|
NESS-0327
NESS-0327 is a drug used in scientific research which acts as an extremely potent and selective antagonist of the cannabinoid receptor CB1. It is much more potent an antagonist, and more selective for the CB1 receptor over CB2, than the more commonly used ligand rimonabant, with a Ki at CB1 of 350fM (i.e. 0.00035nM) and a selectivity of over 60,000x for CB1 over CB2. Independently, two other groups have described only modest nanomolar CB1 affinity for this compound (125nM and 18.4nM). Also unlike rimonabant, NESS-0327 does not appear to act as an inverse agonist In pharmacology, an inverse agonist is a drug that binds to the same receptor as an agonist but induces a pharmacological response opposite to that of the agonist. A neutral antagonist has no activity in the absence of an agonist or inverse ago ... at higher doses, instead being a purely neutral antagonist which blocks the CB1 receptor but does not produce any physiological effect of its own. See also * Discover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discovery And Development Of Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Antagonists
A cannabinoid receptor antagonist, also known simply as a cannabinoid antagonist or as an anticannabinoid, is a type of cannabinoidergic drug that binds to cannabinoid receptors (CBR) and prevents their activation by endocannabinoids. They include antagonists, inverse agonists, and antibodies of CBRs. The discovery of the endocannabinoid system led to the development of CB1 receptor antagonists. The first CBR inverse agonist, rimonabant, was described in 1994. Rimonabant blocks the CB1 receptor selectively and has been shown to decrease food intake and regulate body-weight gain. The prevalence of obesity worldwide is increasing dramatically and has a great impact on public health. The lack of efficient and well-tolerated drugs to cure obesity has led to an increased interest in research and development of CBR antagonists. Cannabidiol (CBD), a naturally occurring cannabinoid, is a non-competitive CB1/CB2 receptor antagonist. And Δ9-tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV), a naturally occur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NESS-040C5
NESS-040C5 is a potent cannabinoid agonist which was developed for the treatment of glaucoma Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that result in damage to the optic nerve (or retina) and cause vision loss. The most common type is open-angle (wide angle, chronic simple) glaucoma, in which the drainage angle for aqueous humor, fluid withi .... It has reasonable selectivity for the CB2 receptor subtype, having a CB2 affinity of 0.4nM, and 25x selectivity over the related CB1 receptor. See also * AB-FUBINACA * NESS-0327 * SR-144,528 References {{cannabinoid-stub Cannabinoids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antagonist (pharmacology)
A receptor antagonist is a type of receptor ligand or drug that blocks or dampens a biological response by binding to and blocking a receptor rather than activating it like an agonist. Antagonist drugs interfere in the natural operation of receptor proteins.Pharmacology Guide: In vitro pharmacology: concentration-response curves " '' GlaxoWellcome.'' Retrieved on December 6, 2007. They are sometimes called blockers; examples include alpha blockers, |
Cannabinoid Receptor
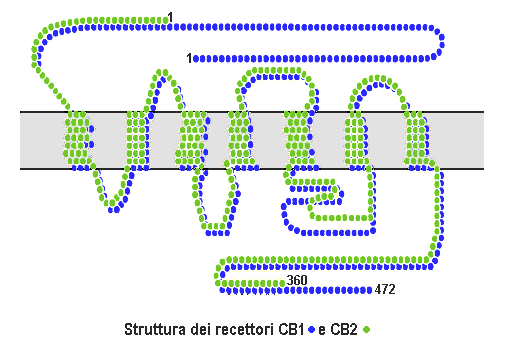
Cannabinoid receptors, located throughout the body, are part of the endocannabinoid system a class of cell membrane receptors in the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily. As is typical of G protein-coupled receptors, the cannabinoid receptors contain seven transmembrane spanning domains. Cannabinoid receptors are activated by three major groups of ligands: endocannabinoids; plant cannabinoids (such as Tetrahydrocannabinol, produced by the cannabis plant); and synthetic cannabinoids (such as HU-210). All of the endocannabinoids and phytocannabinoids (plant based cannabinoids) are lipophilic. There are two known subtypes of cannabinoid receptors, termed CB1 and CB2. The CB1 receptor is expressed mainly in the brain (central nervous system or "CNS"), but also in the lungs, liver and kidneys. The CB2 receptor is expressed mainly in the immune system, in hematopoietic cells, and in parts of the brain. The protein sequences of CB1 and CB2 receptors are about 44% similar. When ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabinoid Receptor 1
Cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1), also known as cannabinoid receptor 1, is a G protein-coupled cannabinoid receptor that in humans is encoded by the ''CNR1'' gene. The human CB1 receptor is expressed in the peripheral nervous system and central nervous system. It is activated by: endocannabinoids, a group of retrograde neurotransmitters that include anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG); plant phytocannabinoids, such as the compound THC which is an active ingredient of the psychoactive drug cannabis; and, synthetic analogs of THC. CB1 is antagonized by the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV). The primary endogenous agonist of the human CB1 receptor is anandamide. Structure The CB1 receptor shares the structure characteristic of all G-protein-coupled receptors, possessing seven transmembrane domains connected by three extracellular and three intracellular loops, an extracellular N-terminal tail, and an intracellular C-terminal tail. The receptor may exist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rimonabant
Rimonabant (also known as SR141716; trade names Acomplia, Zimulti) is an anorectic antiobesity drug that was first approved in Europe in 2006 but was withdrawn worldwide in 2008 due to serious psychiatric side effects; it was never approved in the United States. Rimonabant is an inverse agonist for the cannabinoid receptor CB1 and was the first drug approved in that class. History Rimonabant is a selective CB1 receptor blocker and was discovered and developed by Sanofi-Aventis; On 21 June 2006, the European Commission approved the sale of rimonabant in the then-25-member European Union as a prescription drug for use in conjunction with diet and exercise for patients with a body mass index (BMI) greater than 30 kg/m2, or patients with a BMI greater than 27 kg/m2 with associated risk factors, such as type 2 diabetes or dyslipidaemia. FroEMA index page/ref> It was first in its class to be approved anywhere in the world. Rimonabant was submitted to the Food and Dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissociation Constant
In chemistry, biochemistry, and pharmacology, a dissociation constant (K_D) is a specific type of equilibrium constant that measures the propensity of a larger object to separate (dissociate) reversibly into smaller components, as when a complex falls apart into its component molecules, or when a salt splits up into its component ions. The dissociation constant is the inverse of the association constant. In the special case of salts, the dissociation constant can also be called an ionization constant. For a general reaction: : A_\mathit B_\mathit \mathit A + \mathit B in which a complex \ce_x \ce_y breaks down into ''x'' A subunits and ''y'' B subunits, the dissociation constant is defined as : K_D = \frac where and ''x'' B''y''are the equilibrium concentrations of A, B, and the complex A''x'' B''y'', respectively. One reason for the popularity of the dissociation constant in biochemistry and pharmacology is that in the frequently encount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inverse Agonist
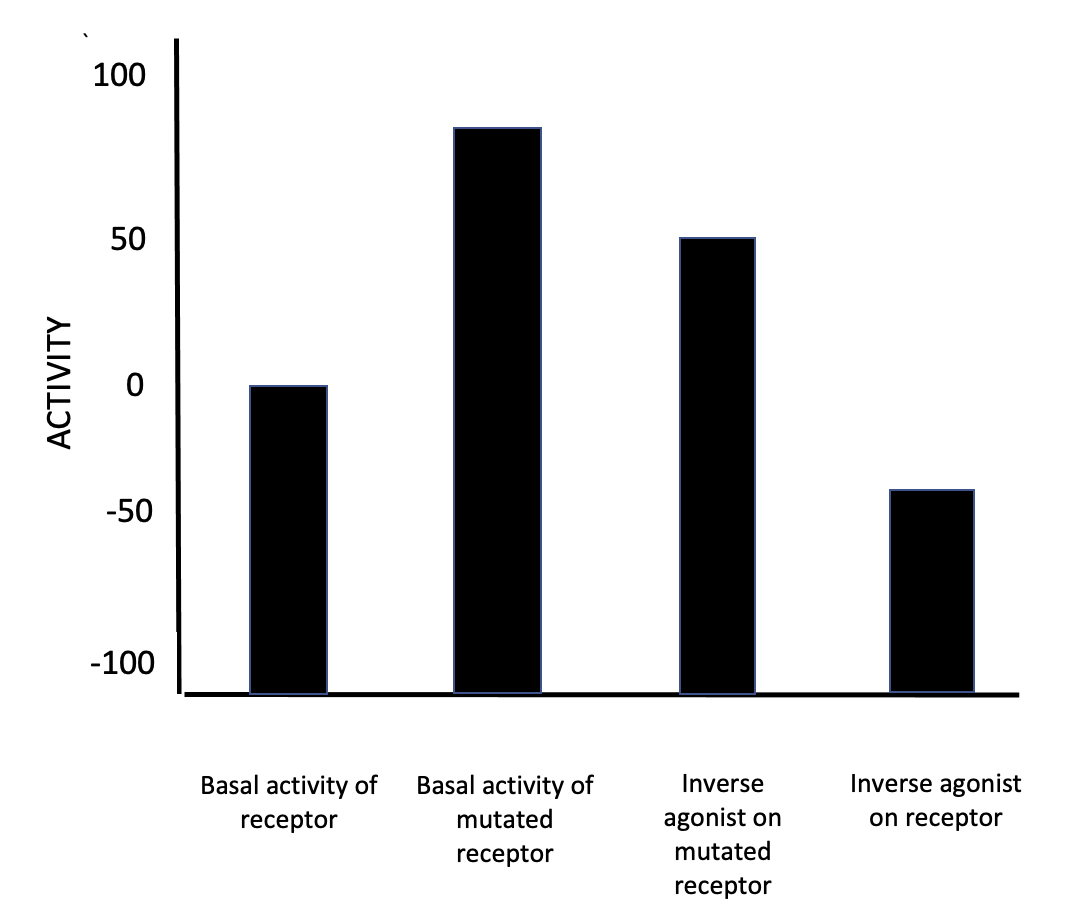
In pharmacology, an inverse agonist is a drug that binds to the same receptor as an agonist but induces a pharmacological response opposite to that of the agonist. A neutral antagonist has no activity in the absence of an agonist or inverse agonist but can block the activity of either. Inverse agonists have opposite actions to those of agonists but the effects of both of these can be blocked by antagonists. A prerequisite for an inverse agonist response is that the receptor must have a constitutive (also known as intrinsic or basal) level of activity in the absence of any ligand. An agonist increases the activity of a receptor above its basal level, whereas an inverse agonist decreases the activity below the basal level. The efficacy of a full agonist is by definition 100%, a neutral antagonist has 0% efficacy, and an inverse agonist has < 0% (i.e., negative) efficacy. Examples Receptors for which inverse agonists have been identified include the[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutral Antagonist
A receptor antagonist is a type of receptor ligand or drug that blocks or dampens a biological response by binding to and blocking a receptor rather than activating it like an agonist. Antagonist drugs interfere in the natural operation of receptor proteins.Pharmacology Guide: In vitro pharmacology: concentration-response curves " '' GlaxoWellcome.'' Retrieved on December 6, 2007. They are sometimes called blockers; examples include alpha blockers, |
Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids () are several structural classes of compounds found in the cannabis plant primarily and most animal organisms (although insects lack such receptors) or as synthetic compounds. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) (delta-9-THC), the primary intoxicating compound in cannabis. Cannabidiol (CBD) is a major constituent of temperate Cannabis plants and a minor constituent in tropical varieties. At least 113 distinct phytocannabinoids have been isolated from cannabis, although only four (i.e., THCA, CBDA, CBCA and their common precursor CBGA) have been demonstrated to have a biogenetic origin. It was reported in 2020 that phytocannabinoids can be found in other plants such as rhododendron, licorice and liverwort, and earlier in Echinacea. Phytocannabinoids are multi-ring phenolic compounds structurally related to THC, but endocannabinoids are fatty acid derivatives. Nonclassical synthetic cannabinoids (cannabimimetics) include amin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CB1 Receptor Antagonists
{{Letter-NumberCombDisambig ...
CB1 may refer to: * CB1, a postcode district in the CB postcode area * Cannabinoid receptor 1, a receptor for cannabinoids in the brain * ''Crash Bandicoot'' (video game), the first game in the ''Crash Bandicoot'' series * Manhattan Community Board 1 The Manhattan Community Board 1 is a New York City community board encompassing the neighborhoods of Battery Park City, the Financial District, the South Street Seaport, and TriBeCa in Lower Manhattan in the borough of Manhattan as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |