|
NILFS
NILFS or NILFS2 (''New Implementation of a Log-structured File System'') is a log-structured file system implementation for the Linux kernel. It was developed by Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation (NTT) CyberSpace Laboratories and a community from all over the world. NILFS was released under the terms of the GNU General Public License (GPL). Design "NILFS is a log-structured file system, in that the storage medium is treated like a circular buffer and new blocks are always written to the end. ��og-structured file systems are often used for flash media since they will naturally perform wear-leveling; ��ILFS emphasizes snapshots. The log-structured approach is a specific form of copy-on-write behavior, so it naturally lends itself to the creation of file system snapshots. The NILFS developers talk about the creation of "continuous snapshots" which can be used to recover from user-initiated file system problems ��" Using a copy-on-write technique known as "nothing in life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nippon Telegraph And Telephone
, commonly known as NTT, is a Japanese telecommunications company headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. Ranked 55th in ''Fortune'' Global 500, NTT is the fourth largest telecommunications company in the world in terms of revenue, as well as the third largest publicly traded company in Japan after Toyota and Sony, as of June 2022. The company is incorporated pursuant to the NTT Law (). The purpose of the company defined by the law is to own all the shares issued by Nippon Telegraph and Telephone East Corporation (NTT East) and Nippon Telegraph and Telephone West Corporation (NTT West) and to ensure proper and stable provision of telecommunications services all over Japan including remote rural areas by these companies as well as to conduct research relating to the telecommunications technologies that will form the foundation for telecommunications. On 1 July 2019, NTT Corporation launched NTT Ltd., an $11 billion de facto holding company business consisting of 28 brands from across NTT ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
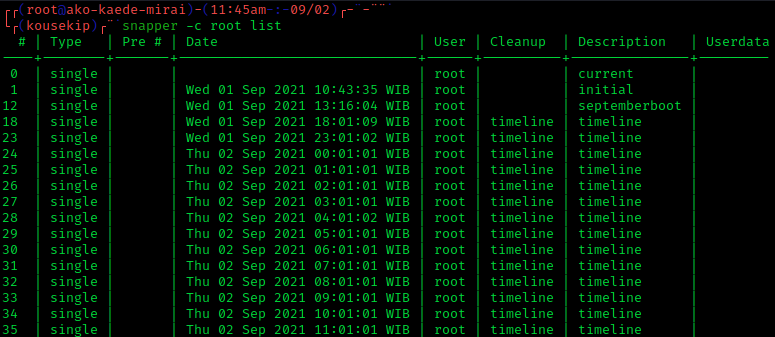
Snapshot (computer Storage)
In computer systems, a snapshot is the state of a system at a particular point in time. The term was coined as an analogy to that in photography. It can refer to an actual copy of the state of a system or to a capability provided by certain systems. Rationale A full backup of a large data set may take a long time to complete. On multi-tasking or multi-user systems, there may be writes to that data while it is being backed up. This prevents the backup from being atomic and introduces a version skew that may result in data corruption. For example, if a user moves a file into a directory that has already been backed up, then that file would be completely missing on the backup media, since the backup operation had already taken place before the addition of the file. Version skew may also cause corruption with files which change their size or contents underfoot while being read. One approach to safely backing up live data is to temporarily disable write access to data during th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Udisks
udev (userspace ) is a device manager for the Linux kernel. As the successor of devfsd and hotplug, udev primarily manages device nodes in the directory. At the same time, udev also handles all user space events raised when hardware devices are added into the system or removed from it, including firmware loading as required by certain devices. Rationale It is an operating system's kernel that is responsible for providing an abstract interface of the hardware to the rest of the software. Being a monolithic kernel, the Linux kernel does exactly that: device drivers are part of the Linux kernel, and make up more than half of its source code. Hardware can be accessed through system calls or over their device nodes. To be able to deal with peripheral devices that are hotplug-capable in a user-friendly way, a part of handling all of these hotplug-capable hardware devices was handed over from the kernel to a daemon running in user-space. Running in user space serves security and stab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blkid
In computing, the fdisk command-line utility provides disk-partitioning functions, preparatory to defining file systems. fdisk features in the DOS, DR FlexOS, IBM OS/2, and Microsoft Windows operating systems, and in certain ports of FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenBSD, DragonFly BSD and macOS for compatibility reasons. In versions of the Windows NT operating-system line from Windows 2000 onwards, is replaced by a more advanced tool called diskpart. Similar utilities exist for Unix-like systems, for example, BSD disklabel. Implementations IBM PC DOS IBM introduced , Fixed Disk Setup Program version 1.00, with the March 1983 release of the IBM PC/XT, the first PC to store data on a hard disk, and the IBM Personal Computer DOS version 2.0. Version 1 could be used to create one FAT12 DOS partition, delete it, change the active partition, or display partition data. writes the master boot record, which supported up to four partitions. The other three were intended for other opera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Util-linux
is a standard package distributed by the Linux Kernel Organization for use as part of the Linux operating system. A fork, (with meaning "next generation"), was created when development stalled, but has been renamed back to , and is the official version of the package. Contents Included It includes the following utilities: Removed Utilities formerly included, but removed : * arch * chkdupexe * clock * cytune * ddate (removed from default build before being removed altogether) * elvtune * fastboot * fasthalt * halt * initctl * ramsize (formerly a symlink to rdev) * rdev * reboot * rootflags (formerly a symlink to rdev) * shutdown * simpleinit * tailf * vidmode (formerly a symlink to rdev) See also * BusyBox * cat (Unix) * CUPS * GNU Core Utilities * Toybox Toybox is a free and open-source software implementation of over 200 Unix command line utilities such as '' ls'', '' cp'', and '' mv''. The Toybox project was started in 2006, and became a 0BSD licensed BusyB ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNU GRUB
GNU GRUB (short for GNU GRand Unified Bootloader, commonly referred to as GRUB) is a boot loader package from the GNU Project. GRUB is the reference implementation of the Free Software Foundation's Multiboot Specification, which provides a user the choice to boot one of multiple operating systems installed on a computer or select a specific kernel configuration available on a particular operating system's partitions. GNU GRUB was developed from a package called the ''Grand Unified Bootloader'' (a play on Grand Unified Theory). It is predominantly used for Unix-like systems. The GNU operating system uses GNU GRUB as its boot loader, as do most Linux distributions and the Solaris operating system on x86 systems, starting with the Solaris 10 1/06 release. Operation Booting When a computer is turned on, its BIOS finds the primary bootable device (usually the computer's hard disk) and runs the initial bootstrap program from the master boot record (MBR). The MBR is the firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilobyte
The kilobyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. The International System of Units (SI) defines the prefix '' kilo'' as 1000 (103); per this definition, one kilobyte is 1000 bytes.International Standard IEC 80000-13 Quantities and Units – Part 13: Information science and technology, International Electrotechnical Commission (2008). The internationally recommended unit symbol for the kilobyte is kB. In some areas of information technology, particularly in reference to solid-state memory capacity, ''kilobyte'' instead typically refers to 1024 (210) bytes. This arises from the prevalence of sizes that are powers of two in modern digital memory architectures, coupled with the accident that 210 differs from 103 by less than 2.5%. A kibibyte is defined by Clause 4 of IEC 80000-13 as 1024 bytes. Definitions and usage Base 10 (1000 bytes) In the International System of Units (SI) the prefix '' kilo'' means 1000 (103); therefore, one kilobyte is 1000 bytes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Page (computer Memory)
A page, memory page, or virtual page is a fixed-length contiguous block of virtual memory, described by a single entry in the page table. It is the smallest unit of data for memory management in a virtual memory operating system. Similarly, a page frame is the smallest fixed-length contiguous block of physical memory into which memory pages are mapped by the operating system. A transfer of pages between main memory and an auxiliary store, such as a hard disk drive, is referred to as paging or swapping. Page size trade-off Page size is usually determined by the processor architecture. Traditionally, pages in a system had uniform size, such as 4,096 bytes. However, processor designs often allow two or more, sometimes simultaneous, page sizes due to its benefits. There are several points that can factor into choosing the best page size. Page table size A system with a smaller page size uses more pages, requiring a page table that occupies more space. For example, if a 23 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Block Size (data Storage And Transmission)
In computing (specifically data transmission and data storage), a block, sometimes called a physical record, is a sequence of bytes or bits, usually containing some whole number of records, having a maximum length; a ''block size''. Data thus structured are said to be ''blocked''. The process of putting data into blocks is called ''blocking'', while ''deblocking'' is the process of extracting data from blocks. Blocked data is normally stored in a data buffer, and read or written a whole block at a time. Blocking reduces the overhead and speeds up the handling of the data stream. For some devices, such as magnetic tape and CKD disk devices, blocking reduces the amount of external storage required for the data. Blocking is almost universally employed when storing data to 9-track magnetic tape, NAND flash memory, and rotating media such as floppy disks, hard disks, and optical discs. Most file systems are based on a block device, which is a level of abstraction for the hardware ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garbage Collection (computer Science)
In computer science, garbage collection (GC) is a form of automatic memory management. The ''garbage collector'' attempts to reclaim memory which was allocated by the program, but is no longer referenced; such memory is called '' garbage''. Garbage collection was invented by American computer scientist John McCarthy around 1959 to simplify manual memory management in Lisp. Garbage collection relieves the programmer from doing manual memory management, where the programmer specifies what objects to de-allocate and return to the memory system and when to do so. Other, similar techniques include stack allocation, region inference, and memory ownership, and combinations thereof. Garbage collection may take a significant proportion of a program's total processing time, and affect performance as a result. Resources other than memory, such as network sockets, database handles, windows, file descriptors, and device descriptors, are not typically handled by garbage collectio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
POSIX
The Portable Operating System Interface (POSIX) is a family of standards specified by the IEEE Computer Society for maintaining compatibility between operating systems. POSIX defines both the system- and user-level application programming interfaces (APIs), along with command line shells and utility interfaces, for software compatibility (portability) with variants of Unix and other operating systems. POSIX is also a trademark of the IEEE. POSIX is intended to be used by both application and system developers. Name Originally, the name "POSIX" referred to IEEE Std 1003.1-1988, released in 1988. The family of POSIX standards is formally designated as IEEE 1003 and the ISO/IEC standard number is ISO/ IEC 9945. The standards emerged from a project that began in 1984 building on work from related activity in the ''/usr/group'' association. Richard Stallman suggested the name ''POSIX'' (pronounced as ''pahz-icks,'' as in ''positive'', not as ''poh-six'') to the IEEE instead of f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year 2038 Problem
The year 2038 problem (also known as Y2038, Y2K38, or the Epochalypse) is a time formatting bug in computer systems with representing times after 03:14:07 UTC on 19 January 2038. The problem exists in systems which measure Unix time – the number of seconds elapsed since the ''Unix epoch'' (00:00:00 UTC on 1 January 1970) – and store it in a signed 32-bit integer. The data type is only capable of representing integers between −(2) and 231 − 1, meaning the latest time that can be properly encoded is 2 − 1 seconds after epoch (03:14:07 UTC on 19 January 2038). Attempting to increment to the following second (03:14:08) will cause the integer to overflow, setting its value to −(2) which systems will interpret as 2 seconds ''before'' epoch (20:45:52 UTC on 13 December 1901). The problem is similar in nature to the year 2000 problem. Computer systems that use time for critical computations may encounter fatal errors if the Y2038 pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |