|
NMR Tube
An NMR tube is a thin glass walled tube used to contain samples in nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Typically NMR tubes come in 5 mm diameters but 10 mm and 3 mm samples are known. It is important that the tubes are uniformly thick and well-balanced to ensure that NMR tube spins at a regular rate (i.e., they do not wobble), usually about 20 Hz in the NMR spectrometer. Construction NMR tubes are typically made of borosilicate glass. They are available in seven and eight inch lengths; a 5 mm tube outer diameter is most common, but 3 mm and 10 mm outer diameters are available as well. Where boron NMR is desired, quartz NMR tubes containing low concentrations of boron (as opposed to borosilicate glass) are available. Specialized closures such as J. Young valves and screwcap closures are available aside from more common polyethylene caps. Two common specifications for NMR tubes are concentricity and camber. Concentricity refers to the variatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NMR Sample
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a physical phenomenon in which nuclei in a strong constant magnetic field are perturbed by a weak oscillating magnetic field (in the near field) and respond by producing an electromagnetic signal with a frequency characteristic of the magnetic field at the nucleus. This process occurs near resonance, when the oscillation frequency matches the intrinsic frequency of the nuclei, which depends on the strength of the static magnetic field, the chemical environment, and the magnetic properties of the isotope involved; in practical applications with static magnetic fields up to ca. 20 tesla, the frequency is similar to VHF and UHF television broadcasts (60–1000 MHz). NMR results from specific magnetic properties of certain atomic nuclei. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is widely used to determine the structure of organic molecules in solution and study molecular physics and crystals as well as non-crystalline materials. NM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dichloromethane
Dichloromethane (DCM or methylene chloride, methylene bichloride) is an organochlorine compound with the formula . This colorless, volatile liquid with a chloroform-like, sweet odour is widely used as a solvent. Although it is not miscible with water, it is slightly polar, and miscible with many organic solvents.Rossberg, M. ''et al.'' (2006) "Chlorinated Hydrocarbons" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. . Occurrence Natural sources of dichloromethane include oceanic sources, macroalgae, wetlands, and volcanoes. However, the majority of dichloromethane in the environment is the result of industrial emissions. Production DCM is produced by treating either chloromethane or methane with chlorine gas at 400–500 °C. At these temperatures, both methane and chloromethane undergo a series of reactions producing progressively more chlorinated products. In this way, an estimated 400,000 tons were produced in the US, Europe, and Japan in 1993. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultraviolet Light
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight, and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights. Although long-wavelength ultraviolet is not considered an ionizing radiation because its photons lack the energy to ionize atoms, it can cause chemical reactions and causes many substances to glow or fluoresce. Consequently, the chemical and biological effects of UV are greater than simple heating effects, and many practical applications of UV radiation derive from its interactions with organic molecules. Short-wave ultraviolet light damages DNA and sterilizes surfaces with which it comes into contact. For h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polythiophene
Polythiophenes (PTs) are polymerized thiophenes, a sulfur heterocyclic compound, heterocycle. The parent PT is an insoluble colored solid with the formula (C4H2S)n. The rings are linked through the 2- and 5-positions. Poly(alkylthiophene)s have Alkyl, alkyl substituents at the 3- or 4-position(s). They are also colored solids, but tend to be soluble in organic solvents. PTs become Conductive polymer, conductive when oxidized. The electrical resistivity and conductivity, electrical conductivity results from the Delocalized electron, delocalization of electrons along the polymer backbone. Conductivity however is not the only interesting property resulting from electron delocalization. The optical properties of these materials respond to environmental stimuli, with dramatic color shifts in response to changes in solvent, temperature, Electric potential, applied potential, and binding to other molecules. Changes in both color and conductivity are induced by the same mechanism, tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Aspirator
A vacuum ejector, or simply ejector is a type of vacuum pump, which produces vacuum by means of the Venturi effect. In an ejector, a working fluid (liquid or gaseous) flows through a jet nozzle into a tube that first narrows and then expands in cross-sectional area. The fluid leaving the jet is flowing at a high velocity which due to Bernoulli's principle results in it having low pressure, thus generating a vacuum. The outer tube then narrows into a mixing section where the high velocity working fluid mixes with the fluid that is drawn in by the vacuum, imparting enough velocity for it to be ejected, the tube then typically expands in order to decrease the velocity of the ejected stream, allowing the pressure to smoothly increase to the external pressure. The strength of the vacuum produced depends on the velocity and shape of the fluid jet and the shape of the constriction and mixing sections, but if a liquid is used as the working fluid the strength of the vacuum produced is l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norell
Norell is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: *Arne Norell (1917–1971), Swedish furniture designer *Ingeborg Norell (born 1727), the first Finnish female to have received an official decoration *Mark Norell (born 1957), American paleontologist and molecular geneticist *Michael Norell (born 1937), American screenwriter/actor and Executive Producer *Norman Norell (1900–1972), American fashion designer *Ola Norell or Ola Rapace (born 1971), Swedish actor *Paul Norell (born 1952), English actor residing in New Zealand See also *Norell Oson Bard, a Swedish songwriting and production trio made up of Tim Norell, Ola Håkansson and Alexander Bard *Nordell *Norvell (other) *Norvelle (other) Norvelle may refer to: * Norvelle, West Virginia, an unincorporated community in Raleigh County *Duncan Norvelle Duncan Norvelle (born 2 April 1958, Hoton, Loughborough, Leicestershire, England) is an English comedian in the variety tradition, ... * Norwell (dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paramagnetic
Paramagnetism is a form of magnetism whereby some materials are weakly attracted by an externally applied magnetic field, and form internal, induced magnetic fields in the direction of the applied magnetic field. In contrast with this behavior, diamagnetic materials are repelled by magnetic fields and form induced magnetic fields in the direction opposite to that of the applied magnetic field. Paramagnetic materials include most chemical elements and some compounds; they have a relative magnetic permeability slightly greater than 1 (i.e., a small positive magnetic susceptibility) and hence are attracted to magnetic fields. The magnetic moment induced by the applied field is linear in the field strength and rather weak. It typically requires a sensitive analytical balance to detect the effect and modern measurements on paramagnetic materials are often conducted with a SQUID magnetometer. Paramagnetism is due to the presence of unpaired electrons in the material, so most atoms wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
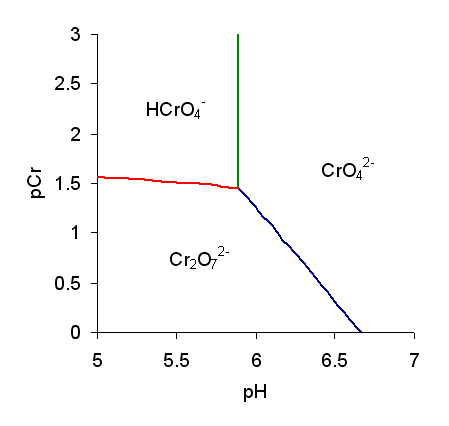
Chromic Acid
The term chromic acid is usually used for a mixture made by adding concentrated sulfuric acid to a dichromate, which may contain a variety of compounds, including solid chromium trioxide. This kind of chromic acid may be used as a cleaning mixture for glass. Chromic acid may also refer to the molecular species, H2CrO4 of which the trioxide is the anhydride. Chromic acid features chromium in an oxidation state of +6 (or VI). It is a strong and corrosive oxidising agent. Molecular chromic acid Molecular chromic acid, H2CrO4, has much in common with sulfuric acid, H2SO4. Only sulfuric acid can be classified as part of the 7 strong acids list. Due to the laws pertinent to the concept of "first order ionization energy", the first proton is lost most easily. It behaves extremely similar to sulfuric acid deprotonation. Since the process of polyvalent acid-base titrations have more than one proton (especially when the acid is starting substance and the base is the titrant), proton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piranha Solution
Piranha solution, also known as piranha etch, is a mixture of sulfuric acid () and hydrogen peroxide (), used to clean organic residues off substrates. Because the mixture is a strong oxidizing agent, it will decompose most organic matter, and it will also hydroxylate most surfaces (by adding –OH groups), making them highly hydrophilic (water-compatible). This means the solution can also easily dissolve fabric and skin, potentially causing severe damage and chemical burns in case of inadvertent contact. Preparation and use Many different mixture ratios are commonly used, and all are called piranha. A typical mixture is 3 parts of concentrated sulfuric acid and 1 part of hydrogen peroxide solution; other protocols may use a 4:1 or even 7:1 mixture. A closely related mixture, sometimes called "base piranha", is a 3:1 mixture of ammonia solution (, or ) with hydrogen peroxide. As hydrogen peroxide is less stable at high pH than under acidic conditions, (pH c. 11.6) also accele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |