|
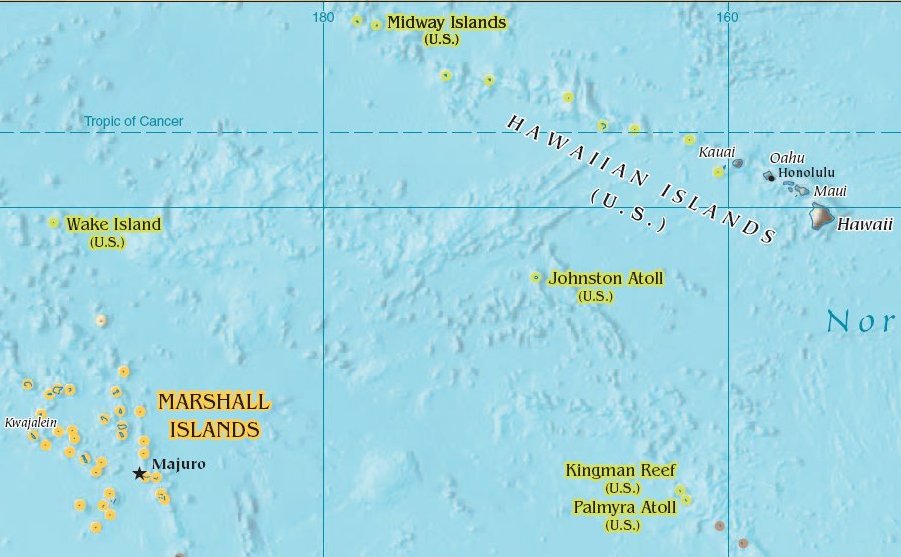
NAS Johnston Island
Johnston Island Air Force Base is a former United States Air Force base on the Johnston Atoll in the United States Minor Outlying Islands, in the Pacific Ocean several hundred kilometers southwest of Hawaii. After its closure, it briefly operated as Johnston Atoll Airport, until that also closed in 2005. History In 1935 personnel from the United States Navy's Patrol Wing Two carried out some minor construction to develop the atoll for seaplane operations. They erected some buildings and a boat landing on Sand Island and blasted coral to clear a seaplane landing. In November 1939 further work by civilian contractors commenced on Sand Island to allow the operation of one squadron of patrol planes with seaplane tender support. Part of the lagoon was dredged and the excavated material was used to make a plane parking area connected by a causeway to Sand Island. Three seaplane landings were cleared; one of them was , and the other two were cross-landings, each and dredged to a dep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johnston Atoll
Johnston Atoll is an Unincorporated territories of the United States, unincorporated territory of the United States, currently administered by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS). Johnston Atoll is a National Wildlife Refuge and part of the Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument. It is closed to public entry, and limited access for management needs is only granted by Letter of Authorization from the United States Air Force and a Special Use Permit from the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. For nearly 70 years, the isolated atoll was under the control of the United States Armed Forces, U.S. military. During that time, it was variously used as a naval refueling depot, an Johnston Island Air Force Base, airbase, a testing site for nuclear and biological weapons, a secret missile base, and a site for the storage and disposal of chemical weapons and Agent Orange. Those activities left the area environmentally contaminated, and monitoring continues. The island i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attack On Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service upon the United States against the naval base at Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Territory of Hawaii, just before 8:00a.m. (local time) on Sunday, December 7, 1941. The United States was a neutral country at the time; the attack led to its formal entry into World War II the next day. The Japanese military leadership referred to the attack as the Hawaii Operation and Operation AI, and as Operation Z during its planning. Japan intended the attack as a preventive action. Its aim was to prevent the United States Pacific Fleet from interfering with its planned military actions in Southeast Asia against overseas territories of the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, and those of the United States. Over the course of seven hours there were coordinated Japanese attacks on the US-held Philippines, Guam, and Wake Island and on the British Empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consolidated PBY Catalina
The Consolidated PBY Catalina is a flying boat and amphibious aircraft that was produced in the 1930s and 1940s. In Canadian service it was known as the Canso. It was one of the most widely used seaplanes of World War II. Catalinas served with every branch of the United States Armed Forces and in the air forces and navies of many other nations. The last military PBYs served until the 1980s. As of 2021, 86 years after its first flight, the aircraft continues to fly as a waterbomber (or airtanker) in aerial firefighting operations in some parts of the world. None remain in military service. Design and development Background The PBY was originally designed to be a patrol bomber, an aircraft with a long operational range intended to locate and attack enemy transport ships at sea in order to disrupt enemy supply lines. With a mind to a potential conflict in the Pacific Ocean, where troops would require resupply over great distances, the U.S. Navy in the 1930s invested millions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VP-11
Patrol Squadron 11 (VP-11), nicknamed ''Proud Pegasus'', was a Patrol Squadron of the U.S. Navy. The squadron was established at NAS Quonset Point, Rhode Island on 15 May 1952 and was disestablished on 2 August 1997. It was the fourth squadron to be designated VP-11, the first VP-11 was redesignated VP-54 on 1 October 1937, the second VP-11 was redesignated VP-21 on 1 February 1941 and the third VP-11 was redesignated VPB-11 on 1 October 1944. Operational history *15 May 1952: VP-11 was established at NAS Quonset Point, with a complement of 12 P4Y-2 Privateer patrol aircraft. *January–June 1953: VP-11 conducted its first deployment to Naval Station Argentia, Newfoundland. Upon return, the squadron was assigned new P2V-5 Neptunes as replacements for the WWII vintage Privateers. *November 1960–March 1961: VP-11 participated in underwater sound tests (Project Breezeway) with the Office of Naval Research from November to December 1960. The squadron was again called upon to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VP-148
VP-148 was a Patrol Squadron of the U.S. Navy. The squadron was established as Bombing Squadron 148 (VB-148) on 16 August 1943, redesignated Patrol Bombing Squadron 148 (VPB-148) on 1 October 1944, redesignated Patrol Squadron 148 (VP-148) on 15 May 1946 and disestablished on 14 June 1946. Operational history *16 August 1943 – 16 January 1944: VB-148 was established at NAS Alameda, California, as a medium bombing squadron flying the PV-1 Ventura. During its entire training phase, the squadron remained under the operational control of FAW-8. After forming, the squadron was relocated to a training facility at NAAS Vernalis, California, where squadron personnel received ground training. On 3 October, the first Venturas arrived for the flight training phase of the syllabus. Upon completion of the flight training phase, the squadron’s aircraft were flown to the Naval Ordnance Testing Station at Inyokern, California, where rocket launcher rails were installed. Training in use of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
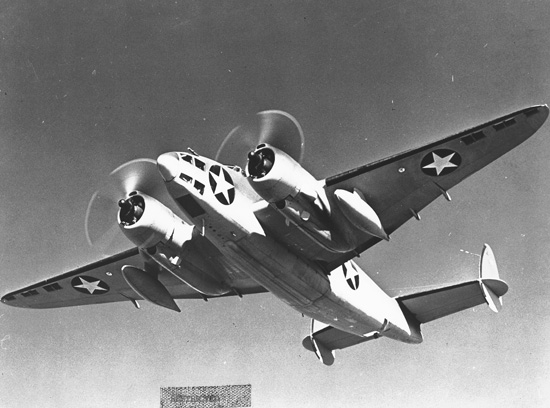
Lockheed Ventura
The Lockheed Ventura is a twin-engine medium bomber and patrol bomber of World War II. The Ventura first entered combat in Europe as a bomber with the RAF in late 1942. Designated PV-1 by the United States Navy (US Navy), it entered combat in 1943 in the Pacific. The bomber was also used by the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF), which designated it the Lockheed B-34 (''Lexington'') and B-37 as a trainer. British Commonwealth forces also used it in several guises, including antishipping and antisubmarine search and attack. The Ventura was developed from the Lockheed Model 18 Lodestar transport, as a replacement for the Lockheed Hudson bombers then in service with the Royal Air Force. Used in daylight attacks against occupied Europe, they proved to have weaknesses and were removed from bomber duty and some used for patrols by Coastal Command. After USAAF monopolization of land-based bombers was removed, the US Navy ordered a revised design which entered service as the PV-2 H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VP-142
VP-142 was a Patrol Squadron of the U.S. Navy. The squadron was established as Bombing Squadron 142 (VB-142) on 1 June 1943, redesignated Patrol Bombing Squadron 142 (VPB-142) on 1 October 1944, redesignated Patrol Squadron 142 (VP-142) on 15 May 1946 and disestablished on 14 June 1946. Operational history *1 June 1943: VB-142 was established at NAS Whidbey Island, Washington, as a medium bomber squadron flying the PV-1 Ventura. During the training period the squadron came under the operational control of FAW-6. *7–19 August 1943: VB-142 departed NAS Whidbey Island for NAS Alameda, California, where the squadron prepared its aircraft and equipment for shipment to NAS Kaneohe Bay, Hawaii. On 10 August, the squadron loaded its equipment, aircraft and personnel aboard . The squadron arrived at Naval Base Pearl Harbor on the 16th and proceeded to unload and assemble the aircraft for the short hop to NAS Kaneohe Bay, arriving there on 18 and 19 August 1943. *28 A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dictionary Of American Naval Aviation Squadrons
The ''Dictionary of American Naval Aviation Squadrons'' (''DANAS'') is a multivolume work published by Naval Historical Center of the U.S. Department of the Navy's Naval History & Heritage Command. It covers naval aviation in much the same way as the ''Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships'' (''DANFS'') covers commissioned vessels. Two volumes have been published to date: Volume 1, covering the history of attack and strike fighter squadrons, and Volume 2, covering the history of patrol squadrons. Other volumes are forthcoming. The squadron histories are quite detailed, typically including sections on lineage, insignia and nickname, chronology of significant events, home port assignments, commanding officers, aircraft assigned, major overseas deployments, airwing assignments, and unit awards received. ''DANAS'' volumes are available online and as PDF files on CD-ROM. Publication data Volume 1 (1995) includes about 140 histories and other data covering every squadron in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B-24 Liberator
The Consolidated B-24 Liberator is an American heavy bomber, designed by Consolidated Aircraft of San Diego, California. It was known within the company as the Model 32, and some initial production aircraft were laid down as export models designated as various LB-30s, in the Land Bomber design category. At its inception, the B-24 was a modern design featuring a highly efficient shoulder-mounted, high aspect ratio Davis wing. The wing gave the Liberator a high cruise speed, long range and the ability to carry a heavy bomb load. Early RAF Liberators were the first aircraft to cross the Atlantic Ocean as a matter of routine. In comparison with its contemporaries, the B-24 was relatively difficult to fly and had poor low-speed performance; it also had a lower ceiling and was less robust than the Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress. While aircrews tended to prefer the B-17, General Staff favored the B-24 and procured it in huge numbers for a wide variety of roles. At approximately 18,5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VP-22 (1943-94)
VP-22 was a Patrol Squadron of the U.S. Navy. The squadron was established as Patrol Squadron 4D-14 (VP-4D14) on 15 September 1928, redesignated Patrol Squadron 4-B (VP-4B) on 21 January 1931, redesignated Patrol Squadron 4-F (VP-4F) on 17 July 1933, redesignated Patrol Squadron 4 (VP-4) on 1 October 1937, redesignated Patrol Squadron 22 (VP-22) on 1 July 1939 and disestablished on 18 April 1942, with the squadron assets merged with VP-101. Operational history *15 September 1928: VP-4D14 established at NAS Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, with the D14 representing the 14th Naval District. The squadron began operations with six H-16 seaplanes. Primary mission of the squadron was patrol and bombing in connection with the plan of defense for the Hawaiian Islands. *20 February 1929: Mechanics from the Wright Aeronautical Corporation arrived to begin alterations on the engines of the H-16 and new T2D aircraft. *28 February 1930: The first PD-1 aircraft was received by the squadron for testing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |