|
NMDA
''N''-methyl--aspartic acid or ''N''-methyl--aspartate (NMDA) is an amino acid derivative that acts as a specific agonist at the NMDA receptor mimicking the action of glutamate, the neurotransmitter which normally acts at that receptor. Unlike glutamate, NMDA only binds to and regulates the NMDA receptor and has no effect on other glutamate receptors (such as those for AMPA and kainate). NMDA receptors are particularly important when they become overactive during, for example, withdrawal from alcohol as this causes symptoms such as agitation and, sometimes, epileptiform seizures. Biological function In 1962, J.C. Watkins reported synthesizing NMDA, an isomer of the previously know''N''-Methyl--aspartic-acid (PubChem ID 4376) NMDA is a water-soluble -alpha-amino acid — an aspartic acid derivative with an ''N''-methyl substituent and - configuration — found across Animalia from lancelets to mammals. At homeostatic levels NMDA plays an essential role as a neurotransmitter and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
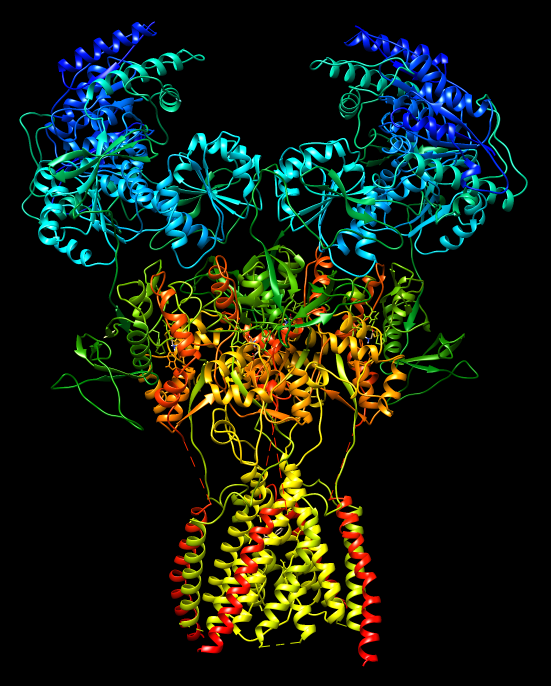
NMDA Receptor
The ''N''-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (also known as the NMDA receptor or NMDAR), is a glutamate receptor and ion channel found in neurons. The NMDA receptor is one of three types of ionotropic glutamate receptors, the other two being AMPA receptor, AMPA and kainate receptors. Depending on its subunit composition, its Ligand (biochemistry), ligands are glutamate and glycine (or D-Serine, D-serine). However, the binding of the ligands is typically not sufficient to open the channel as it may be blocked by Magnesium, Mg2+ ions which are only removed when the neuron is sufficiently depolarized. Thus, the channel acts as a “coincidence detector” and only once both of these conditions are met, the channel opens and it allows cation, positively charged ions (cations) to flow through the cell membrane. The NMDA receptor is thought to be very important for controlling synaptic plasticity and mediating learning and memory functions. The NMDA receptor is ionotropic, meaning it is a pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketamine
Ketamine is a dissociative anesthetic used medically for induction and maintenance of anesthesia. It is also used as a recreational drug. It is one of the safest anesthetics, as, in contrast with opiates, ether, and propofol, it suppresses neither respiration nor heart rate. Ketamine is also simple to administer and highly tolerable compared to drugs with similar effects which are flammable, irritating, or even explosive. Ketamine is a novel compound, derived from PCP, created in pursuit of a safer anesthetic with similar characteristics. Ketamine is also used for acute pain management. At anesthetic doses, ketamine induces a state of "dissociative anesthesia", a trance-like state providing pain relief, sedation, and amnesia. The distinguishing features of ketamine anesthesia are preserved breathing and airway reflexes, stimulated heart function with increased blood pressure, and moderate bronchodilation. At lower, sub-anesthetic doses, ketamine is a promising agent for pain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excitotoxicity
In excitotoxicity, nerve cells suffer damage or death when the levels of otherwise necessary and safe neurotransmitters such as glutamate become pathologically high, resulting in excessive stimulation of receptors. For example, when glutamate receptors such as the NMDA receptor or AMPA receptor encounter excessive levels of the excitatory neurotransmitter, glutamate, significant neuronal damage might ensue. Excess glutamate allows high levels of calcium ions (Ca2+) to enter the cell. Ca2+ influx into cells activates a number of enzymes, including phospholipases, endonucleases, and proteases such as calpain. These enzymes go on to damage cell structures such as components of the cytoskeleton, membrane, and DNA. In evolved, complex adaptive systems such as biological life it must be understood that mechanisms are rarely, if ever, simplistically direct. For example, NMDA in subtoxic amounts induces neuronal survival of otherwise toxic levels of glutamate. Excitotoxicity may be inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell. Neurotransmitters are released from synaptic vesicles into the synaptic cleft where they are able to interact with neurotransmitter receptors on the target cell. The neurotransmitter's effect on the target cell is determined by the receptor it binds. Many neurotransmitters are synthesized from simple and plentiful precursors such as amino acids, which are readily available and often require a small number of biosynthetic steps for conversion. Neurotransmitters are essential to the function of complex neural systems. The exact number of unique neurotransmitters in humans is unknown, but more than 100 have been identified. Common neurotransmitters include glutamate, GABA, acetylcholine, glycine and norepinephrine. Mechanism and cycle Synthes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
APV (NMDAR Antagonist)
AP5 (also known as APV, (2''R'')-amino-5-phosphonovaleric acid, or (2''R'')-amino-5-phosphonopentanoate) is a chemical compound used as a biochemical tool to study various cellular processes. It is a selective NMDA receptor antagonist that competitively inhibits the ligand (glutamate) binding site of NMDA receptors. AP5 blocks NMDA receptors in micromolar concentrations (~50 μM). AP5 blocks the cellular analog of classical conditioning in the sea slug ''Aplysia californica'', and has similar effects on ''Aplysia'' long-term potentiation (LTP), since NMDA receptors are required for both. It is sometimes used in conjunction with the calcium chelator BAPTA to determine whether NMDARs are required for a particular cellular process. AP5/APV has also been used to study NMDAR-dependent LTP in the mammalian hippocampus.Gustafsson B., Wigström H., Abraham W.C., and Huang Y.Y. Long-Term Potentiation in the Hippocampus Using Depolarizing Current Pulses as the Conditioning Stimulu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptor Agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a Receptor (biochemistry), receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are Cell (biology), cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an Receptor antagonist, antagonist blocks the action of the agonist, while an inverse agonist causes an action opposite to that of the agonist. Etymology From the Ancient Greek language, Greek αγωνιστής (agōnistēs), contestant; champion; rival < αγων (agōn), contest, combat; exertion, struggle < αγω (agō), I lead, lead towards, conduct; drive Types of agonists Receptor (biochemistry), Receptors can be activated by either endogenous agonists (such as hormones and neurotransmitters) or exogenous agonists (such as medication, drugs), resulting in a biological response. A physiological agonism and ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
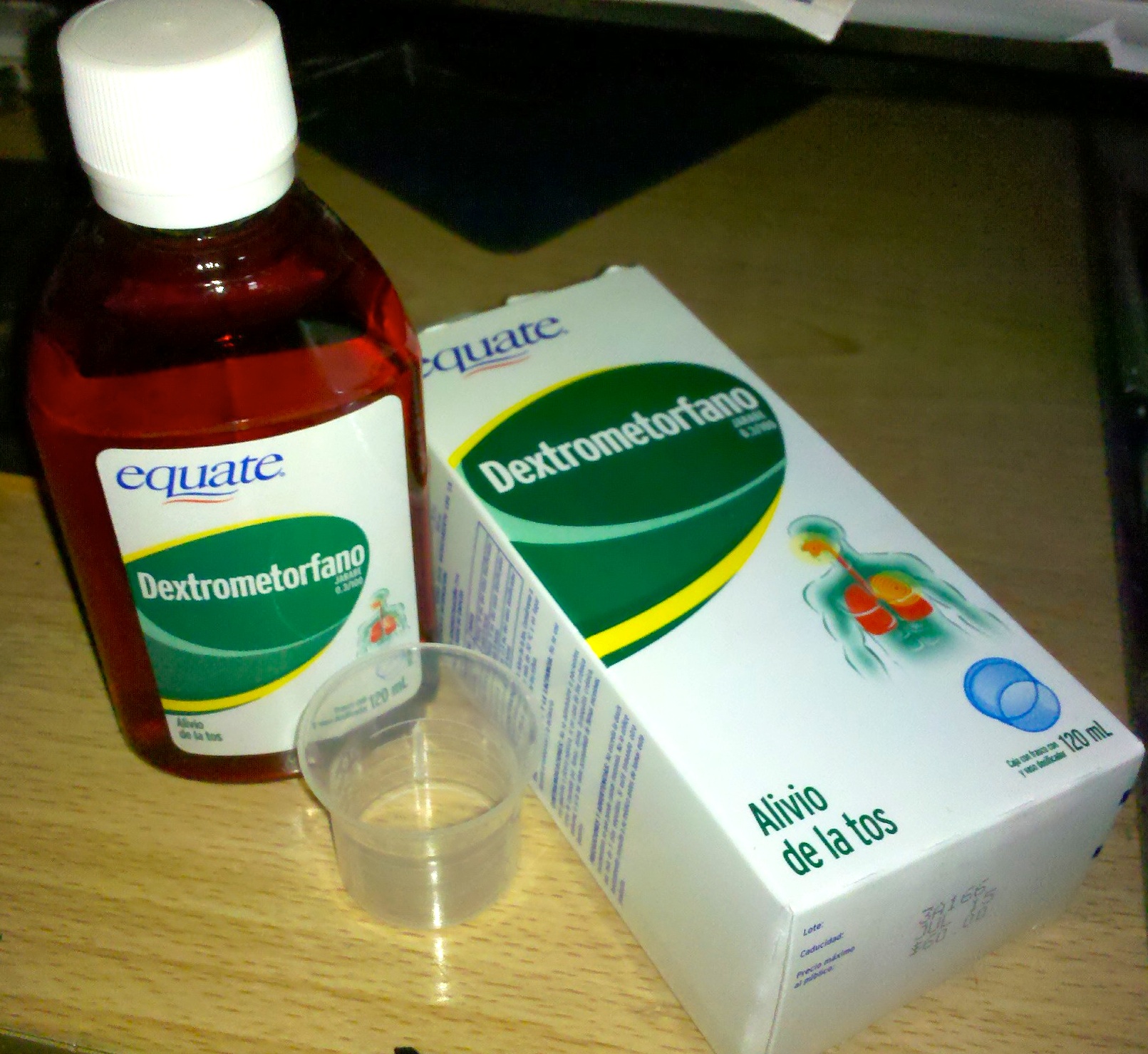
Dextromethorphan
Dextromethorphan (DXM) is a medication most often used as a cough suppressant in over-the-counter cold and cough medicines. It is sold in syrup, tablet, spray, and lozenge forms. In 2022, the FDA approved a formulation of it combined with bupropion named Auvelity to serve as a rapid acting antidepressant in patients with major depressive disorder. It is in the morphinan class of medications with sedative, dissociative, and stimulant properties (at lower doses). Dextromethorphan does not have a significant affinity for the mu-opioid receptor activity typical of morphinan compounds and exerts its therapeutic effects through several other receptors. In its pure form, dextromethorphan occurs as a white powder. Dextromethorphan is also used recreationally. When exceeding approved dosages, dextromethorphan acts as a dissociative hallucinogen. It has multiple mechanisms of action, including actions as a nonselective serotonin reuptake inhibitor and a sigma-1 receptor agonis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amantadine
Amantadine, sold under the brand name Gocovri among others, is a medication used to treat dyskinesia associated with parkinsonism and influenza caused by type A influenzavirus, though its use for the latter is no longer recommended due to widespread drug resistance. It acts as a nicotinic antagonist, dopamine agonist, and noncompetitive NMDA antagonist. The antiviral mechanism of action is antagonism of the influenzavirus A M2 proton channel, which prevents endosomal escape (i.e. the release of viral genetic material into the host cytoplasm). Amantadine was first used for the treatment of influenza A. After antiviral properties were initially reported in 1963, amantadine received approval for prophylaxis against the influenza virus A in 1976. However, amantadine-resistant influenza viruses were first reported during the 1980 influenza A epidemic and resistance frequency continued to rise into the early 2000s. Currently, amantadine is no longer recommended for the treatment of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiletamine
Tiletamine is a dissociative anesthetic and pharmacologically classified as an NMDA receptor antagonist. It is related chemically to ketamine. Tiletamine hydrochloride exists as odorless white crystals. It is used in veterinary medicine in the combination product Telazol (tiletamine/zolazepam, 50 mg/ml of each in 5 ml vial) as an injectable anesthetic for use in cats and dogs. It is sometimes used in combination with xylazine (Rompun) to chemically immobilize large mammals such as polar bears and wood bison. Telazol is the only commercially available tiletamine product in the United States. It is contraindicated in patients of an ASA score of III or greater and in animals with CNS signs, hyperthyroidism, cardiac disease, pancreatic or renal disease, pregnancy, glaucoma, or penetrating eye injuries. Recreational use of telazol has been documented. Animal studies have also shown that tiletamine produces rewarding and reinforcing effects. Tiletamine products are classified ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptor Antagonist
A receptor antagonist is a type of receptor ligand or drug that blocks or dampens a biological response by binding to and blocking a receptor rather than activating it like an agonist. Antagonist drugs interfere in the natural operation of receptor proteins.Pharmacology Guide: In vitro pharmacology: concentration-response curves " '' GlaxoWellcome.'' Retrieved on December 6, 2007. They are sometimes called blockers; examples include alpha blockers, |
Coincidence Detection In Neurobiology
Coincidence detection in the context of neurobiology is a process by which a neuron or a neural circuit can encode information by detecting the occurrence of temporally close but spatially distributed input signals. Coincidence detectors influence neuronal information processing by reducing temporal jitter, reducing spontaneous activity, and forming associations between separate neural events. This concept has led to a greater understanding of neural processes and the formation of computational maps in the brain. Principles of coincidence detection Coincidence detection relies on separate inputs converging on a common target. Consider a basic neural circuit with two input neurons, A and B, that have excitatory synaptic terminals converging on a single output neuron, C (Fig. 1). If each input neuron's EPSP is subthreshold for an action potential at C, then C will not fire unless the two inputs from A and B are temporally close together. Synchronous arrival of these two inputs m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethylglycine
Dimethylglycine (DMG) is a derivative of the amino acid glycine with the structural formula (CH3)2NCH2COOH. It can be found in beans and liver, and has a sweet taste. It can be formed from trimethylglycine upon the loss of one of its methyl groups. It is also a byproduct of the metabolism of choline. When DMG was first discovered, it was referred to as Vitamin B16, but, unlike true B vitamins, deficiency of DMG in the diet does not lead to any ill-effects and it is synthesized by the human body in the citric acid cycle meaning it does not meet the definition of a vitamin. Uses Dimethylglycine has been suggested for use as an athletic performance enhancer, immunostimulant, and a treatment for autism, epilepsy, or mitochondrial disease. There is no evidence that dimethylglycine is effective for treating mitochondrial disease. Published studies on the subject have shown little to no difference between DMG treatment and placebo in autism spectrum disorders. Biological activity Dime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)