|
Nag Mundari (Unicode Block)
Nag Mundari is a Unicode block containing the letters for writing the Mundari language Mundari (Munɖari) is a Munda language of the Austroasiatic language family spoken by the Munda tribes in eastern Indian states of Jharkhand, Odisha and West Bengal. It is closely related to Santali. Mundari Bani, a script specifically to .... Nag Mundari is encoded as a unicameral alphabet. The Nag Mundari block contains 27 letters plus five diacritics and ten digits. Block History The following Unicode-related documents record the purpose and process of defining specific characters in the Nag Mundari block: References {{reflist Unicode blocks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
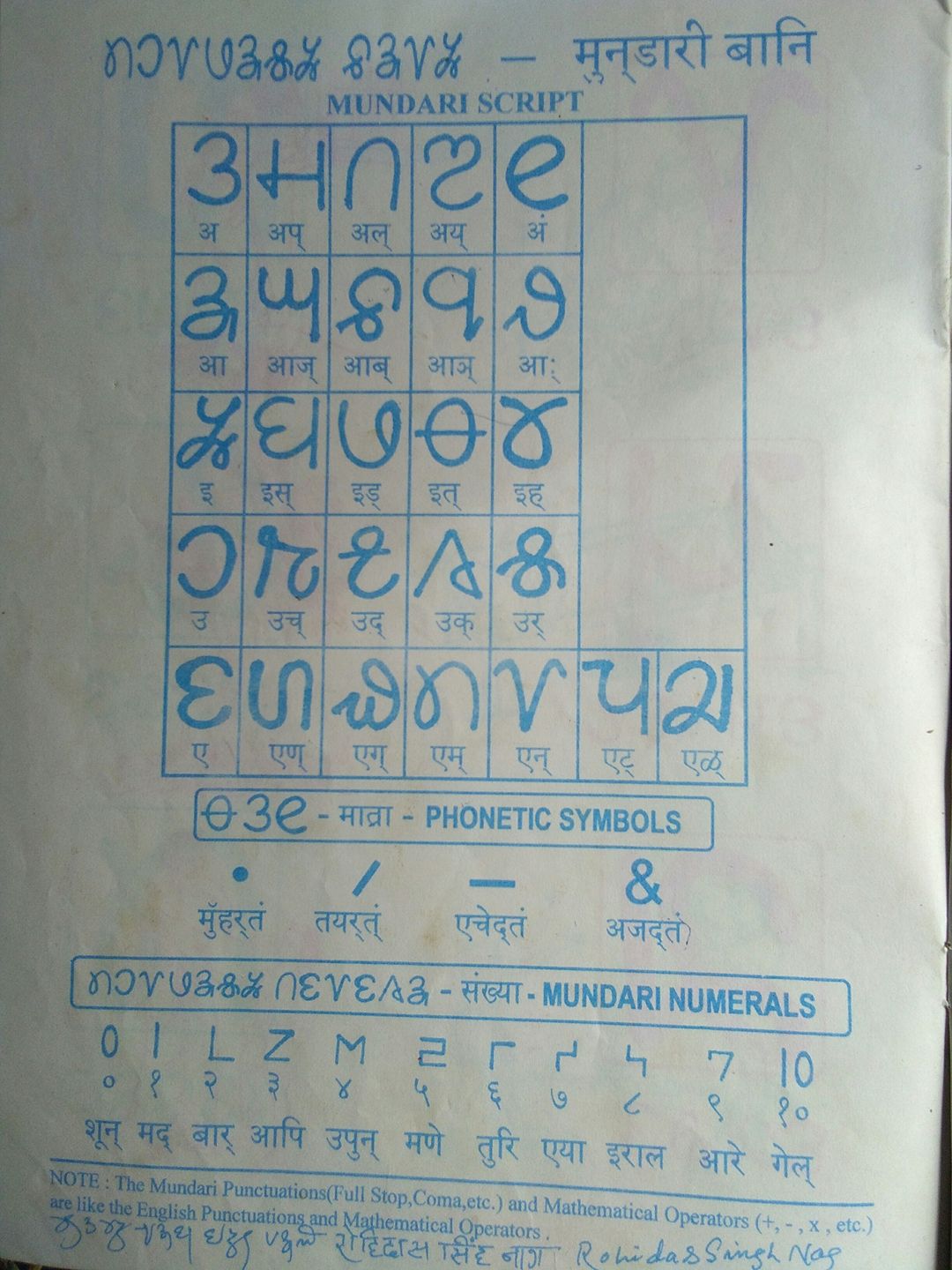
Mundari Bani
Mundari Bani (Mundari: 𞓗𞓕𞓨𞓚 ''Bani'' 'alphabet', also known as Mundari Bani Hisir ''Hisir'' 'writing', Nag Mundari, or the Mundari alphabet) is the writing system created for the Mundari language, spoken in eastern India. Mundari is an Austroasiatic language. Mundari Bani has 27 letters and five diacritics, the forms of which are intended to evoke natural shapes. The script is written from left to right. Community elder and author Rohidas Singh Nag invented and published in late 1980 the alphabetic writing system Mundari Bani, which has seen limited but increasing use in literature, education, and computing. History Rohidas Singh Nag started designing the initial characters of Mundari bani in 1949 while in grade school, which he wrote on the walls using clay. By 1953 he had finished a set of 35 characters. He further simplified the alphabet in 1980 by reducing it to 27 alphabetical characters. In 2008 Bharat Munda Samaj, Mundari Samaj Sanwar Jamda and Nag reformed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unicode Block
A Unicode block is one of several contiguous ranges of numeric character codes (code points) of the Unicode character set that are defined by the Unicode Consortium for administrative and documentation purposes. Typically, proposals such as the addition of new glyphs are discussed and evaluated by considering the relevant block or blocks as a whole. Each block is generally, but not always, meant to supply glyphs used by one or more specific languages, or in some general application area such as mathematics, surveying, decorative typesetting, social forums, etc. Design and implementation Unicode blocks are identified by unique names, which use only ASCII characters and are usually descriptive of the nature of the symbols, in English; such as "Tibetan" or "Supplemental Arrows-A". (When comparing block names, one is supposed to equate uppercase with lowercase letters, and ignore any whitespace, hyphens, and underbars; so the last name is equivalent to "supplemental_arrows__a" a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mundari Language
Mundari (Munɖari) is a Munda language of the Austroasiatic language family spoken by the Munda tribes in eastern Indian states of Jharkhand, Odisha and West Bengal. It is closely related to Santali. Mundari Bani, a script specifically to write Mundari, was invented by Rohidas Singh Nag. It has also been written in the Devanagari, Odia, Bengali, and Latin writing systems. History According to linguist Paul Sidwell (2018), Munda languages probably arrived on coast of Odisha from Indochina about 4000–3500 years ago and spread after Indo-Aryan migration to Odisha. Geographical distribution Mundari is spoken in the Ranchi, Khunti, Seraikela Kharsawan and West Singhbhum, East Singhbhum district of Jharkhand, and in the Mayurbhanj, Kendujhar, Baleshwar, Sundargarh district of Odisha by at least 1.1 million people. Another 500,000, mainly in Odisha and Assam, are recorded in the census as speaking "Munda," potentially another name for Mundari. Dialects Toshiki Osada ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unicase
A unicase or unicameral alphabet has just one case for its letters. Arabic, Brahmic scripts like Telugu, Kannada, Malayalam, Tamil, Old Hungarian (Hungarian Runic), Hebrew, Iberian, Georgian, and Hangul are unicase writing systems, while (modern) Latin, Greek, Cyrillic, and Armenian are ''bicameral'', as they have two cases for each letter, e.g., B/b, Β/β, Б/б, Բ/բ. Individual characters can also be called unicameral if they are used as letters with a generally bicameral alphabet but have only one form for both cases; for example, ʻokina (), used in Polynesian languages, and glottal stop (ʔ) as used in Nuu-chah-nuulth. Most alphabets today with two cases were once unicase. Latin used to be written with a unicase alphabet in imperial Roman times; it was only later that scribes developed new sets of symbols for running text, which became the lower case of the Latin alphabet, while the letterforms of Ancient Rome came to be called capitals or upper case. A unicase ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unicode
Unicode, formally The Unicode Standard,The formal version reference is is an information technology standard for the consistent encoding, representation, and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems. The standard, which is maintained by the Unicode Consortium, defines as of the current version (15.0) 149,186 characters covering 161 modern and historic scripts, as well as symbols, emoji (including in colors), and non-visual control and formatting codes. Unicode's success at unifying character sets has led to its widespread and predominant use in the internationalization and localization of computer software. The standard has been implemented in many recent technologies, including modern operating systems, XML, and most modern programming languages. The Unicode character repertoire is synchronized with Universal Coded Character Set, ISO/IEC 10646, each being code-for-code identical with the other. ''The Unicode Standard'', however, includes more th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Committee For Information Technology Standards
The InterNational Committee for Information Technology Standards (INCITS), (pronounced "insights"), is an ANSI-accredited standards development organization composed of Information technology developers. It was formerly known as the X3 and NCITS. INCITS is the central U.S. forum dedicated to creating technology standards. INCITS is accredited by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and is affiliated with the Information Technology Industry Council, a global policy advocacy organization that represents U.S. and global innovation companies. INCITS coordinates technical standards activity between ANSI in the US and joint ISO/ IEC committees worldwide. This provides a mechanism to create standards that will be implemented in many nations. As such, INCITS' Executive Board also serves as ANSI's Technical Advisory Group for ISO/IEC Joint Technical Committee 1. JTC 1 is responsible for International standardization in the field of information technology. INCITS operates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |