|
NaCl (software)
NaCl (Networking and Cryptography Library, pronounced "salt") is a public domain, high-speed software library for cryptography. NaCl was created by the mathematician and programmer Daniel J. Bernstein, who is best known for the creation of qmail and Curve25519. The core team also includes Tanja Lange and Peter Schwabe. The main goal while creating NaCl, according to the team's 2011 paper, was to "avoid various types of cryptographic disasters suffered by previous cryptographic libraries". The team does so by safer designs that avoid issues such as side-channel leakage and loss of randomness, by being performant enough that safety features do not get disabled by the user, and by picking better cryptographic primitives. The high-level "box" API is designed to encourage the use of authenticated encryption. Functions Public-key cryptography * , public-key authenticated encryption. Key agreement happens via X25519; encryption is done by Salsa20-Poly1305. * , scalar multiplicati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel J
Daniel commonly refers to: * Daniel (given name), a masculine given name and a surname * List of people named Daniel * List of people with surname Daniel * Daniel (biblical figure) * Book of Daniel, a biblical apocalypse, "an account of the activities and visions of Daniel" Daniel may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Literature * ''Daniel'' (Old English poem), an adaptation of the Book of Daniel * ''Daniel'', a 2006 novel by Richard Adams * ''Daniel'' (Mankell novel), 2007 Music * "Daniel" (Bat for Lashes song) (2009) * "Daniel" (Elton John song) (1973) * "Daniel", a song from '' Beautiful Creature'' by Juliana Hatfield * ''Daniel'' (album), a 2024 album by Real Estate Other arts and entertainment * ''Daniel'' (1983 film), by Sidney Lumet * ''Daniel'' (2019 film), a Danish film * Daniel (comics), a character in the ''Endless'' series Businesses * Daniel (department store), in the United Kingdom * H & R Daniel, a producer of English porcelain between 1827 and 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced Encryption Standard
The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), also known by its original name Rijndael (), is a specification for the encryption of electronic data established by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in 2001. AES is a variant of the Rijndael block cipher developed by two Belgium, Belgian cryptographers, Joan Daemen and Vincent Rijmen, who submitted a proposal to NIST during the Advanced Encryption Standard process, AES selection process. Rijndael is a family of ciphers with different key size, key and Block size (cryptography), block sizes. For AES, NIST selected three members of the Rijndael family, each with a block size of 128 bits, but three different key lengths: 128, 192 and 256 bits. AES has been adopted by the Federal government of the United States, U.S. government. It supersedes the Data Encryption Standard (DES), which was published in 1977. The algorithm described by AES is a symmetric-key algorithm, meaning the same key is used for both encrypting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Build Automation
Build automation is the practice of building software systems in a relatively unattended fashion. The build is configured to run with minimized or no software developer interaction and without using a developer's personal computer. Build automation encompasses the act of configuring the build system as well the resulting system itself. Build automation encompasses both sequencing build operations via non-interactive interface tools and running builds on a shared server. Tools Build automation tools allow for sequencing the tasks of building software via a non-interactive interface. Existing tools such as Make can be used via custom configuration file or using the command-line. Custom tools such as shell scripts can also be used, although they become increasingly cumbersome as the codebase grows more complex. Some tools, such as shell scripts, are task-oriented declarative programming. They encode sequences of commands to perform with usually minimal conditional logic. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
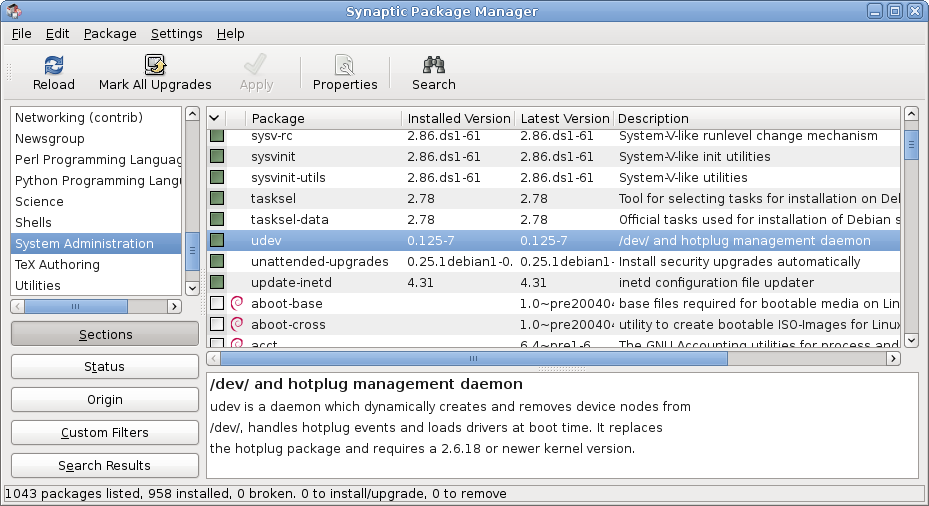
Package Manager
A package manager or package management system is a collection of software tools that automates the process of installing, upgrading, configuring, and removing computer programs for a computer in a consistent manner. A package manager deals with ''packages'', distributions of software and data in archive files. Packages contain metadata, such as the software's name, description of its purpose, version number, vendor, checksum (preferably a cryptographic hash function), and a list of dependencies necessary for the software to run properly. Upon installation, metadata is stored in a local package database. Package managers typically maintain a database of software dependencies and version information to prevent software mismatches and missing prerequisites. They work closely with software repositories, binary repository managers, and app stores. Package managers are designed to eliminate the need for manual installs and updates. This can be particularly useful for large e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamic Library
A dynamic library is a library that contains functions and data that can be consumed by a computer program at run-time as loaded from a file separate from the program executable. Dynamic linking or late binding allows for using a dynamic library by linking program library references with the associated objects in the library either at load-time or run-time. At program build-time, the linker records what library objects the program uses. When the program is run, a ''dynamic linker'' or ''linking loader'' associates program library references with the associated objects in the library. A dynamic library can be linked at build-time to a stub for each library resource that is resolved at run-time. Alternatively, a dynamic library can be loaded without linking to stubs. Most modern operating systems use the same format for both a dynamic library and an executableSome older systems, e.g., Burroughs MCP, Multics, also have a single format which affords two main advantages: it nec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fork (software Development)
In software development, a fork is a codebase that is created by duplicating an existing codebase and, generally, is subsequently modified independently of the original. Software built from a fork initially has identical behavior as software built from the original code, but as the source code is increasingly modified, the resulting software tends to have increasingly different behavior compared to the original. A fork is a form of branching, but generally involves storing the forked files separately from the original; not in the repository. Reasons for forking a codebase include user preference, stagnated or discontinued development of the original software or a schism in the developer community. Forking proprietary software (such as Unix) is prohibited by copyright law without explicit permission, but free and open-source software, by definition, may be forked without permission. Etymology The word ''fork'' has been used to mean "to divide in branches, go separate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Python (programming Language)
Python is a high-level programming language, high-level, general-purpose programming language. Its design philosophy emphasizes code readability with the use of significant indentation. Python is type system#DYNAMIC, dynamically type-checked and garbage collection (computer science), garbage-collected. It supports multiple programming paradigms, including structured programming, structured (particularly procedural programming, procedural), object-oriented and functional programming. It is often described as a "batteries included" language due to its comprehensive standard library. Guido van Rossum began working on Python in the late 1980s as a successor to the ABC (programming language), ABC programming language, and he first released it in 1991 as Python 0.9.0. Python 2.0 was released in 2000. Python 3.0, released in 2008, was a major revision not completely backward-compatible with earlier versions. Python 2.7.18, released in 2020, was the last release of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inline Assembler
In computer programming, an inline assembler is a feature of some compilers that allows low-level code written in assembly language to be embedded within a program, among code that otherwise has been compiled from a high-level language, higher-level language such as C (programming language), C or Ada programming language, Ada. Motivation and alternatives The embedding of assembly language code is usually done for one of these reasons: * Optimization (computer science), Optimization: Programmers can use assembly language code to implement the most performance-sensitive parts of their program's algorithm, algorithms, code that is apt to be more efficient than what might otherwise be generated by the compiler. * Access to processor-specific Instruction (computer science), instructions: Most processors offer special instructions, such as Compare-and-swap, Compare and Swap and Test-and-set, Test and Set instructions which may be used to construct Semaphore (programming), semaphores or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C (programming Language)
C (''pronounced'' '' – like the letter c'') is a general-purpose programming language. It was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie and remains very widely used and influential. By design, C's features cleanly reflect the capabilities of the targeted Central processing unit, CPUs. It has found lasting use in operating systems code (especially in Kernel (operating system), kernels), device drivers, and protocol stacks, but its use in application software has been decreasing. C is commonly used on computer architectures that range from the largest supercomputers to the smallest microcontrollers and embedded systems. A successor to the programming language B (programming language), B, C was originally developed at Bell Labs by Ritchie between 1972 and 1973 to construct utilities running on Unix. It was applied to re-implementing the kernel of the Unix operating system. During the 1980s, C gradually gained popularity. It has become one of the most widely used programming langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SHA-256
SHA-2 (Secure Hash Algorithm 2) is a set of cryptographic hash functions designed by the United States National Security Agency (NSA) and first published in 2001. They are built using the Merkle–Damgård construction, from a one-way compression function itself built using the Davies–Meyer structure from a specialized block cipher. SHA-2 includes significant changes from its predecessor, SHA-1. The SHA-2 family consists of six hash functions with digests (hash values) that are 224, 256, 384 or 512 bits: SHA-224, SHA-256, SHA-384, SHA-512, SHA-512/224, SHA-512/256. SHA-256 and SHA-512 are hash functions whose digests are eight 32-bit and 64-bit words, respectively. They use different shift amounts and additive constants, but their structures are otherwise virtually identical, differing only in the number of rounds. SHA-224 and SHA-384 are truncated versions of SHA-256 and SHA-512 respectively, computed with different initial values. SHA-512/224 and SHA-512/256 are also trunc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SHA-512
SHA-2 (Secure Hash Algorithm 2) is a set of cryptographic hash functions designed by the United States National Security Agency (NSA) and first published in 2001. They are built using the Merkle–Damgård construction, from a one-way compression function itself built using the One-way compression function#Davies–Meyer, Davies–Meyer structure from a specialized block cipher. SHA-2 includes significant changes from its predecessor, SHA-1. The SHA-2 family consists of six hash functions with digests (hash values) that are 224, 256, 384 or 512 bits: SHA-224, SHA-256, SHA-384, SHA-512, SHA-512/224, SHA-512/256. SHA-256 and SHA-512 are hash functions whose digests are eight 32-bit and 64-bit words, respectively. They use different shift amounts and additive constants, but their structures are otherwise virtually identical, differing only in the number of rounds. SHA-224 and SHA-384 are truncated versions of SHA-256 and SHA-512 respectively, computed with different initial values. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptographic Hash Function
A cryptographic hash function (CHF) is a hash algorithm (a map (mathematics), map of an arbitrary binary string to a binary string with a fixed size of n bits) that has special properties desirable for a cryptography, cryptographic application: * the probability of a particular n-bit output result (hash value) for a random input string ("message") is 2^ (as for any good hash), so the hash value can be used as a representative of the message; * finding an input string that matches a given hash value (a ''pre-image'') is infeasible, ''assuming all input strings are equally likely.'' The ''resistance'' to such search is quantified as security strength: a cryptographic hash with n bits of hash value is expected to have a ''preimage resistance'' strength of n bits, unless the space of possible input values is significantly smaller than 2^ (a practical example can be found in ); * a ''second preimage'' resistance strength, with the same expectations, refers to a similar problem of f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |