|
NGC 2536
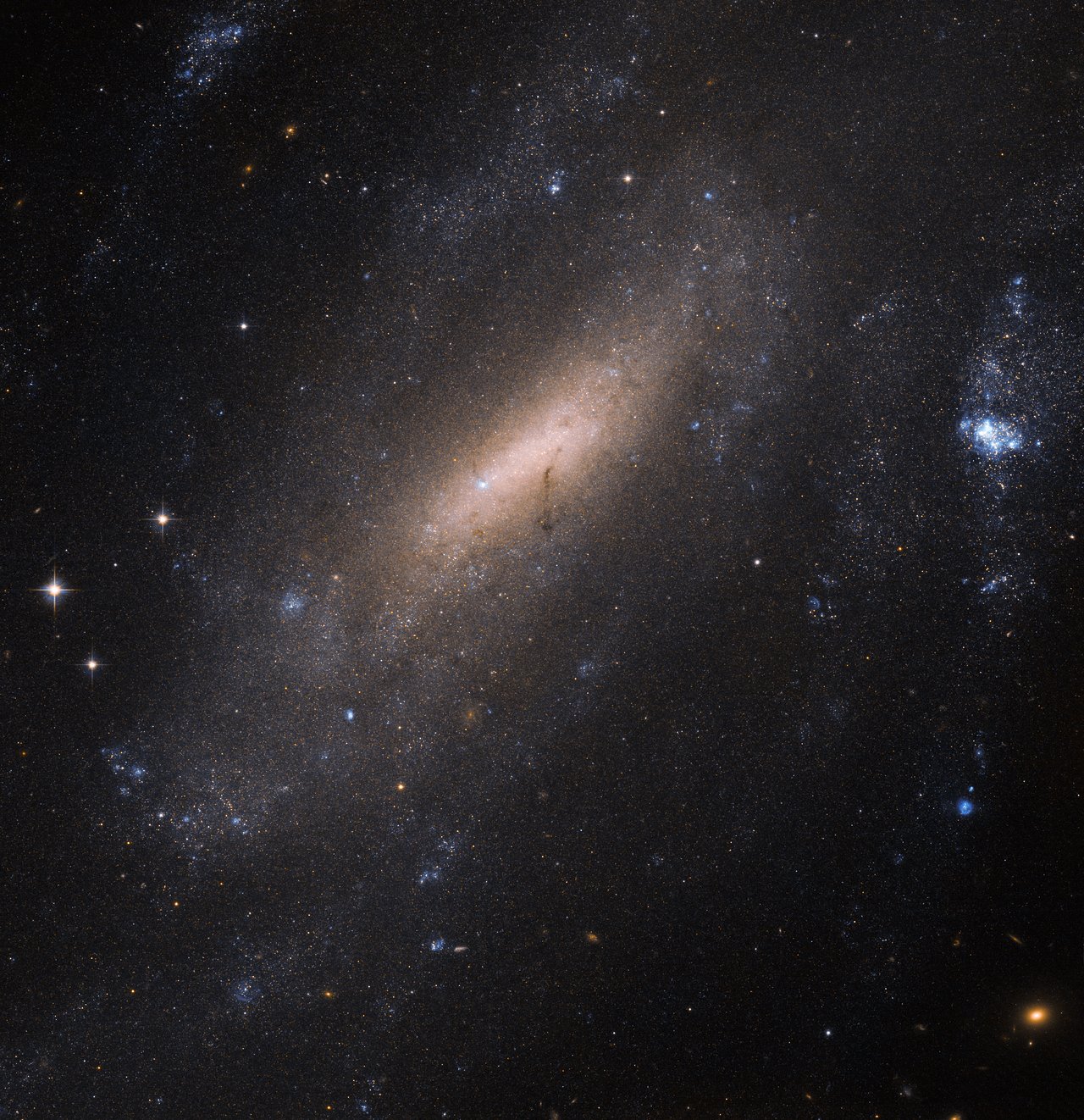
NGC 2536 is a barred spiral galaxy with a prominent inner ring structure encircling the bar in the constellation Cancer that is interacting Interaction is action that occurs between two or more objects, with broad use in philosophy and the sciences. It may refer to: Science * Interaction hypothesis, a theory of second language acquisition * Interaction (statistics) * Interactions o ... with NGC 2535. The two galaxies are listed together in the '' Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies'' as an example of a spiral galaxy with a high surface brightness companion. References External links * Spitzer Space Telescope page on NGC 2536 Barred spiral galaxies Interacting galaxies Peculiar galaxies Cancer (constellation) 2536 04264 22958 082 {{Spiral-galaxy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New General Catalogue
The ''New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars'' (abbreviated NGC) is an astronomical catalogue of deep-sky objects compiled by John Louis Emil Dreyer in 1888. The NGC contains 7,840 objects, including galaxies, star clusters and emission nebulae. Dreyer published two supplements to the NGC in 1895 and 1908, known as the ''Index Catalogues'' (abbreviated IC), describing a further 5,386 astronomical objects. Thousands of these objects are best known by their NGC or IC numbers, which remain in widespread use. The NGC expanded and consolidated the cataloguing work of William and Caroline Herschel, and John Herschel's ''General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars''. Objects south of the celestial equator are catalogued somewhat less thoroughly, but many were included based on observation by John Herschel or James Dunlop. The NGC contained multiple errors, but attempts to eliminate them were made by the ''Revised New General Catalogue'' (RNGC) by Jack W. Sulent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlas Of Peculiar Galaxies
The ''Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies'' is a catalog of peculiar galaxies produced by Halton Arp in 1966. A total of 338 galaxies are presented in the atlas, which was originally published in 1966 by the California Institute of Technology. The primary goal of the catalog was to present photographs of examples of the different kinds of peculiar structures found among galaxies. (online version, including Arp's original tabular data, and PDF link) Background Arp realized that the reason why galaxies formed into spiral or elliptical shapes was not well understood. He perceived peculiar galaxies as small "experiments" that astronomers could use to understand the physical processes that distort spiral or elliptical galaxies. With this atlas, astronomers had a sample of peculiar galaxies that they could study in more detail. The atlas does not present a complete overview of every peculiar galaxy in the sky but instead provides examples of the different phenomena as observed in nearby ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UGC Objects
UGC may refer to: Science and technology * Universal gravitational constant G, in physics * Uppsala General Catalogue, an astronomical catalogue of galaxies * UGC, a codon for cysteine * Unique games conjecture In computational complexity theory, the unique games conjecture (often referred to as UGC) is a conjecture made by Subhash Khot in 2002. The conjecture postulates that the problem of determining the approximate ''value'' of a certain type of gam ..., a conjecture in computational complexity Organisations * UGC (cinema operator), a European cinema chain, formerly Union Générale Cinématographique * UGC Fox Distribution, a former French-American film production company formed in 1995 * Union Graduate College, Schenectady, New York * United Grain Company, a Russian grain trading company based in Moscow * University Grants Commission (other) * University Grants Committee (other) * UnitedGlobalCom, former name of the cable TV operator Liberty Global * Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NGC Objects
The ''New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars'' (abbreviated NGC) is an astronomical catalogue of deep-sky objects compiled by John Louis Emil Dreyer in 1888. The NGC contains 7,840 objects, including galaxies, star clusters and emission nebulae. Dreyer published two supplements to the NGC in 1895 and 1908, known as the ''Index Catalogues'' (abbreviated IC), describing a further 5,386 astronomical objects. Thousands of these objects are best known by their NGC or IC numbers, which remain in widespread use. The NGC expanded and consolidated the cataloguing work of William and Caroline Herschel, and John Herschel's ''General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars''. Objects south of the celestial equator are catalogued somewhat less thoroughly, but many were included based on observation by John Herschel or James Dunlop. The NGC contained multiple errors, but attempts to eliminate them were made by the ''Revised New General Catalogue'' (RNGC) by Jack W. Sulenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peculiar Galaxies
A peculiar galaxy is a galaxy of unusual size, shape, or composition. Between five and ten percent of known galaxies are categorized as peculiar. Astronomers have identified two types of peculiar galaxies: ''interacting galaxies'' and ''active galactic nuclei'' (AGN). When two galaxies come close to each other, their mutual gravitational forces can cause them to acquire highly irregular shapes. The terms 'peculiar galaxy' and 'interacting galaxy' have now become synonymous because the majority of peculiar galaxies attribute their forms to such gravitational forces. Formation Scientists hypothesize that many peculiar galaxies are formed by the collision of two or more galaxies. As such, peculiar galaxies tend to host more active galactic nuclei than normal galaxies, indicating that they contain supermassive black holes. Many peculiar galaxies experience starbursts, or episodes of rapid star formation, due to the galaxies merging. The periods of elevated star formation and the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interacting Galaxies
Interacting galaxies (''colliding galaxies'') are galaxies whose gravitational fields result in a disturbance of one another. An example of a minor interaction is a satellite galaxy disturbing the primary galaxy's spiral arms. An example of a major interaction is a galactic collision, which may lead to a galaxy merger. Satellite interaction A giant galaxy interacting with its satellites is common. A satellite's gravity could attract one of the primary's spiral arms. Alternatively, the secondary satellite can dive into the primary galaxy, as in the Sagittarius Dwarf Elliptical Galaxy diving into the Milky Way. That can possibly trigger a small amount of star formation. Such orphaned clusters of stars were sometimes referred to as "blue blobs" before they were recognized as stars. Galaxy collision Colliding galaxies are common during galaxy evolution. The extremely tenuous distribution of matter in galaxies means these are not collisions in the traditional sense of the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barred Spiral Galaxies
A barred spiral galaxy is a spiral galaxy with a central bar-shaped structure composed of stars. Bars are found in about two thirds of all spiral galaxies, and generally affect both the motions of stars and interstellar gas within spiral galaxies and can affect spiral arms as well. The Milky Way Galaxy, where the Solar System is located, is classified as a barred spiral galaxy. Edwin Hubble classified spiral galaxies of this type as "SB" (spiral, barred) in his Hubble sequence and arranged them into sub-categories based on how open the arms of the spiral are. SBa types feature tightly bound arms, while SBc types are at the other extreme and have loosely bound arms. SBb-type galaxies lie in between the two. SB0 is a barred lenticular galaxy. A new type, SBm, was subsequently created to describe somewhat irregular barred spirals, such as the Magellanic Clouds, which were once classified as irregular galaxies, but have since been found to contain barred spiral structures. Among othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interacting Galaxy
Interacting galaxies (''colliding galaxies'') are galaxies whose gravitational fields result in a disturbance of one another. An example of a minor interaction is a satellite galaxy disturbing the primary galaxy's spiral arms. An example of a major interaction is a galactic collision, which may lead to a galaxy merger. Satellite interaction A giant galaxy interacting with its satellites is common. A satellite's gravity could attract one of the primary's spiral arms. Alternatively, the secondary satellite can dive into the primary galaxy, as in the Sagittarius Dwarf Elliptical Galaxy diving into the Milky Way. That can possibly trigger a small amount of star formation. Such orphaned clusters of stars were sometimes referred to as "blue blobs" before they were recognized as stars. Galaxy collision Colliding galaxies are common during galaxy evolution. The extremely tenuous distribution of matter in galaxies means these are not collisions in the traditional sense of the wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object. The origins of the earliest constellations likely go back to prehistory. People used them to relate stories of their beliefs, experiences, creation myth, creation, or mythology. Different cultures and countries adopted their own constellations, some of which lasted into the early 20th century before today's constellations were internationally recognized. The recognition of constellations has changed significantly over time. Many changed in size or shape. Some became popular, only to drop into obscurity. Some were limited to a single culture or nation. The 48 traditional Western constellations are Greek. They are given in Aratus' work ''Phenomena'' and Ptolemy's ''Almagest'', though their origin probably predates these works by several centuries. Constellation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barred Spiral Galaxy
A barred spiral galaxy is a spiral galaxy with a central bar-shaped structure composed of stars. Bars are found in about two thirds of all spiral galaxies, and generally affect both the motions of stars and interstellar gas within spiral galaxies and can affect spiral arms as well. The Milky Way Galaxy, where the Solar System is located, is classified as a barred spiral galaxy. Edwin Hubble classified spiral galaxies of this type as "SB" (spiral, barred) in his Hubble sequence and arranged them into sub-categories based on how open the arms of the spiral are. SBa types feature tightly bound arms, while SBc types are at the other extreme and have loosely bound arms. SBb-type galaxies lie in between the two. SB0 is a barred lenticular galaxy. A new type, SBm, was subsequently created to describe somewhat irregular barred spirals, such as the Magellanic Clouds, which were once classified as irregular galaxies, but have since been found to contain barred spiral structures. Among o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principal Galaxies Catalogue
The Catalogue of Principal Galaxies (PGC) is an astronomical catalog published in 1989 that lists B1950 and J2000 equatorial coordinates and cross-identifications for 73,197 galaxies. It is based on the Lyon-Meudon Extragalactic Database (LEDA), which was originally started in 1983. 40,932 coordinates (56%) have standard deviations smaller than . A total of 131,601 names from the 38 most common sources are listed. Available mean data for each object are given: * 49,102 morphological descriptions, * 52,954 apparent major and minor axis, * 67,116 apparent magnitudes, * 20,046 radial velocities and * 24,361 position angles. The Lyon-Meudon Extragalactic Database was eventually expanded into HyperLEDA, a database of a few million galaxies. Galaxies in the original PGC catalogue are numbered with their original PGC number in HyperLEDA. Numbers have also been assigned for the other galaxies, although for those galaxies not in the original PGC catalogue, it is not recommended to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NGC 2535
NGC 2535 is an unbarred spiral galaxy exhibiting a weak inner ring structure around the nucleus in the constellation Cancer that is interacting with NGC 2536. The interaction has warped the disk and spiral arms of NGC 2535, producing an elongated structure, visible at ultraviolet wavelengths, that contain many bright, recently formed blue star clusters in addition to enhanced star forming regions around the galaxy center. The two galaxies are listed together in the '' Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies'' as an example of a spiral galaxy with a high surface brightness companion. One supernova has been observed in NGC 2535: SN 1901A (type unknown, mag. 14.7). Retrieved 28 March 2023. See also * |