|
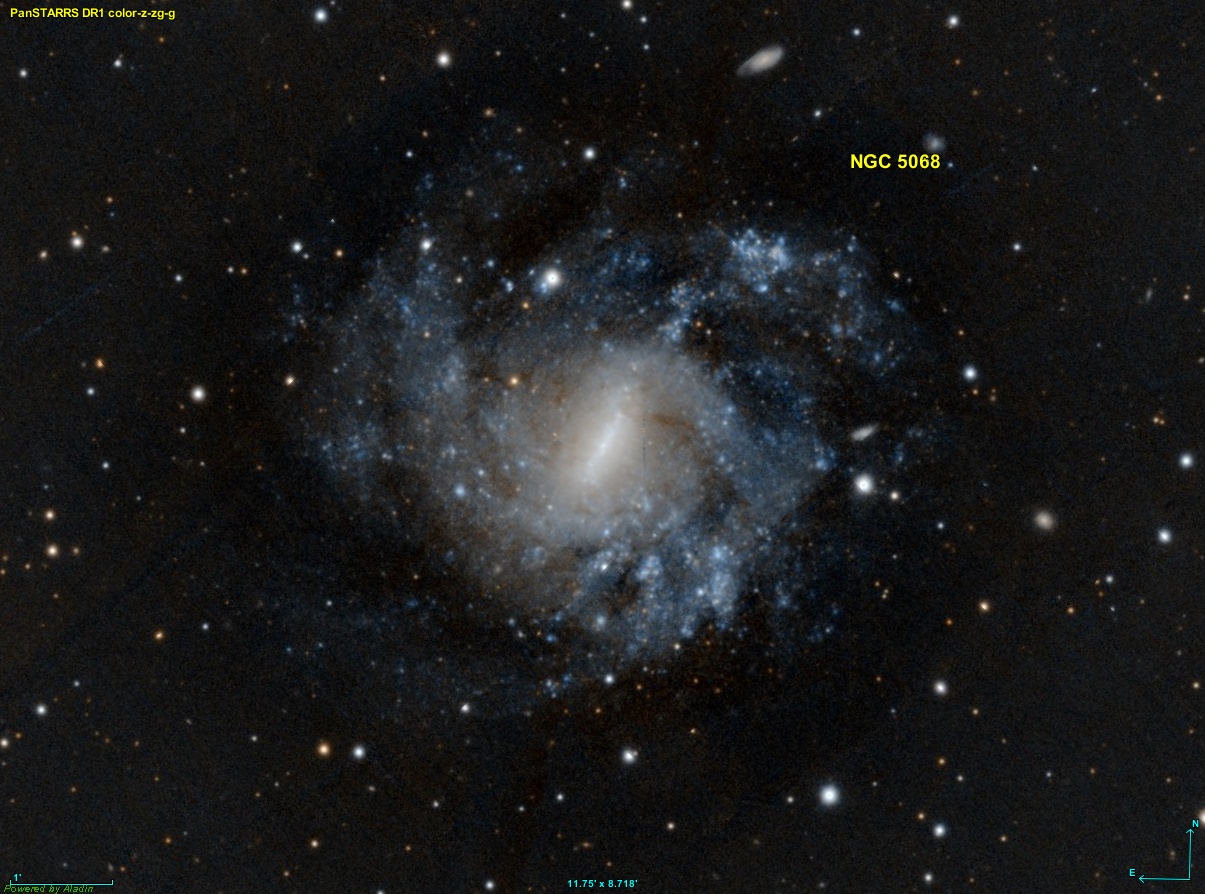
NGC 5068
NGC 5068 is a face-on field barred spiral galaxy in the Virgo constellation. NGC 5068 is located approximately 22 million light-years away and has a diameter that exceeds 45000 light-years. Although no supernovae have been observed in NGC 5068 yet, a luminous red nova A luminous red nova (abbr. ''LRN'', pl. ''luminous red novae'', pl.abbr. ''LRNe'') is a stellar explosion thought to be caused by the merging of two stars. They are characterised by a distinct red colour, and a light curve that fades slowly with ..., designated AT 2020hat, was discovered on 12 April 2020 (type LRN, mag. 17.8). Retrieved 10 November 2023. References External links * *[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NGC 5068 PanS
NGC commonly refers to: * New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars, a catalogue of deep sky objects in astronomy NGC may also refer to: Companies * NGC Corporation Dynegy Inc. is an electric company based in Houston, Texas, in the United States. It owns and operates a number of power stations in the U.S., all of which are natural gas-fueled or coal-fueled. Dynegy was acquired by Vistra Corp on April 9, 20 ..., name of US electric company Dynegy, Inc. from 1995 to 1998 * National Gas Company of Trinidad and Tobago, state-owned natural gas company in Trinidad and Tobago * National Grid plc, a former name of National Grid Electricity Transmission plc, the operator of the British electricity transmission system * Northrop Grumman Corporation, aerospace and defense conglomerate formed from the merger of Northrop Corporation and Grumman Corporation in 1994 * Numismatic Guaranty Corporation, coin certification company in the United States Other uses * National Ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barred Spiral Galaxy
A barred spiral galaxy is a spiral galaxy with a central bar-shaped structure composed of stars. Bars are found in about two thirds of all spiral galaxies, and generally affect both the motions of stars and interstellar gas within spiral galaxies and can affect spiral arms as well. The Milky Way Galaxy, where the Solar System is located, is classified as a barred spiral galaxy. Edwin Hubble classified spiral galaxies of this type as "SB" (spiral, barred) in his Hubble sequence and arranged them into sub-categories based on how open the arms of the spiral are. SBa types feature tightly bound arms, while SBc types are at the other extreme and have loosely bound arms. SBb-type galaxies lie in between the two. SB0 is a barred lenticular galaxy. A new type, SBm, was subsequently created to describe somewhat irregular barred spirals, such as the Magellanic Clouds, which were once classified as irregular galaxies, but have since been found to contain barred spiral structures. Among o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field Galaxies
A field galaxy is a galaxy that does not belong to a larger galaxy group or cluster and hence is gravitationally alone. Roughly 80% of all galaxies located within of the Milky Way are in groups or clusters of galaxies. Most low-surface-brightness galaxies are field galaxies."An Introduction to Galaxies and Cosmology", ''David J. Adams and others'' The median Hubble-type of field galaxies is Sb, a type of spiral galaxy Spiral galaxies form a class of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work ''The Realm of the Nebulae''Local Volume, about Fur ...
|
Barred Spiral Galaxies
A barred spiral galaxy is a spiral galaxy with a central bar-shaped structure composed of stars. Bars are found in about two thirds of all spiral galaxies, and generally affect both the motions of stars and interstellar gas within spiral galaxies and can affect spiral arms as well. The Milky Way Galaxy, where the Solar System is located, is classified as a barred spiral galaxy. Edwin Hubble classified spiral galaxies of this type as "SB" (spiral, barred) in his Hubble sequence and arranged them into sub-categories based on how open the arms of the spiral are. SBa types feature tightly bound arms, while SBc types are at the other extreme and have loosely bound arms. SBb-type galaxies lie in between the two. SB0 is a barred lenticular galaxy. A new type, SBm, was subsequently created to describe somewhat irregular barred spirals, such as the Magellanic Clouds, which were once classified as irregular galaxies, but have since been found to contain barred spiral structures. Among othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
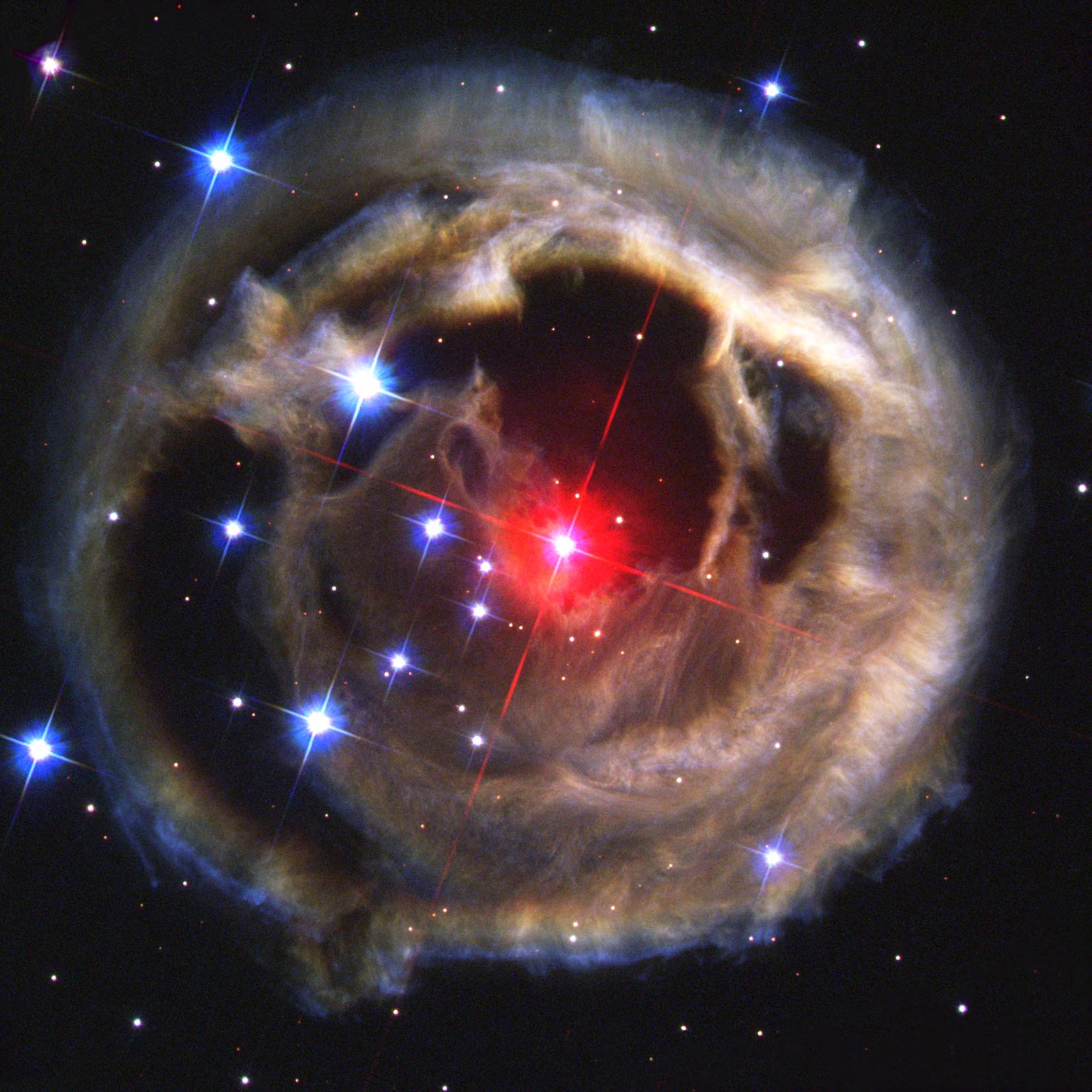
Luminous Red Nova
A luminous red nova (abbr. ''LRN'', pl. ''luminous red novae'', pl.abbr. ''LRNe'') is a stellar explosion thought to be caused by the merging of two stars. They are characterised by a distinct red colour, and a light curve that fades slowly with resurgent brightness in the infrared. Luminous red novae are not related to standard novae, which are explosions that occur on the surface of white dwarf stars. Discovery A small number of objects exhibiting the characteristics of luminous red novae have been observed over the last 30 years or so. The red star M31 RV in the Andromeda Galaxy flared brightly during 1988 and may have been a luminous red nova. In 1994, V4332 Sagittarii, a star in the Milky Way galaxy, flared similarly, and in 2002, V838 Monocerotis followed suit and was studied quite closely. The first confirmed luminous red nova was the object M85 OT2006-1, in the galaxy Messier 85. It was first observed during the Lick Observatory Supernova Search, and subsequently investi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supernova
A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. It has the plural form supernovae or supernovas, and is abbreviated SN or SNe. This transient astronomical event occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion. The original object, called the ''progenitor'', either collapses to a neutron star or black hole, or is completely destroyed. The peak optical luminosity of a supernova can be comparable to that of an entire galaxy before fading over several weeks or months. Supernovae are more energetic than novae. In Latin language, Latin, ''nova'' means "new", referring astronomically to what appears to be a temporary new bright star. Adding the prefix "super-" distinguishes supernovae from ordinary novae, which are far less luminous. The word ''supernova'' was coined by Walter Baade and Fritz Zwicky in 1929. The last supernova to be directly observed in the Milky Way was Kepler's Supernova in 160 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galaxy
A galaxy is a system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, dark matter, bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Greek ' (), literally 'milky', a reference to the Milky Way galaxy that contains the Solar System. Galaxies, averaging an estimated 100 million stars, range in size from dwarfs with less than a hundred million stars, to the largest galaxies known – supergiants with one hundred trillion stars, each orbiting its galaxy's center of mass. Most of the mass in a typical galaxy is in the form of dark matter, with only a few percent of that mass visible in the form of stars and nebulae. Supermassive black holes are a common feature at the centres of galaxies. Galaxies are categorized according to their visual morphology as elliptical, spiral, or irregular. Many are thought to have supermassive black holes at their centers. The Milky Way's central black hole, known as Sagittarius A*, has a mass four million times greater than the Sun. As o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiral Galaxy
Spiral galaxies form a class of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work ''The Realm of the Nebulae''Alt URL pp. 124–151) and, as such, form part of the . Most spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating containing s, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as the |
Field Galaxy
A field galaxy is a galaxy that does not belong to a larger galaxy group or cluster and hence is gravitationally alone. Roughly 80% of all galaxies located within of the Milky Way are in groups or clusters of galaxies. Most low-surface-brightness galaxies are field galaxies."An Introduction to Galaxies and Cosmology", ''David J. Adams and others'' The median Hubble-type of field galaxies is Sb, a type of spiral galaxy Spiral galaxies form a class of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work ''The Realm of the Nebulae''Local Volume, about Fur ...
|
Pan-STARRS
The Panoramic Survey Telescope and Rapid Response System (Pan-STARRS1; List of observatory codes, obs. code: IAU code#F51, F51 and Pan-STARRS2 obs. code: IAU code#F52, F52) located at Haleakala Observatory, Hawaii, US, consists of astronomical cameras, telescopes and a computing facility that is Astronomical survey, surveying the sky for moving or variable objects on a continual basis, and also producing accurate astrometry and photometry (astronomy), photometry of already-detected objects. In January 2019 the second Pan-STARRS data release was announced. At 1.6 petabytes, it is the largest volume of astronomical data ever released. Description The Pan-STARRS Project is a collaboration between the University of Hawaii Institute for Astronomy (Hawaii), Institute for Astronomy, MIT Lincoln Laboratory, MHPCC#Maui High Performance Computing Center (MHPCC), Maui High Performance Computing Center and Science Applications International Corporation. Telescope construction was funded b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principal Galaxies Catalogue
The Catalogue of Principal Galaxies (PGC) is an astronomical catalog published in 1989 that lists B1950 and J2000 equatorial coordinates and cross-identifications for 73,197 galaxies. It is based on the Lyon-Meudon Extragalactic Database (LEDA), which was originally started in 1983. 40,932 coordinates (56%) have standard deviations smaller than . A total of 131,601 names from the 38 most common sources are listed. Available mean data for each object are given: * 49,102 morphological descriptions, * 52,954 apparent major and minor axis, * 67,116 apparent magnitudes, * 20,046 radial velocities and * 24,361 position angles. The Lyon-Meudon Extragalactic Database was eventually expanded into HyperLEDA, a database of a few million galaxies. Galaxies in the original PGC catalogue are numbered with their original PGC number in HyperLEDA. Numbers have also been assigned for the other galaxies, although for those galaxies not in the original PGC catalogue, it is not recommended to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virgo (constellation)
Virgo is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for maiden, and its old astronomical symbol is (♍︎). Lying between Leo (constellation), Leo to the west and Libra (constellation), Libra to the east, it is the second-largest constellation in the sky (after Hydra (constellation), Hydra) and the largest constellation in the zodiac. The ecliptic intersects the celestial equator within this constellation and Pisces (constellation), Pisces. Underlying these technical two definitions, the sun passes directly overhead of the equator, within this constellation, at the September equinox. Virgo can be easily found through its brightest star, Spica. Location Virgo is prominent in the spring sky in the Northern Hemisphere, visible all night in March and April. As the largest zodiac constellation, the Sun takes 44 days to pass through it, longer than any other. From 1990 and until 2062, this will take place from September 16 to October 30. It is located in the third ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |