|
NELL2
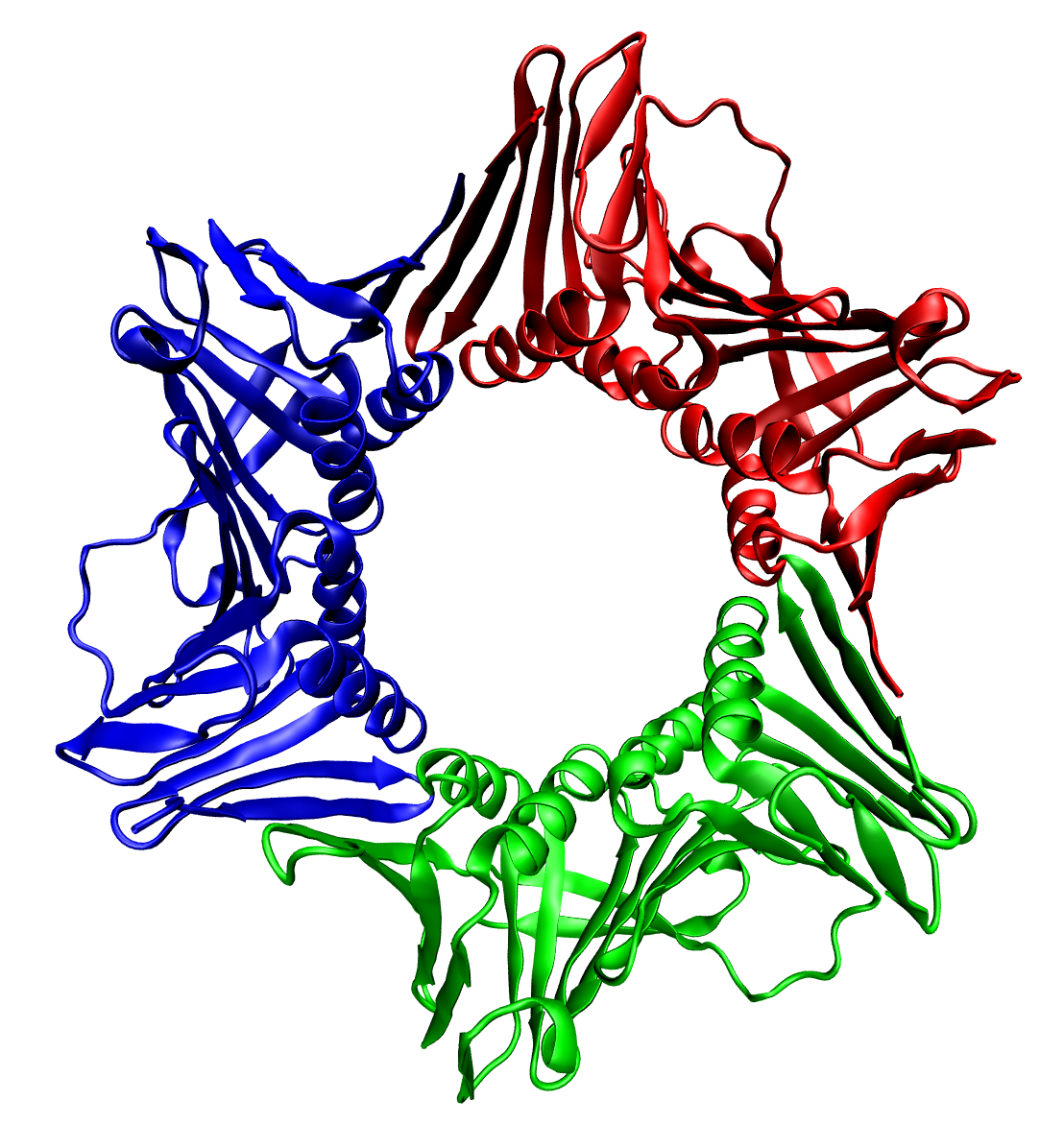
Protein kinase C-binding protein NELL2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''NELL2'' gene. This gene encodes a cytoplasmic protein that contains epidermal growth factor (EGF) -like repeats. The encoded heterotrimeric protein may be involved in cell growth regulation and differentiation. A similar protein in rodents is involved in craniosynostosis. An alternative splice variant Alternative splicing, or alternative RNA splicing, or differential splicing, is an alternative splicing process during gene expression that allows a single gene to code for multiple proteins. In this process, particular exons of a gene may be in ... has been described but its full length sequence has not been determined. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * Human proteins {{gene-12-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoplasmic
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The main components of the cytoplasm are cytosol (a gel-like substance), the organelles (the cell's internal sub-structures), and various cytoplasmic inclusions. The cytoplasm is about 80% water and is usually colorless. The submicroscopic ground cell substance or cytoplasmic matrix which remains after exclusion of the cell organelles and particles is groundplasm. It is the hyaloplasm of light microscopy, a highly complex, polyphasic system in which all resolvable cytoplasmic elements are suspended, including the larger organelles such as the ribosomes, mitochondria, the plant plastids, lipid droplets, and vacuoles. Most cellular activities take place within the cytoplasm, such as many metabolic pathways including glycolysis, and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidermal Growth Factor
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) is a protein that stimulates cell growth and differentiation by binding to its receptor, EGFR. Human EGF is 6-k Da and has 53 amino acid residues and three intramolecular disulfide bonds. EGF was originally described as a secreted peptide found in the submaxillary glands of mice and in human urine. EGF has since been found in many human tissues, including platelets, submandibular gland (submaxillary gland), and parotid gland. Initially, human EGF was known as urogastrone. Structure In humans, EGF has 53 amino acids (sequence NSDSECPLSHDGYCLHDGVCMYIEALDKYACNCVVGYIGERCQYRDLKWWELR), with a molecular mass of around 6 kDa. It contains three disulfide bridges (Cys6-Cys20, Cys14-Cys31, Cys33-Cys42). Function EGF, via binding to its cognate receptor, results in cellular proliferation, differentiation, and survival. Salivary EGF, which seems to be regulated by dietary inorganic iodine, also plays an important physiological role in the maintenance of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterotrimeric
In biochemistry, a protein trimer is a macromolecular Complex (chemistry), complex formed by three, usually covalent bond, non-covalently bound, macromolecules like proteins or nucleic acids. A homotrimer would be formed by three identical molecules. A heterotrimer would be formed by three different macromolecules. Type II Collagen is an example of homotrimeric protein. Porin (protein), Porins usually arrange themselves in membranes as trimers. Bacteriophage T4 tail fiber Multiple copies of a polypeptide encoded by a gene often can form an aggregate referred to as a multimer. When a multimer is formed from polypeptides produced by two different mutant alleles of a particular gene, the mixed multimer may exhibit greater functional activity than the unmixed multimers formed by each of the mutants alone. When a mixed multimer displays increased functionality relative to the unmixed multimers, the phenomenon is referred to as complementation (genetics), intragenic complementation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
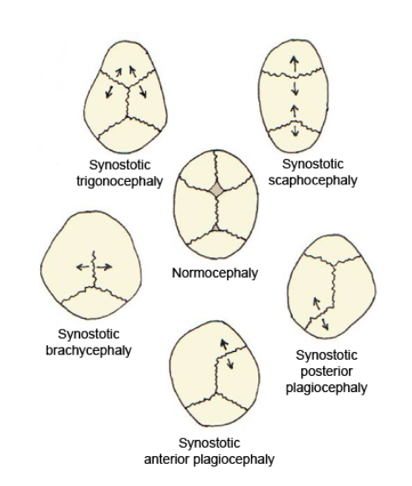
Craniosynostosis
Craniosynostosis is a condition in which one or more of the fibrous sutures in a young infant's skull prematurely fuses by turning into bone (ossification), thereby changing the growth pattern of the skull. Because the skull cannot expand perpendicular to the fused suture, it compensates by growing more in the direction parallel to the closed sutures. Sometimes the resulting growth pattern provides the necessary space for the growing brain, but results in an abnormal head shape and abnormal facial features. In cases in which the compensation does not effectively provide enough space for the growing brain, craniosynostosis results in increased intracranial pressure leading possibly to visual impairment, sleeping impairment, eating difficulties, or an impairment of mental development combined with a significant reduction in IQ. Craniosynostosis occurs in one in 2000 births. Craniosynostosis is part of a syndrome in 15% to 40% of affected patients, but it usually occurs as an isol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splice Variant
Alternative splicing, or alternative RNA splicing, or differential splicing, is an alternative splicing process during gene expression that allows a single gene to code for multiple proteins. In this process, particular exons of a gene may be included within or excluded from the final, processed messenger RNA (mRNA) produced from that gene. This means the exons are joined in different combinations, leading to different (alternative) mRNA strands. Consequently, the proteins translated from alternatively spliced mRNAs will contain differences in their amino acid sequence and, often, in their biological functions (see Figure). Biologically relevant alternative splicing occurs as a normal phenomenon in eukaryotes, where it increases the number of proteins that can be encoded by the genome. In humans, it is widely believed that ~95% of multi-exonic genes are alternatively spliced to produce functional alternative products from the same gene but many scientists believe that most of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |