|
Naldham House
Naldham House is a heritage-listed office building located at 193 Mary Street, Brisbane CBD, City of Brisbane, Queensland, Australia. It was built from 1864 to 1889. It is also known as AUSN House. It was added to the Queensland Heritage Register on 21 October 1992. History The building was built initially in 1864, extended in the late 1870s, but substantially rebuilt in 1889 for the Australian United Steam Navigation Company. It served for almost a century as a shipping office. In 1988 major external and internal alternations were carried out in converting the building into premises for a club. The site, adjacent to the Brisbane River, was acquired by the Australasian Steam Navigation Company (ASN) in March 1852 although the company did not construct wharves until 1859 the company's first wharf had been erected on the new site followed by a second wharf near Eagle Street in 1861. In 1864 a two-storeyed office was erected and occupied by Henry O'Reilly, the ASN's Brisbane a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Street, Brisbane
Mary Street is a major road in the Brisbane central business district. The street is one of a number that were named after female queens and princesses of the royal family shortly after the penal colony was settled. Charlotte Street is positioned parallel to the north and Margaret Street runs next to the south. Mary Street begins in the Government Precinct at a T-intersection with George Street opposite the Executive Building. Also at the elevated southern end is Education House containing state government offices and the Department of Mines and Energy, Queensland are located opposite in the Queensland Minerals & Energy Centre. Felix Tower is located on the corner of Mary and Felix Streets. Waterfront Place and Forestry House are nearby in the lower northern section, close to the river. Vision Brisbane was a planned residential skyscraper on Mary Street that would have been Brisbane's tallest building. Mary Street was home to the first premises used by the Queensland Cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Courier-Mail
''The Courier-Mail'' is an Australian newspaper published in Brisbane. Owned by News Corp Australia, it is published daily from Monday to Saturday in Tabloid (newspaper format), tabloid format. Its editorial offices are located at Bowen Hills, Queensland, Bowen Hills, in Brisbane's inner northern suburbs, and it is printed at Murarrie, Queensland, Murarrie, in Brisbane's eastern suburbs. It is available for purchase throughout Queensland, most regions of Northern New South Wales and parts of the Northern Territory. History The history of ''The Courier-Mail'' is through four Nameplate (publishing), mastheads. The ''Moreton Bay Courier'' later became ''The Courier (Brisbane), The Courier'', then the ''Brisbane Courier'' and, since a merger with the Daily Mail in 1933, ''The Courier-Mail''. The ''Moreton Bay Courier'' was established as a weekly paper in June 1846. Issue frequency increased steadily to bi-weekly in January 1858, tri-weekly in December 1859, then daily under the ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balusters
A baluster is an upright support, often a vertical moulded shaft, square, or lathe-turned form found in stairways, parapets, and other architectural features. In furniture construction it is known as a spindle. Common materials used in its construction are wood, stone, and less frequently metal and ceramic. A group of balusters supporting a handrail, coping, or ornamental detail are known as a balustrade. The term baluster shaft is used to describe forms such as a candlestick, upright furniture support, and the stem of a brass chandelier. The term banister (also bannister) refers to a baluster or to the system of balusters and handrail of a stairway. It may be used to include its supporting structures, such as a supporting newel post. Etymology According to the ''Oxford English Dictionary'', "baluster" is derived through the french: balustre, from it, balaustro, from ''balaustra'', "pomegranate flower" [from a resemblance to the swelling form of the half-open flower (''illus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parapet
A parapet is a barrier that is an extension of the wall at the edge of a roof, terrace, balcony, walkway or other structure. The word comes ultimately from the Italian ''parapetto'' (''parare'' 'to cover/defend' and ''petto'' 'chest/breast'). Where extending above a roof, a parapet may simply be the portion of an exterior wall that continues above the edge line of the roof surface, or may be a continuation of a vertical feature beneath the roof such as a fire wall or party wall. Parapets were originally used to defend buildings from military attack, but today they are primarily used as guard rails, to conceal rooftop equipment, reduce wind loads on the roof, and to prevent the spread of fires. In the Bible the Hebrews are obligated to build a parapet on the roof of their houses to prevent people falling (Deuteronomy 22:8). Parapet types Parapets may be plain, embattled, perforated or panelled, which are not mutually exclusive terms. *Plain parapets are upward extensions of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornice
In architecture, a cornice (from the Italian ''cornice'' meaning "ledge") is generally any horizontal decorative moulding that crowns a building or furniture element—for example, the cornice over a door or window, around the top edge of a pedestal, or along the top of an interior wall. A simple cornice may be formed just with a crown, as in crown moulding atop an interior wall or above kitchen cabinets or a bookcase. A projecting cornice on a building has the function of throwing rainwater free of its walls. In residential building practice, this function is handled by projecting gable ends, roof eaves and gutters. However, house eaves may also be called "cornices" if they are finished with decorative moulding. In this sense, while most cornices are also eaves (overhanging the sides of the building), not all eaves are usually considered cornices. Eaves are primarily functional and not necessarily decorative, while cornices have a decorative aspect. A building's projecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frieze
In architecture, the frieze is the wide central section part of an entablature and may be plain in the Ionic or Doric order, or decorated with bas-reliefs. Paterae are also usually used to decorate friezes. Even when neither columns nor pilasters are expressed, on an astylar wall it lies upon the architrave ("main beam") and is capped by the moldings of the cornice. A frieze can be found on many Greek and Roman buildings, the Parthenon Frieze being the most famous, and perhaps the most elaborate. This style is typical for the Persians. In interiors, the frieze of a room is the section of wall above the picture rail and under the crown moldings or cornice. By extension, a frieze is a long stretch of painted, sculpted or even calligraphic decoration in such a position, normally above eye-level. Frieze decorations may depict scenes in a sequence of discrete panels. The material of which the frieze is made of may be plasterwork, carved wood or other decorative medium. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
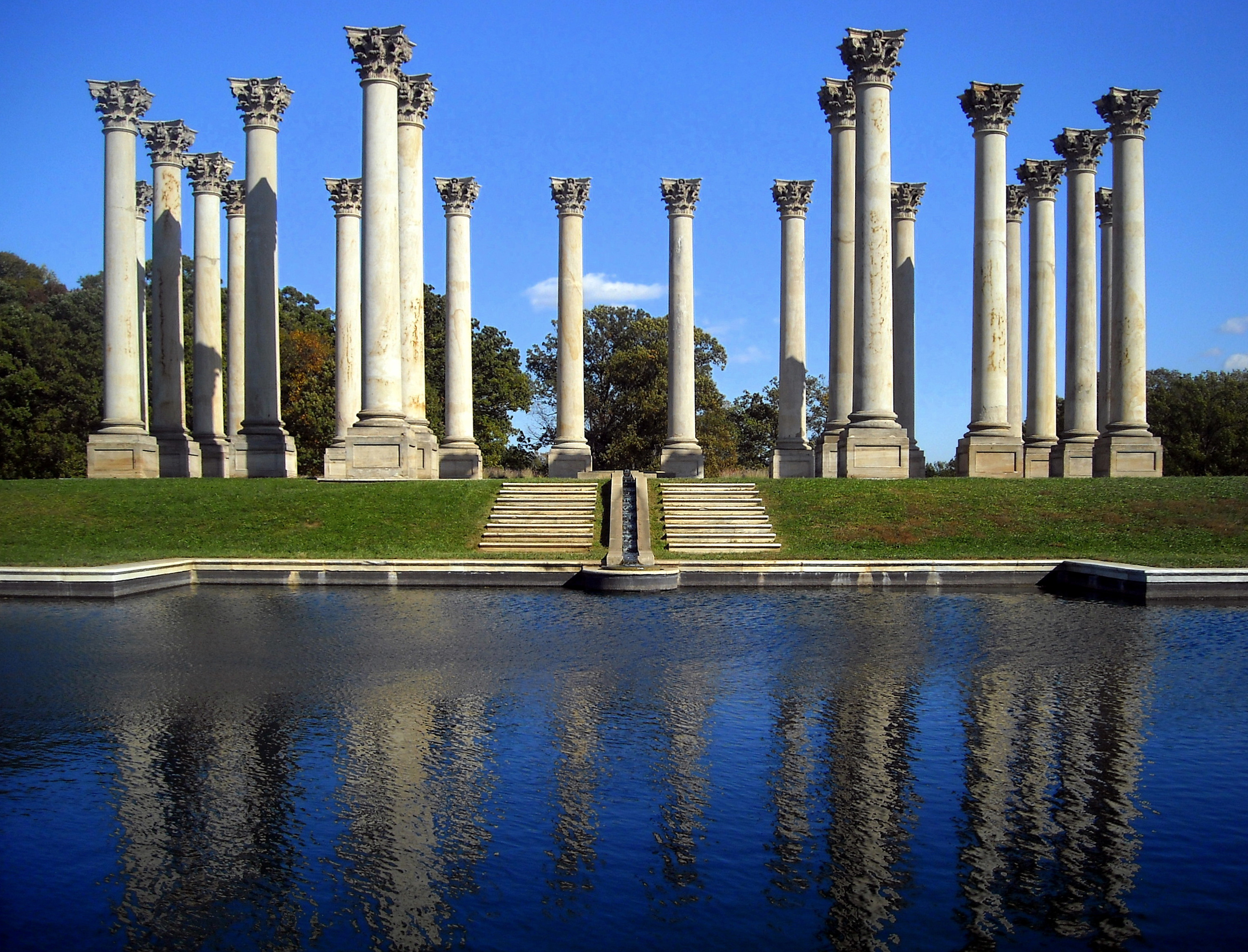
Corinthian Order
The Corinthian order (Greek: Κορινθιακός ρυθμός, Latin: ''Ordo Corinthius'') is the last developed of the three principal classical orders of Ancient Greek architecture and Roman architecture. The other two are the Doric order which was the earliest, followed by the Ionic order. In Ancient Greek architecture, the Corinthian order follows the Ionic in almost all respects other than the capitals of the columns. When classical architecture was revived during the Renaissance, two more orders were added to the canon: the Tuscan order and the Composite order. The Corinthian, with its offshoot the Composite, is the most ornate of the orders. This architectural style is characterized by slender fluted columns and elaborate capitals decorated with acanthus leaves and scrolls. There are many variations. The name ''Corinthian'' is derived from the ancient Greek city of Corinth, although the style had its own model in Roman practice, following precedents set by the Tem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
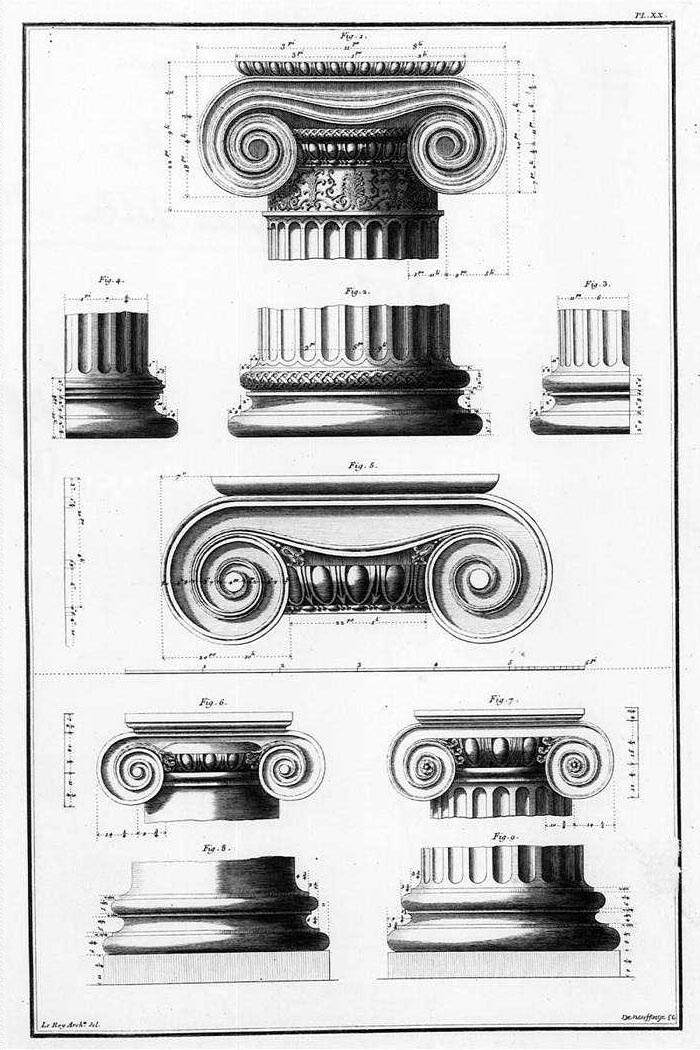
Ionic Order
The Ionic order is one of the three canonic orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric and the Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan (a plainer Doric), and the rich variant of Corinthian called the composite order. Of the three classical canonic orders, the Corinthian order has the narrowest columns, followed by the Ionic order, with the Doric order having the widest columns. The Ionic capital is characterized by the use of volutes. The Ionic columns normally stand on a base which separates the shaft of the column from the stylobate or platform while the cap is usually enriched with egg-and-dart. The ancient architect and architectural historian Vitruvius associates the Ionic with feminine proportions (the Doric representing the masculine). Description Capital The major features of the Ionic order are the volutes of its capital, which have been the subject of much theoretical and practical discourse, based on a brief and obscure passage i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columns
A column or pillar in architecture and structural engineering is a structural element that transmits, through compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. In other words, a column is a compression member. The term ''column'' applies especially to a large round support (the shaft of the column) with a capital and a base or pedestal, which is made of stone, or appearing to be so. A small wooden or metal support is typically called a ''post''. Supports with a rectangular or other non-round section are usually called '' piers''. For the purpose of wind or earthquake engineering, columns may be designed to resist lateral forces. Other compression members are often termed "columns" because of the similar stress conditions. Columns are frequently used to support beams or arches on which the upper parts of walls or ceilings rest. In architecture, "column" refers to such a structural element that also has certain proportional and decorative feat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital (architecture)
In architecture the capital (from the Latin ''caput'', or "head") or chapiter forms the topmost member of a column (or a pilaster). It mediates between the column and the load thrusting down upon it, broadening the area of the column's supporting surface. The capital, projecting on each side as it rises to support the abacus, joins the usually square abacus and the usually circular shaft of the column. The capital may be convex, as in the Doric order; concave, as in the inverted bell of the Corinthian order; or scrolling out, as in the Ionic order. These form the three principal types on which all capitals in the classical tradition are based. The Composite order established in the 16th century on a hint from the Arch of Titus, adds Ionic volutes to Corinthian acanthus leaves. From the highly visible position it occupies in all colonnaded monumental buildings, the capital is often selected for ornamentation; and is often the clearest indicator of the architectural orde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilasters
In classical architecture, a pilaster is an architectural element used to give the appearance of a supporting column and to articulate an extent of wall, with only an ornamental function. It consists of a flat surface raised from the main wall surface, usually treated as though it were a column, with a capital at the top, plinth (base) at the bottom, and the various other column elements. In contrast to a pilaster, an engaged column or buttress can support the structure of a wall and roof above. In human anatomy, a pilaster is a ridge that extends vertically across the femur, which is unique to modern humans. Its structural function is unclear. Definition In discussing Leon Battista Alberti's use of pilasters, which Alberti reintroduced into wall-architecture, Rudolf Wittkower wrote: "The pilaster is the logical transformation of the column for the decoration of a wall. It may be defined as a flattened column which has lost its three-dimensional and tactile value." A pil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonnade
In classical architecture, a colonnade is a long sequence of columns joined by their entablature, often free-standing, or part of a building. Paired or multiple pairs of columns are normally employed in a colonnade which can be straight or curved. The space enclosed may be covered or open. In St. Peter's Square in Rome, Bernini's great colonnade encloses a vast open elliptical space. When in front of a building, screening the door (Latin ''porta''), it is called a portico. When enclosing an open court, a peristyle. A portico may be more than one rank of columns deep, as at the Pantheon in Rome or the stoae of Ancient Greece. When the intercolumniation is alternately wide and narrow, a colonnade may be termed "araeosystyle" (Gr. αραιος, "widely spaced", and συστυλος, "with columns set close together"), as in the case of the western porch of St Paul's Cathedral and the east front of the Louvre. History Colonnades have been built since ancient times and inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)