|
Namgung Eok
Namgung is an East Asian surname that sees varying levels of use in Vietnam, China, Japan, and Korea. Regardless of country, Namgung is considered to be an uncommon surname, as only a small number of people have the surname. Mainland China In Mainland China, the surname Nangong appears in the Song dynasty book ''Hundred Family Surnames''. According to a statistical analysis released by the National Bureau of Statistics of China in 2014, Nangong is estimated to be the surname for 13,000 people in China in 2010. Hong Kong In Hong Kong, Namgung is a surname that is often associated with the "Mailbox of Madame Namgung" (), a Dear Abby-style advice column in the 1950s and 1960s that often dispenses tips and advises related to Human sexuality. Japan In Japan, the surname Nang┼½ is estimated to be the surname of about 200 people, with half of them concentrated in the Hy┼Źgo Prefecture, Osaka Prefecture, and Tokyo. Korea In Korea, there are historically 6 Namgung Bon-gwan clans, includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korean Language
Korean ( South Korean: , ''hangugeo''; North Korean: , ''chos┼Ånmal'') is the native language for about 80 million people, mostly of Korean descent. It is the official and national language of both North Korea and South Korea (geographically Korea), but over the past years of political division, the two Koreas have developed some noticeable vocabulary differences. Beyond Korea, the language is recognised as a minority language in parts of China, namely Jilin Province, and specifically Yanbian Prefecture and Changbai County. It is also spoken by Sakhalin Koreans in parts of Sakhalin, the Russian island just north of Japan, and by the in parts of Central Asia. The language has a few extinct relatives whichŌĆöalong with the Jeju language (Jejuan) of Jeju Island and Korean itselfŌĆöform the compact Koreanic language family. Even so, Jejuan and Korean are not mutually intelligible with each other. The linguistic homeland of Korean is suggested to be somewhere in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hy┼Źgo Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located in the Kansai region of Honshu. Hy┼Źgo Prefecture has a population of 5,469,762 () and has a geographic area of . Hy┼Źgo Prefecture borders Kyoto Prefecture to the east, Osaka Prefecture to the southeast, and Okayama Prefecture and Tottori Prefecture to the west. K┼Źbe is the capital and largest city of Hy┼Źgo Prefecture, and the seventh-largest city in Japan, with other major cities including Himeji, Nishinomiya, and Amagasaki. Hy┼Źgo Prefecture's mainland stretches from the Sea of Japan to the Seto Inland Sea, where Awaji Island and a small archipelago of islands belonging to the prefecture are located. Hy┼Źgo Prefecture is a major economic center, transportation hub, and tourist destination in western Japan, with 20% of the prefecture's land area designated as Natural Parks. Hy┼Źgo Prefecture forms part of the Keihanshin metropolitan area, the second-most-populated urban region in Japan after the Greater Tokyo area and one of the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Namgung Woncheng
Namgung is an East Asian surname that sees varying levels of use in Vietnam, China, Japan, and Korea. Regardless of country, Namgung is considered to be an uncommon surname, as only a small number of people have the surname. Mainland China In Mainland China, the surname Nangong appears in the Song dynasty book ''Hundred Family Surnames''. According to a statistical analysis released by the National Bureau of Statistics of China in 2014, Nangong is estimated to be the surname for 13,000 people in China in 2010. Hong Kong In Hong Kong, Namgung is a surname that is often associated with the "Mailbox of Madame Namgung" (), a Dear Abby-style advice column in the 1950s and 1960s that often dispenses tips and advises related to Human sexuality. Japan In Japan, the surname Nang┼½ is estimated to be the surname of about 200 people, with half of them concentrated in the Hy┼Źgo Prefecture, Osaka Prefecture, and Tokyo. Korea In Korea, there are historically 6 Namgung Bon-gwan clans, includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warring States Period
The Warring States period () was an era in History of China#Ancient China, ancient Chinese history characterized by warfare, as well as bureaucratic and military reforms and consolidation. It followed the Spring and Autumn period and concluded with the Qin's wars of unification, Qin wars of conquest that saw the annexation of all other contender states, which ultimately led to the Qin (state), Qin state's victory in 221 BC as the first unified History of China#Imperial China, Chinese empire, known as the Qin dynasty. Although different scholars point toward different dates ranging from 481 BC to 403 BC as the true beginning of the Warring States, Sima Qian's choice of 475 BC is the most often cited. The Warring States era also overlaps with the second half of the Eastern Zhou Period, Eastern Zhou dynasty, though the Chinese sovereign, known as the king of Zhou, ruled merely as a figurehead and served as a backdrop against the machinations of the warring states. The "Warring St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Song (state)
Song (; Old Chinese: *') was a state during the Zhou dynasty of ancient China, with its capital at Shangqiu. The state was founded soon after King Wu of Zhou conquered the Shang dynasty to establish the Zhou dynasty in 1046 BC. It was conquered by the State of Qi in 286 BC, during the Warring States period. Confucius was a descendant of a Song nobleman who moved to the State of Lu. Origin King Zhou of Shang, Di Xin was the younger brother of Zi Qi (who was said in legends to have ruled Gija Joseon in the 11th century BCE) and Zi Yan () (later rulers of Zhou's vassal state Song), father of Wu Geng. After King Wu of Zhou overthrew the last ruler of Shang, marking the transition to the Zhou Dynasty, the victor was honor-bound by a stricture of feudal etiquette known as () to allow the defeated house of Shang to continue offering sacrifices to their ancestors. As a result, for a time Shang became a vassal state of Zhou, with the Shang heir Wu Geng allowed to continue ancesto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhou Dynasty
The Zhou dynasty ( ; Old Chinese ( B&S): *''tiw'') was a royal dynasty of China that followed the Shang dynasty. Having lasted 789 years, the Zhou dynasty was the longest dynastic regime in Chinese history. The military control of China by the royal house, surnamed Ji, lasted initially from 1046 until 771 BC for a period known as the Western Zhou, and the political sphere of influence it created continued well into the Eastern Zhou period for another 500 years. The establishment date of 1046 BC is supported by the XiaŌĆōShangŌĆōZhou Chronology Project and David Pankenier, but David Nivison and Edward L. Shaughnessy date the establishment to 1045 BC. During the Zhou dynasty, centralized power decreased throughout the Spring and Autumn period until the Warring States period in the last two centuries of the dynasty. In the latter period, the Zhou court had little control over its constituent states that were at war with each other until the Qin state consolidated power and forme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nangong Kuo (Western Zhou)
Nangong Kuo (; fl. 11th century BC) was a top official of King Wen of Zhou during the late Shang and early Western Zhou dynasties. In the "Jun Shi" (ÕÉøÕźŁ) chapter of the ''Classic of History'', the Duke of Zhou names him as one of the five key advisers of King Wen, together with Guo Shu, Hong Yao, Tai Dian, and San Yisheng. After King Wen's death, Nangong Kuo became a key adviser of his son King Wu. Bronze inscriptions Nangong Kuo was the founder of a major aristocratic lineage of the Western Zhou. His eldest son probably died early, and his second son Nangong Mao (ÕŹŚÕ«½µ»ø) inherited his title. The famous Da Yu ''ding'', now a national treasure of China, was cast by Nangong Kuo's grandson Yu (ńøé), and dedicated to him. The bronze inscription on the vessel traces Yu's lineage back to Nangong (, Duke of Nan), who is identified by scholars, including Li Xueqin and Li Feng, with Nangong Kuo. Inscriptions on other unearthed bronze vessels indicate that during the late Weste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
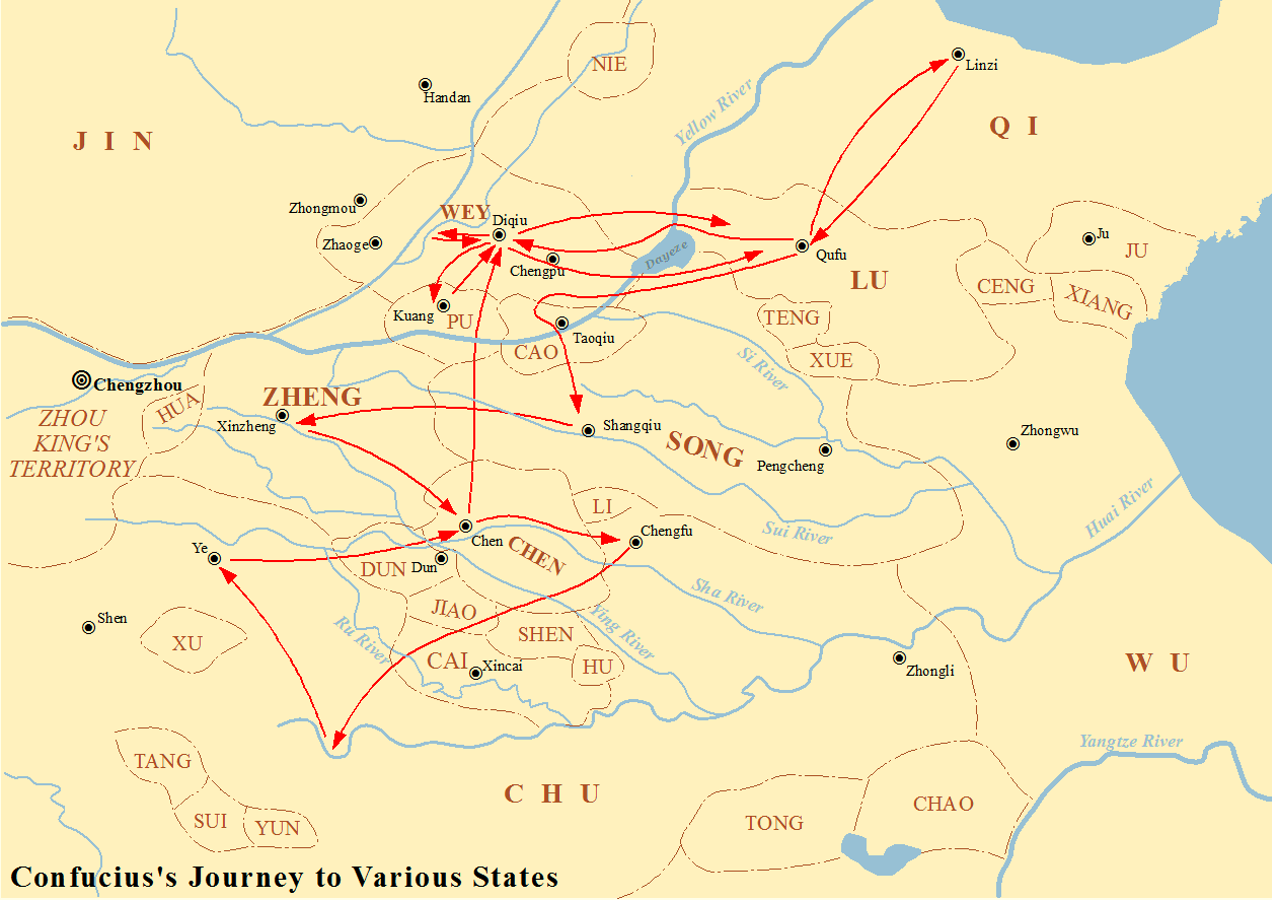
Confucius
Confucius ( ; zh, s=, p=KŪÆng F┼½zŪÉ, "Master KŪÆng"; or commonly zh, s=, p=KŪÆngzŪÉ, labels=no; ŌĆō ) was a Chinese philosopher and politician of the Spring and Autumn period who is traditionally considered the paragon of Chinese sages. Confucius's teachings and philosophy underpin East Asian culture and society, remaining influential across China and East Asia to this day. Confucius considered himself a transmitter for the values of earlier periods which he claimed had been abandoned in his time. His philosophical teachings, called Confucianism, emphasized personal and governmental morality, correctness of social relationships, justice, kindness, and sincerity. His followers competed with many other schools during the Hundred Schools of Thought era, only to be suppressed in favor of the Legalists during the Qin dynasty. After the collapse of Qin and the victory of Han over Chu, Confucius's thoughts received official sanction in the new government. During the Tan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed by the Yellow Sea, while its eastern border is defined by the Sea of Japan. South Korea claims to be the sole legitimate government of the entire peninsula and List of islands of South Korea, adjacent islands. It has a Demographics of South Korea, population of 51.75 million, of which roughly half live in the Seoul Capital Area, the List of metropolitan areas by population, fourth most populous metropolitan area in the world. Other major cities include Incheon, Busan, and Daegu. The Korean Peninsula was inhabited as early as the Lower Paleolithic period. Its Gojoseon, first kingdom was noted in Chinese records in the early 7th century BCE. Following the unification of the Three Kingdoms of Korea into Unified Silla, Silla and Balhae in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Wen Of Zhou
King Wen of Zhou (; 1152ŌĆō1050 BC, the Cultured King) was Count of state of Zhou, Zhou during the late Shang dynasty in ancient China. Although frequently confused with his fourth son Duke of Zhou, also known as "Lord Zhou", they are different historical persons. Although it was his son King Wu of Zhou, Wu who conquered the Shang following the Battle of Muye, Count Wen was posthumously honored as the founder of the Zhou dynasty and posthumously titled King. Many of the hymns of the ''Classic of Poetry'' are praises to the legacy of King Wen. Some consider him the first epic hero of Chinese history. Archaeology Chinese scholars (e.g. Wang Yunwu (:zh:ńÄŗķø▓õ║ö, ńÄŗķø▓õ║ö), Li Xueqin (:zh:µØÄÕŁ”Õŗż, µØÄÕŁ”Õŗż), etc.) identified King Wen with a mentioned in inscriptions H11:82 & H11:84 among oracle bones excavated at Zhouyuan (), Qishan County. Biography Born Ji Chang (), Wen was the son of Tai Ren, Tairen and King Ji of Zhou, Ji Jili, the Count of Predynastic Zhou, Zhou, a vassal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nangong Kuo (disciple Of Confucius)
Nangong Kuo ( commonly known as Nan Rong and also known by his courtesy name Zirong and as Nangong Tao, was a major disciple of Confucius. Commending Nangong Kuo as a gentleman of virtue, Confucius gave the student his niece in marriage. Life Nangong Kuo was a native of the state of Lu. His dates of birth and death are not known. The ''Analects'' (14.5) records Nangong Kuo's observation that Hou Yi and Ao (), powerful military leaders, both ended up being killed; while Yu the Great and Hou Ji, men who took care of the land, ended up with "possession of the world." Confucius commended Nangong as a ''junzi'', a gentleman of virtue. He gave his niece, the daughter of his elder brother Mengpi, to Nangong in marriage. When Nangong Kuo was serving Duke Ai of Lu, a fire broke out at the palace. While others attempted to secure the contents of the treasury, Nangong focussed on saving the palace library. He was then credited with the preservation of the state's copy of the ''Rites of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamyeol Namgung Clan
Hamyeol Namgung clan () is one of the Korean clans. Their Bon-gwan is in Iksan, North Jeolla Province. According to the research held in 2015, the number of Hamyeol Namgung clan was 20715. Namgung su () who was the Imperial family in Zhou dynasty, China started Korean Namgung clan. When Gija conquered Korea, Namgung su () founded Gija Joseon with Gija and worked as Situ (office). Namgung su () taught Koreans etiquette, agriculture, rice farming, sericulture and weaving. The founder of Hamyeol Namgung clan was who was a descendant of Namgung su (). worked as Four-star rank and ''Pingzhangshi'' () in Goryeo. See also * Korean clan names of foreign origin References External links * {{Cite book, author=, date=, title=Doosan Encyclopedia ņÖĖļלĻĘĆĒÖöņä▒ņö© Õż¢õŠåµŁĖÕī¢Õ¦ōµ░Å, publisher=Doosan Encyclopedia ''Doosan Encyclopedia'' is a Korean language encyclopedia published by Doosan Donga (ļæÉņé░ļÅÖņĢä). The encyclopedia is based on the ''Dong-A Color Encyclopedia'' (ļÅ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |