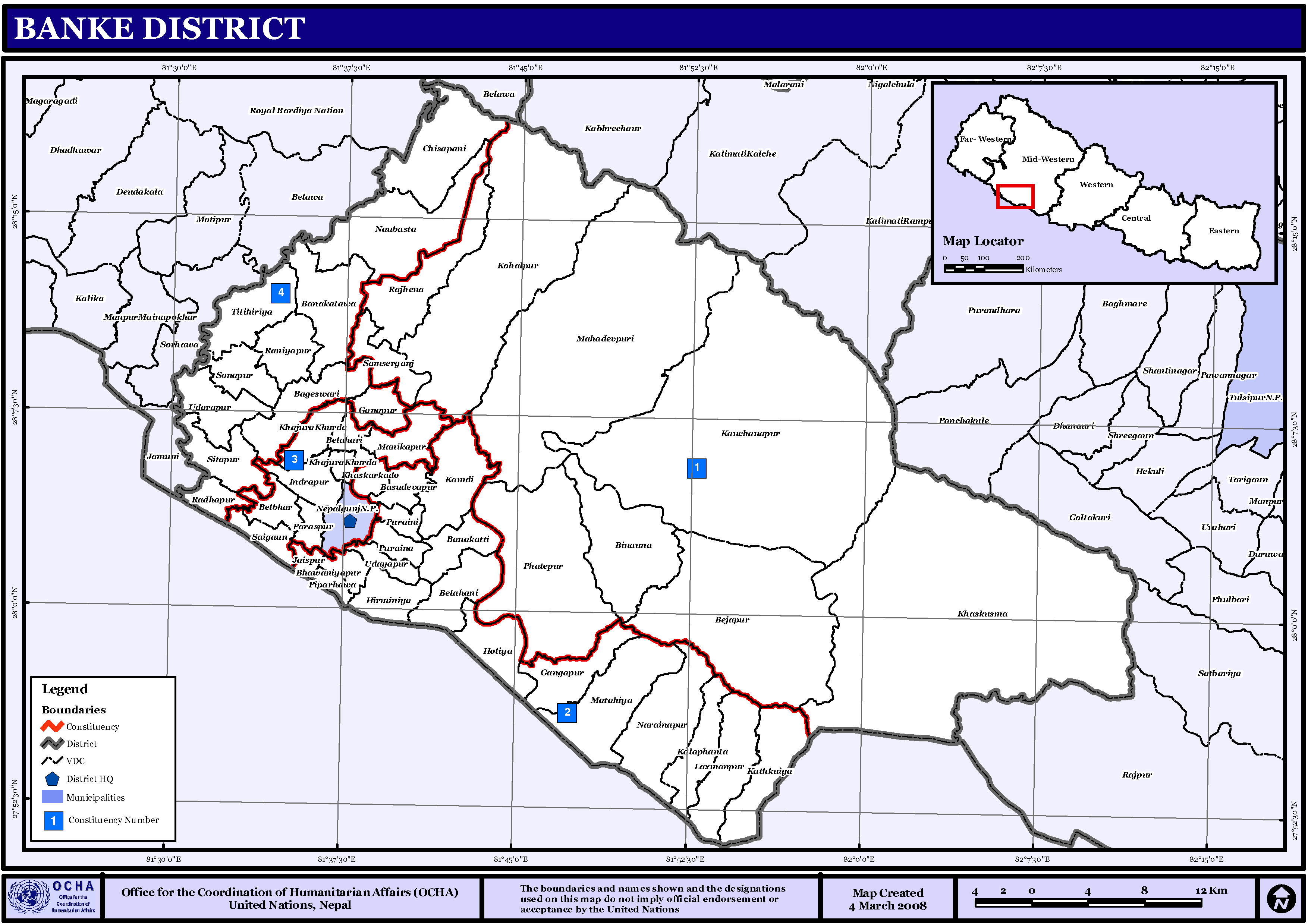
Banke District
Banke District ( ne, बाँके जिल्ला , a part of Lumbini Province, is one of the 77 districts of Nepal. The district, located in midwestern Nepal with Nepalganj as its district headquarters, covers an area of and had a population of 385,840 in 2001 and 491,313 in 2011. There are three main cities in the Banke District: Nepalganj, Kohalpur and Khajura Bajaar. Geography and Climate Banke is bordered on the west by ''Bardiya district''. ''Rapti zone's'' ''Salyan'' and ''Dang Deukhuri Districts'' border to the north and east. To the south lies ''Uttar Pradesh'', India, a country in Asia; specifically ''Shravasti'' and ''Bahraich districts'' of ''Awadh''. East of Nepalganj the international border follows the southern edge of the ''Dudhwa Range'' of the ''Siwaliks''. Most of the district is drained by the ''Rapti'', except the district's western edge is drained by the ''Babai''. Rapti and Babai cross into Uttar Pradesh, a state in India, Nepal's neighboring c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Village Development Committee (Nepal)
A village development committee ( ne, गाउँ विकास समिति; ''gāum̐ vikās samiti'') in Nepal was the lower administrative part of its Ministry of Federal Affairs and Local Development. Each district had several VDCs, similar to municipalities but with greater public-government interaction and administration. There were 3,157 village development committees in Nepal. Each village development committee was further divided into several wards ( ne, वडा) depending on the population of the district, the average being nine wards. Purpose The purpose of village development committees is to organise village people structurally at a local level and creating a partnership between the community and the public sector for improved service delivery system. A village development committee has status as an autonomous institution and authority for interacting with the more centralised institutions of governance in Nepal. In doing so, the village development co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magar Language
Magar Dhut ( ne, मगर ढुट, ) is a Sino-Tibetan Language spoken mainly in Nepal, Southern Bhutan, and in Darjeeling and Sikkim, India, by the Magar people. It is divided into two groups (Eastern and Western) and further dialect divisions give distinct tribal identity. In Nepal 788,530 people speak the language. While the government of Nepal developed Magar language curricula, as provisioned by the constitution, the teaching materials have never successfully reached Magar schools, where most school instruction is in the Nepali language. It is not unusual for groups with their own language to feel that the "mother-tongue" is an essential part of identity. The Dhut Magar language is sometimes lumped with the Magar Kham language spoken further west in Bheri, Dhaulagiri, and Rapti zones. Although the two languages share many common words, they have major structural differences and are not mutually intelligible. Geographical distribution Western Magar Western Magar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ''Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the Muhammad in Islam, main and final Islamic prophet.Peters, F. E. 2009. "Allāh." In , edited by J. L. Esposito. Oxford: Oxford University Press. . (See alsoquick reference) "[T]he Muslims' understanding of Allāh is based...on the Qurʿān's public witness. Allāh is Unique, the Creator, Sovereign, and Judge of mankind. It is Allāh who directs the universe through his direct action on nature and who has guided human history through his prophets, Abraham, with whom he made his covenant, Moses/Moosa, Jesus/Eesa, and Muḥammad, through all of whom he founded his chosen communities, the 'Peoples of the Book.'" It is the Major religious groups, world's second-largest religion behind Christianity, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global population, known as Hindus. The word ''Hindu'' is an exonym, and while Hinduism has been called the oldest religion in the world, many practitioners refer to their religion as '' Sanātana Dharma'' ( sa, सनातन धर्म, lit='the Eternal Dharma'), a modern usage, which refers to the idea that its origins lie beyond human history, as revealed in the Hindu texts. Another endonym is ''Vaidika dharma'', the dharma related to the Vedas. Hinduism is a diverse system of thought marked by a range of philosophies and shared concepts, rituals, cosmological systems, pilgrimage sites, and shared textual sources that discuss theology, metaphysics, mythology, Vedic yajna, yoga, agamic rituals, and temple building, among other to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hajjam
The Hijama, also known as'' cupping'' are an ethnic group in India known for practicing cupping therapy. The word Hijama has been derived from the Arabic word , means "sucking", referring to this therapy. A practitioner was called a ''Hijama'' in Arab countries, and the name was used in India as well. Communities of Arab campaigned in Persia, Egypt to propagate the message of Islam during the Caliphate power of some companions of Muhammad. Then the Persians ran to conquer India. In this way, Hijama came from Arab to Persia, and then to India. In India, they practiced their occupation and included multi practices with Hijama like pulling of teeth, hairdressing, sheep shearing, treating of abscesses, etc. Because of different multi practices besides Hijama, they were named Hijama as they were already called in their original countries. They are now an ethnic group found in North India and Pakistan. In Pakistan, they are established in Sindh and Punjab provinces. They are deemed u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brahmin
Brahmin (; sa, ब्राह्मण, brāhmaṇa) is a varna as well as a caste within Hindu society. The Brahmins are designated as the priestly class as they serve as priests (purohit, pandit, or pujari) and religious teachers (guru or acharya). The other three varnas are the Kshatriya, Vaishya and Shudra. The traditional occupation of Brahmins is that of priesthood at the Hindu temples or at socio-religious ceremonies, and rite of passage rituals such as solemnising a wedding with hymns and prayers.James Lochtefeld (2002), Brahmin, The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Hinduism, Vol. 1: A–M, Rosen Publishing, , page 125 Traditionally, the Brahmins are accorded the highest ritual status of the four social classes. Their livelihood is prescribed to be one of strict austerity and voluntary poverty ("A Brahmin should acquire what just suffices for the time, what he earns he should spend all that the same day"). In practice, Indian texts suggest that some Brahmins historicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhobi
Dhobi known in some places as Dhoba or Rajaka, Madivala is a group of community in India and the greater Indian subcontinent whose traditional occupations are washing and ironing, Cultivator, agricultural workers. They are a large community, distributed across northern, central, western and eastern India; as well as in Bangladesh, Pakistan, Nepal, and Sri Lanka. A majority of the community associate themselves with Hinduism. Many religiously follow Sant Gadge (Gadge Maharaj), whose ''jayanti'' (birth anniversary) they celebrate every 23 February. The word ''dhobi'' is derived from the Hindi word ''dhona'', which means 'to wash'. As such, Dhobi communities in many areas today come under the status of Schedule Caste in many status, while Other Backward Class in other states and region. In 2017, Supreme Court of India noted calling people ''dhobi'' was offensive. Origins In mythology There is a tradition that they are descendants of the mythological hero Virabhadra,who wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tharu People
The Tharu people are an ethnic group indigenous to the Terai in southern Nepal and northern India. They speak Tharu languages. They are recognized as an official nationality by the Government of Nepal. In the Indian Terai, they live foremost in Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh and Bihar. The Government of India recognizes the Tharu people as a scheduled tribe. Etymology The word (''thāru'') is thought to be derived from '' sthavir'' meaning follower of Theravada Buddhism. The Tharu people in the central Nepali Terai see themselves as the original people of the land and descendants of Gautama Buddha. Rana Tharu people of western Nepal connect the name to the Thar Desert and understand themselves as descendants of Rajputs who migrated to the forests in the 16th century. Possible is also that the name is derived from the classical Tibetan words ''mtha'-ru'i brgyud'', meaning the 'country at the border', which the Tibetan scholar Taranatha used in the 16th century in his book on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kushwaha
Kushwaha (sometimes, Kushvaha) is a community of the Indo-Gangetic Plain which has traditionally been involved in agriculture (including beekeeping). The term has been used to represent different subcastes, being those of the Kachhis, Koeris and Muraos. Under the Indian governments system of positive discrimination, the Kushwahas are classified as a "Backward" or "Other Backward class". From the 20th century onwards, they began to claim descent from the Suryavansh (Solar) dynasty via Kusha, who was one of the twin sons of Rama and Sita. Previously, they had worshipped Shiva and Shakta. Origin The Kushwaha claim descent from the Suryavansh dynasty through Kusha, a son of the mythological Rama, an avatar of Vishnu, a myth of origin developed in the twentieth century. Prior to that time, the various branches that form the Kushwaha community - the Kachhis, Koeris, and Muraos - favoured a connection with Shiva and Shakta. Ganga Prasad Gupta, a proponent of Kushwah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paswan
The Paswan, also known as Dusadh, are a Dalit community from eastern India. They are found mainly in the states of Bihar, Uttar Pradesh and Jharkhand. The Urdu word ''Paswan'' means bodyguard or "one who defends". The origin of the word, per the belief of the community, lies in their participation in the battle against Siraj-ud-daulah, the Nawab of Bengal at the behest of British East India Company, after which they were rewarded with the post of '' Chowkidars'' and lathi wielding tax collector for the ''Zamindars''. They follow certain rituals such as walking on fire to assert their valour. Etymology The Paswans claim their origin from a number of folk and epic characters in order to seek upliftment in their social status. Some Paswan believe that they have originated from Rahu, a superhuman and one of the planets in Hindu mythology, while others claim their origin from Dushasana, one of the Kaurava princes. Claims regarding origin from "Gahlot Kshatriya" are also persistent amo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chamar
Chamar is a Dalit community classified as a Scheduled Caste under modern India's system of affirmative action. Historically subject to untouchability, they were traditionally outside the Hindu ritual ranking system of castes known as varna. They are found throughout the Indian subcontinent, mainly in the northern states of India and in Pakistan and Nepal. History Ramnarayan Rawat posits that the association of the Chamar community with a traditional occupation of tanning was constructed, and that the Chamars were instead historically agriculturists. The term ''chamar'' is used as a pejorative word for dalits in general. It has been described as a casteist slur by the Supreme Court of India and the use of the term to address a person as a violation of the Scheduled Caste and Scheduled Tribe (Prevention of Atrocities) Act, 1989. Chamars have remained one of the most discriminated community within Hinduism. In reference to villages of Rohtas and Bhojpur district of Bihar, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

_Bhumi_Puja%2C_yajna.jpg)