|
NGC 188
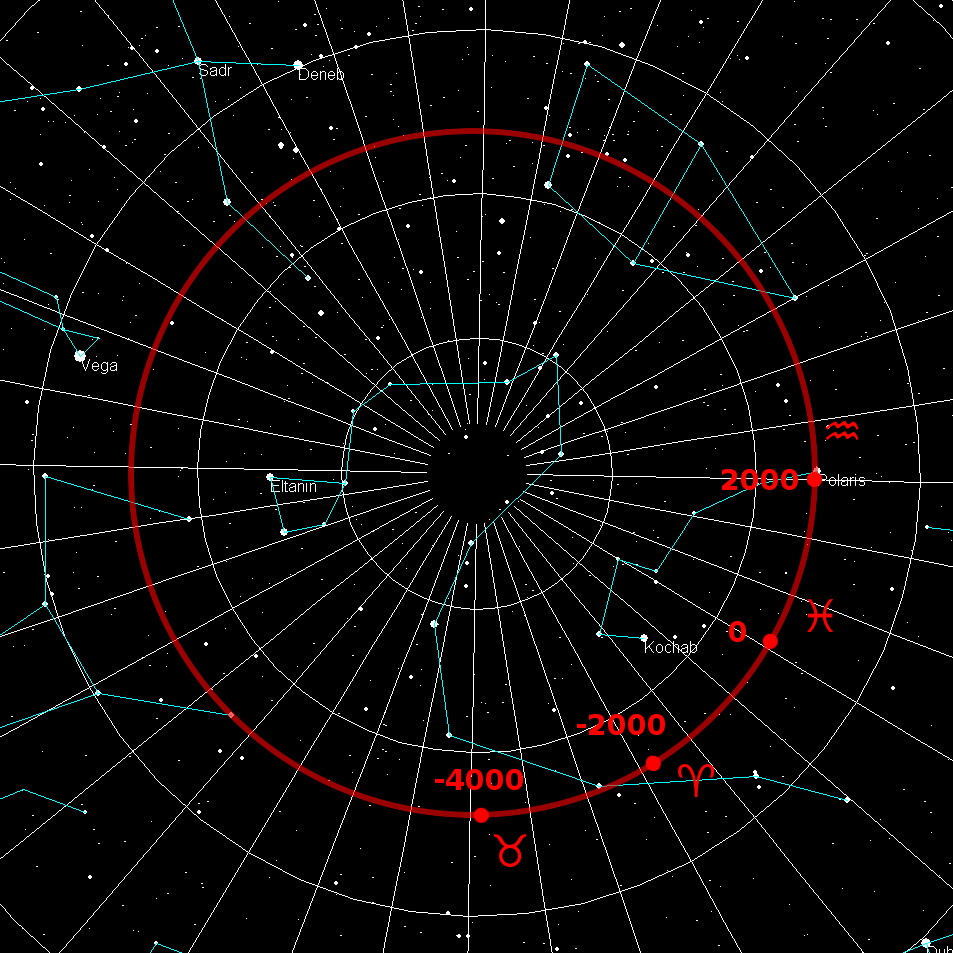
NGC 188 (also known as Caldwell 1) is an open cluster in the constellation Cepheus. It was discovered by John Herschel in 1825. Unlike most open clusters that drift apart after a few million years because of the gravitational interaction of our Milky Way galaxy, NGC 188 lies far above the plane of the galaxy and is one of the most ancient of open clusters known, at approximately 6.8 billion years old. NGC 188 is very close to the North Celestial Pole, under five degrees away, and in the constellation of Cepheus at an estimated 5,000 light-year A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 1012 ...s' distance, this puts it slightly above the Milky Way's disc and further from the center of the galaxy than the Sun. References External links * NGC 188at SEDS NGC objects pages NGC 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New General Catalogue
The ''New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars'' (abbreviated NGC) is an astronomical catalogue of deep-sky objects compiled by John Louis Emil Dreyer in 1888. The NGC contains 7,840 objects, including galaxies, star clusters and emission nebulae. Dreyer published two supplements to the NGC in 1895 and 1908, known as the ''Index Catalogues'' (abbreviated IC), describing a further 5,386 astronomical objects. Thousands of these objects are best known by their NGC or IC numbers, which remain in widespread use. The NGC expanded and consolidated the cataloguing work of William and Caroline Herschel, and John Herschel's ''General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars''. Objects south of the celestial equator are catalogued somewhat less thoroughly, but many were included based on observation by John Herschel or James Dunlop. The NGC contained multiple errors, but attempts to eliminate them were made by the ''Revised New General Catalogue'' (RNGC) by Jack W. Sulent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Herschel
Sir John Frederick William Herschel, 1st Baronet (; 7 March 1792 – 11 May 1871) was an English polymath active as a mathematician, astronomer, chemist, inventor, experimental photographer who invented the blueprint and did botanical work. Herschel originated the use of the Julian day system in astronomy. He named seven moons of Saturn and four moons of Uranus – the seventh planet, discovered by his father Sir William Herschel. He made many contributions to the science of photography, and investigated colour blindness and the chemical power of ultraviolet rays. His ''Preliminary Discourse'' (1831), which advocated an inductive approach to scientific experiment and theory-building, was an important contribution to the philosophy of science. Early life and work on astronomy Herschel was born in Slough, Buckinghamshire, the son of Mary Baldwin and astronomer William Herschel. He was the nephew of astronomer Caroline Herschel. He studied shortly at Eton College an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NGC Objects
The ''New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars'' (abbreviated NGC) is an astronomical catalogue of deep-sky objects compiled by John Louis Emil Dreyer in 1888. The NGC contains 7,840 objects, including galaxies, star clusters and emission nebulae. Dreyer published two supplements to the NGC in 1895 and 1908, known as the ''Index Catalogues'' (abbreviated IC), describing a further 5,386 astronomical objects. Thousands of these objects are best known by their NGC or IC numbers, which remain in widespread use. The NGC expanded and consolidated the cataloguing work of William and Caroline Herschel, and John Herschel's ''General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars''. Objects south of the celestial equator are catalogued somewhat less thoroughly, but many were included based on observation by John Herschel or James Dunlop. The NGC contained multiple errors, but attempts to eliminate them were made by the ''Revised New General Catalogue'' (RNGC) by Jack W. Sulenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
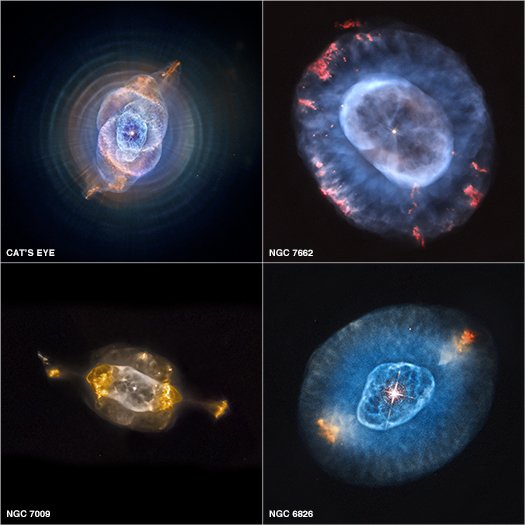
Open Clusters
An open cluster is a type of star cluster made of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way galaxy, and many more are thought to exist. They are loosely bound by mutual gravitational attraction and become disrupted by close encounters with other clusters and clouds of gas as they orbit the Galactic Center. This can result in a migration to the main body of the galaxy and a loss of cluster members through internal close encounters. Open clusters generally survive for a few hundred million years, with the most massive ones surviving for a few billion years. In contrast, the more massive globular clusters of stars exert a stronger gravitational attraction on their members, and can survive for longer. Open clusters have been found only in spiral and irregular galaxies, in which active star formation is occurring. Young open clusters may be cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light-year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 1012 (one million million, or billion in long scale). As defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a light-year is the distance that light travels in a vacuum in one Julian year (365.25 days). Because it includes the time-measurement word "year", the term ''light-year'' is sometimes misinterpreted as a unit of time. The ''light-year'' is most often used when expressing distances to stars and other distances on a galactic scale, especially in non-specialist contexts and popular science publications. The unit most commonly used in professional astronomy is the parsec (symbol: pc, about 3.26 light-years) which derives from astrometry; it is the distance at which one astronomical unit subtends an angle of one second of arc. Defini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celestial Pole
The north and south celestial poles are the two points in the sky where Earth's rotation around a fixed axis, axis of rotation, indefinitely extended, intersects the celestial sphere. The north and south celestial poles appear permanently directly overhead to observers at Earth's North Pole and South Pole, respectively. As Earth spins on its axis, the two celestial poles remain fixed in the sky, and all other celestial points appear to rotate around them, completing one circuit per day (strictly, per sidereal time, sidereal day). The celestial poles are also the poles of the celestial equatorial coordinate system, meaning they have declinations of +90 degrees and −90 degrees (for the north and south celestial poles, respectively). Despite their apparently fixed positions, the celestial poles in the long term do not actually remain permanently fixed against the background of the stars. Because of a phenomenon known as the precession of the equinoxes, the poles trace out ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Publications Of The Astronomical Society Of The Pacific
''Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific'' (often abbreviated as ''PASP'' in references and literature) is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal managed by the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. It publishes research and review papers, instrumentation papers and dissertation summaries in the fields of astronomy and astrophysics. Between 1999 and 2016 it was published by the University of Chicago Press and since 2016, it has been published by IOP Publishing. The current editor-in-chief is Jeff Mangum of the National Radio Astronomy Observatory. ''PASP'' has been published monthly since 1899, and along with ''The Astrophysical Journal'', ''The Astronomical Journal'', ''Astronomy and Astrophysics'', and the ''Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society'', is one of the primary journals for the publication of astronomical research. See also * ''List of astronomy journals This is a list of scientific journals publishing articles in astronomy, astroph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. The term ''Milky Way'' is a translation of the Latin ', from the Greek ('), meaning "milky circle". From Earth, the Milky Way appears as a band because its disk-shaped structure is viewed from within. Galileo Galilei first resolved the band of light into individual stars with his telescope in 1610. Until the early 1920s, most astronomers thought that the Milky Way contained all the stars in the Universe. Following the 1920 Great Debate between the astronomers Harlow Shapley and Heber Curtis, observations by Edwin Hubble showed that the Milky Way is just one of many galaxies. The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy with an estimated D25 isophotal diameter of , but only about 1,000 light years thick at the spiral arms (more at the bulg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philibert Jacques Melotte
Philibert Jacques Melotte (29 January 1880 – 30 March 1961) was a British astronomer whose parents emigrated from Belgium. In 1908 he discovered a moon of Jupiter, today known as Pasiphaë. It was simply designated "Jupiter VIII" and was not given its present name until 1975. The outer main-belt asteroid 676 Melitta, the only asteroid he discovered, is named after the Attic form of the Greek ''Melissa'', the bee, but its resemblance to the discoverer's name is not fortuitous. The conspicuous star cluster in the Coma Berenices constellation is commonly designated Mel 111 since it appeared in Melotte's 1915 catalogue of star clusters,Melotte, P. J"A Catalogue of Star Clusters shown on Franklin-Adams Chart Plates" ''MmRAS'', 1915 but not in Charles Messier's famous catalogue of deep sky objects or in the New General Catalogue since it was not proved to be a true cluster until 1938 by the astronomer R J Trumpler. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NGC 0188 DSS
NGC commonly refers to: * New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars, a catalogue of deep sky objects in astronomy NGC may also refer to: Companies * NGC Corporation, name of US electric company Dynegy, Inc. from 1995 to 1998 * National Gas Company of Trinidad and Tobago, state-owned natural gas company in Trinidad and Tobago * National Grid plc, a former name of National Grid Electricity Transmission plc, the operator of the British electricity transmission system * Northrop Grumman Corporation, aerospace and defense conglomerate formed from the merger of Northrop Corporation and Grumman Corporation in 1994 * Numismatic Guaranty Corporation, coin certification company in the United States Other uses * National Gallery of Canada, art gallery founded in 1880 in Ottawa, Canada * National Geographic, documentary and reality television channel established in the United States in 2001 formerly called National Geographic Channel * Native Girls Code, US non-profit orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collinder Catalogue
In astronomy, the Collinder catalogue is a catalogue of 471 open clusters by Swedish astronomer Per Collinder. It was published in 1931 as an appendix to Collinder's paper ''On structural properties of open galactic clusters and their spatial distribution''. Catalogue objects are denoted by ''Collinder'', e.g. "Collinder 399". Dated prefixes include as ''Col + catalogue number'', or ''Cr + catalogue number'', e.g. "Cr 399". Vital statistics * The catalogue contains 471 objects: 452 open clusters, 11 globular clusters, 6 Asterism (astronomy), asterisms, 1 Stellar kinematics#Moving groups, stellar moving group, and 1 Stellar kinematics#Stellar associations, stellar association. * Objects are spread out across the entire celestial sphere. * NGC 188, Cr 8 is the northernmost Collinder object, located at a declination of +85º in the constellation Camelopardalis. * Cr 411 is the southernmost Collinder object, located at a declination of -79º in the constellation Octans. Collinder obj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caldwell Catalogue
The Caldwell catalogue is an astronomical catalogue of 109 star clusters, nebulae, and galaxies for observation by amateur astronomers. The list was compiled by Patrick Moore as a complement to the Messier catalogue. While the Messier catalogue is used by amateur astronomers as a list of deep-sky objects for observation, Moore noted that Messier's list was not compiled for that purpose and excluded many of the sky's brightest deep-sky objects, such as the Hyades, the Double Cluster ( NGC 869 and NGC 884), and the Sculptor Galaxy (NGC 253). The Messier catalogue was actually compiled as a list of known objects that might be confused with comets. Moore also observed that since Messier compiled his list from observations in Paris, it did not include bright deep-sky objects visible in the Southern Hemisphere, such as Omega Centauri, Centaurus A, the Jewel Box, and 47 Tucanae. Moore compiled a list of 109 objects to match the commonly accepted number of Messier objects (he exclud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |