|
NWChem
NWChem is an ab initio computational chemistry software package which includes quantum chemical and molecular dynamics functionality. It was designed to run on high-performance parallel supercomputers as well as conventional workstation clusters. It aims to be scalable both in its ability to treat large problems efficiently, and in its usage of available parallel computing resources. NWChem has been developed by the Molecular Sciences Software group of the Theory, Modeling & Simulation program of the Environmental Molecular Sciences Laboratory (EMSL) at the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL). The early implementation was funded by the EMSL Construction Project. NWChem is currently being redesigned and reimplemented for exascale computing platforms (NWChemEx ). Capabilities * Molecular mechanics * Molecular dynamics * Hartree–Fock (self-consistent field method) * Density functional theory * Time-dependent density functional theory * Post-Hartree–Fock met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Molecular Sciences Laboratory
The Environmental Molecular Sciences Laboratory (EMSL, pronounced em-zul) is a Department of Energy, Office of Science facility at Pacific Northwest National Laboratory in Richland, Washington, United States. Research EMSL scientists and collaborators perform fundamental research that focuses on the biological, biogeochemical, and physical principles to predict processes occurring at the molecular and genomics-controlled smallest scales to the environmental Earth system changes at the largest scales. The Functional and Systems Biology Science Area focuses on understanding enzymes and biochemical pathways that connect protein structures and functions to phenotypic responses and interactions within cells, among cells in communities, and between cellular membrane surfaces and their environment for microbes and plants. The Environmental Transformations and Interactions Science Area focuses on the mechanistic and predictive understanding of the environmental (physiochemical, hydrologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensible Computational Chemistry Environment
The Extensible Computational Chemistry Environment (ECCE, pronounced "etch-ā") provides a sophisticated graphical user interface, scientific visualization tools, and the underlying data management framework enabling scientists to efficiently set up calculations and store, retrieve, and analyze the rapidly growing volumes of data produced by computational chemistry studies. Major features * Support for building molecular models. * Graphical user interface to a broad range of electronic structure theory types. Supported codes currently include NWChem, GAMESS (UK), Gaussian 03, Gaussian 98, and Amica. Other codes are registered based on user requirements. * Graphical user interface for basis set selection. * Remote submission of calculations to UNIX and Linux workstations, Linux clusters, and supercomputers. Supported queue management systems include PBS, LSF, NQE/NQS, LoadLeveler and Maui Scheduler. * Three-dimensional visualization and graphical display of molecular data pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
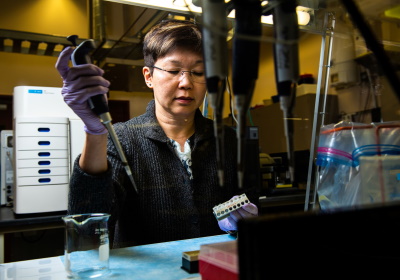
Theresa Windus
Theresa Lynn Windus is an American chemist who is a Distinguished Professor at Iowa State University and the Ames Laboratory. Her research involves the development and use of high performance computational chemistry methods to tackle environmental challenges, including the development of new catalysts and renewable energy sources. She was elected a Fellow of the American Chemical Society in 2020. Early life and education Windus was an undergraduate student at Minot State University, where she majored in chemistry, mathematics and computer sciences. She moved to Iowa State University for her graduate studies, where she considered chemical bonding in various molecular systems as well as early development of algorithms for the use of high performance computers in chemistry. Research and career Windus worked at the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, where she led the Molecular Science Software Group. She has developed advanced algorithms for high performance computing in chem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascalaph Designer
Ascalaph Designer is a computer program for general purpose molecular modelling for molecular design and simulations. It provides a graphical environment for the common programs of quantum and classical molecular modelling ORCA, NWChem, Firefly, CP2K and MDynaMix . The molecular mechanics calculations cover model building, energy optimizations and molecular dynamics. Firefly (formerly named PC GAMESS) covers a wide range of quantum chemistry methods. Ascalaph Designer is free and open-source software, released under the GNU General Public License, version 2 (GPLv2). Key features Uses See also * List of software for molecular mechanics modeling * Molecular design software * Molecule editor * Abalone Abalone ( or ; via Spanish , from Rumsen ''aulón'') is a common name for any of a group of small to very large marine gastropod molluscs in the family (biology), family Haliotidae. Other common name In biology, a common name of a taxon o ... References Exter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ONIOM
The ONIOM (short for 'Our own n-layered Integrated molecular Orbital and Molecular mechanics') method is a computational approach developed by Morokuma and co-workers. ONIOM is a hybrid method that enables different ab initio, semi-empirical, or molecular mechanics methods to be applied to different parts of a molecule/system in combination to produce reliable geometry and energy at reduced computational cost. The ONIOM computational approach has been found to be particularly useful for modeling biomolecular systems as well as for transition metal complexes and catalysts. Codes that support ONIOM *Gaussian *NWChem * ORCA (quantum chemistry program) See also *QM/MM *Steric effects Steric effects arise from the spatial arrangement of atoms. When atoms come close together there is a rise in the energy of the molecule. Steric effects are nonbonding interactions that influence the shape ( conformation) and reactivity of ions ... (ONIOM to separate Steric effects vs. electronic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coupled Cluster
Coupled cluster (CC) is a numerical technique used for describing many-body systems. Its most common use is as one of several post-Hartree–Fock ab initio quantum chemistry methods in the field of computational chemistry, but it is also used in nuclear physics. Coupled cluster essentially takes the basic Hartree–Fock molecular orbital method and constructs multi-electron wavefunctions using the exponential cluster operator to account for electron correlation. Some of the most accurate calculations for small to medium-sized molecules use this method. The method was initially developed by Fritz Coester and Hermann Kümmel in the 1950s for studying nuclear-physics phenomena, but became more frequently used when in 1966 Jiří Čížek (and later together with Josef Paldus) reformulated the method for electron correlation in atoms and molecules. It is now one of the most prevalent methods in quantum chemistry that includes electronic correlation. CC theory is simply the pert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time-dependent Density Functional Theory
Time-dependent density-functional theory (TDDFT) is a quantum mechanical theory used in physics and chemistry to investigate the properties and dynamics of many-body systems in the presence of time-dependent potentials, such as electric or magnetic fields. The effect of such fields on molecules and solids can be studied with TDDFT to extract features like excitation energies, frequency-dependent response properties, and photoabsorption spectra. TDDFT is an extension of density-functional theory (DFT), and the conceptual and computational foundations are analogous – to show that the (time-dependent) wave function is equivalent to the (time-dependent) electronic density, and then to derive the effective potential of a fictitious non-interacting system which returns the same density as any given interacting system. The issue of constructing such a system is more complex for TDDFT, most notably because the time-dependent effective potential at any given instant depends o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Northwest National Laboratory
Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) is one of the United States Department of Energy national laboratories, managed by the Department of Energy's (DOE) Office of Science. The main campus of the laboratory is in Richland, Washington. Originally named the Pacific Northwest Laboratory, PNL was established in 1965 when research and development at the Hanford Site was separated from other Hanford operations. In 1995, the laboratory was renamed the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory also known as PNNL. Facilities PNNL houses several scientific user facilities and research facilities. Scientific user facilities The Environmental Molecular Sciences Laboratory (EMSL) is a U.S. Department of Energy national scientific user facility. EMSL provides researchers around the world with integrated capabilities in oxide and mineral interface chemistry, high-performance computing and computational chemistry software, mass spectrometry, high-field magnetic resonance, and subsurfa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Chemistry Software
Computation is any type of arithmetic or non-arithmetic calculation that follows a well-defined model (e.g., an algorithm). Mechanical or electronic devices (or, historically, people) that perform computations are known as '' computers''. An especially well-known discipline of the study of computation is computer science. Physical process of Computation Computation can be seen as a purely physical process occurring inside a closed physical system called a computer. Examples of such physical systems are digital computers, mechanical computers, quantum computers, DNA computers, molecular computers, microfluidics-based computers, analog computers, and wetware computers. This point of view has been adopted by the physics of computation, a branch of theoretical physics, as well as the field of natural computing. An even more radical point of view, pancomputationalism (inaudible word), is the postulate of digital physics that argues that the evolution of the universe is itself a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QM/MM
The hybrid QM/MM (quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics) approach is a molecular simulation method that combines the strengths of ''ab initio'' QM calculations (accuracy) and MM (speed) approaches, thus allowing for the study of chemical processes in solution and in proteins. The QM/MM approach was introduced in the 1976 paper of Warshel and Levitt. They, along with Martin Karplus, won the 2013 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for "the development of multiscale models for complex chemical systems". Efficiency An important advantage of QM/MM methods is their efficiency. The cost of doing classical molecular mechanics (MM) simulations in the most straightforward case scales as ''O''(''N''2), where ''N'' is the number of atoms in the system. This is mainly due to electrostatic interactions term (every particle interacts with everything else). However, use of cutoff radius, periodic pair-list updates and more recently the variations of the particle mesh Ewald (PME) method has reduced this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Configuration Interaction
Configuration interaction (CI) is a post-Hartree–Fock linear variational method for solving the nonrelativistic Schrödinger equation within the Born–Oppenheimer approximation for a quantum chemical multi-electron system. Mathematically, ''configuration'' simply describes the linear combination of Slater determinants used for the wave function. In terms of a specification of orbital occupation (for instance, (1s)2(2s)2(2p)1...), ''interaction'' means the mixing (interaction) of different electronic configurations (states). Due to the long CPU time and large memory required for CI calculations, the method is limited to relatively small systems. In contrast to the Hartree–Fock method, in order to account for electron correlation, CI uses a variational wave function that is a linear combination of configuration state functions (CSFs) built from spin orbitals (denoted by the superscript ''SO''), : \Psi = \sum_ c_ \Phi_^ = c_0\Phi_0^ + c_1\Phi_1^ + where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |