|
NAPA (gene)
N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor Attachment Protein Alpha, also known as SNAP-α, is a SNAP protein that is involved in the intra-cellular trafficking and fusing of vesicles to target membranes in cells. Function The 'SNARE hypothesis' is a model explaining the process of docking and fusion of vesicles to their target membranes. According to this model, membrane proteins from the vesicle (v-SNAREs) and proteins from the target membrane (t-SNAREs) govern the specificity of vesicle targeting and docking through mutual recognition. Once the 2 classes of SNAREs bind to each other, they form a complex that recruits the general elements of the fusion apparatus, namely NSF (N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor) and SNAPs (soluble NSF-attachment proteins), to the site of membrane fusion, thereby forming the 20S fusion complex. Alpha- and gamma-SNAP are found in a wide range of tissues and act synergistically in intra-Golgi transport. The sequence of the predicted 295-amino acid human pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soluble NSF Attachment Protein
Soluble ''N''-ethylmaleimide-Sensitive Factor Attachment Proteins (SNAP, or Sec17p in yeast) are a family of cytosolic adaptor proteins involved in vesicular fusion at membranes during intracellular transport and exocytosis. SNAPs interact with proteins of the SNARE complex and NSF to play a key role in recycling the components of the fusion complex. SNAPs are involved in the priming of the vesicle fusion complex during assembly, as well as in the disassembly following a vesicle fusion event. Following membrane fusion, the tethering SNARE proteins complex disassembles in response to steric changes originating from the ATPase NSF. The energy provided by NSF is transferred throughout the SNARE complex and SNAP, allowing the proteins to untangle, and recycled for future fusion events. Mammals have three SNAP genes: α-SNAP, β-SNAP, and γ-SNAP. α- and γ-SNAP are expressed throughout the body, while β-SNAP is specific to the brain. The yeast homolog of the human SNAP is Sec17, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STX4
Syntaxin-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''STX4'' gene. Interactions STX4 has been shown to interact with: * Gelsolin, * NAPA, * RAB4A, * SNAP-25, * SNAP23, * STXBP1, * STXBP5, * Syntaxin binding protein 3, * TXLNB, * VAMP2, * VAMP3, and * Vesicle-associated membrane protein 8 Vesicle-associated membrane protein 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''VAMP8'' gene. Synaptobrevins/VAMPs, syntaxins, and the 25-kD synaptosomal-associated protein SNAP25 are the main components of a protein complex involved in the .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * {{Vesicular transport proteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ORAI1
Calcium release-activated calcium channel protein 1 is a calcium selective ion channel that in humans is encoded by the ''ORAI1'' gene. Orai channels play an important role in the activation of T-lymphocytes. The loss of function mutation of Orai1 causes severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) in humans The mammalian orai family has two additional homologs, Orai2 and Orai3. Orai proteins share no homology with any other ion channel family of any other known proteins. They have 4 transmembrane domains and form hexamers. Structure and function Orai channels are activated upon the depletion of internal calcium stores, which is called the "store-operated" or the "capacitative" mechanism. They are molecular constituents of the "calcium release activated calcium currents" ( ICRAC). Upon activation of phospholipase C by various cell surface receptors, inositol trisphosphate is formed that releases calcium from the endoplasmic reticulum. The decreased calcium concentration in the endopl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STX5
Syntaxin-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''STX5'' gene. Interactions STX5 has been shown to interact with: * BET1L, * GOSR1, * GOSR2, * NAPA, and * USO1 General vesicular transport factor p115 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''USO1'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a peripheral membrane protein which recycles between the cytosol and the Golgi apparatus during i .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-11-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STX1A
Syntaxin-1A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''STX1A'' gene. Function Synaptic vesicles store neurotransmitters that are released during calcium-regulated exocytosis. The specificity of neurotransmitter release requires the localization of both synaptic vesicles and calcium channels to the presynaptic In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target effector cell. Synapses are essential to the transmission of nervous impulses from ... active zone. Syntaxins function in this vesicle fusion process. Syntaxin-1A is a member of the syntaxin superfamily. Syntaxins are nervous system-specific proteins implicated in the docking of synaptic vesicles with the presynaptic plasma membrane. Syntaxins possess a single C-terminus, C-terminal transmembrane domain, a SNARE (protein), SNARE [Soluble NSF (N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein)-Attachment protei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SNAP23
Synaptosomal-associated protein 23 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SNAP23'' gene. Two alternative transcript variants encoding different protein isoforms have been described for this gene. Function Specificity of vesicular transport is regulated, in part, by the interaction of a vesicle-associated membrane protein termed synaptobrevin/VAMP with a target compartment membrane protein termed syntaxin. These proteins, together with SNAP25 (synaptosome-associated protein of 25 kDa), form a complex which serves as a binding site for the general membrane fusion machinery. Synaptobrevin/VAMP and syntaxin are believed to be involved in vesicular transport in most, if not all cells, while SNAP25 is present almost exclusively in the brain, suggesting that a ubiquitously expressed homolog of SNAP25 exists to facilitate transport vesicle/target membrane fusion in other tissues. SNAP23 is structurally and functionally similar to SNAP25 and binds tightly to multiple syntaxins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
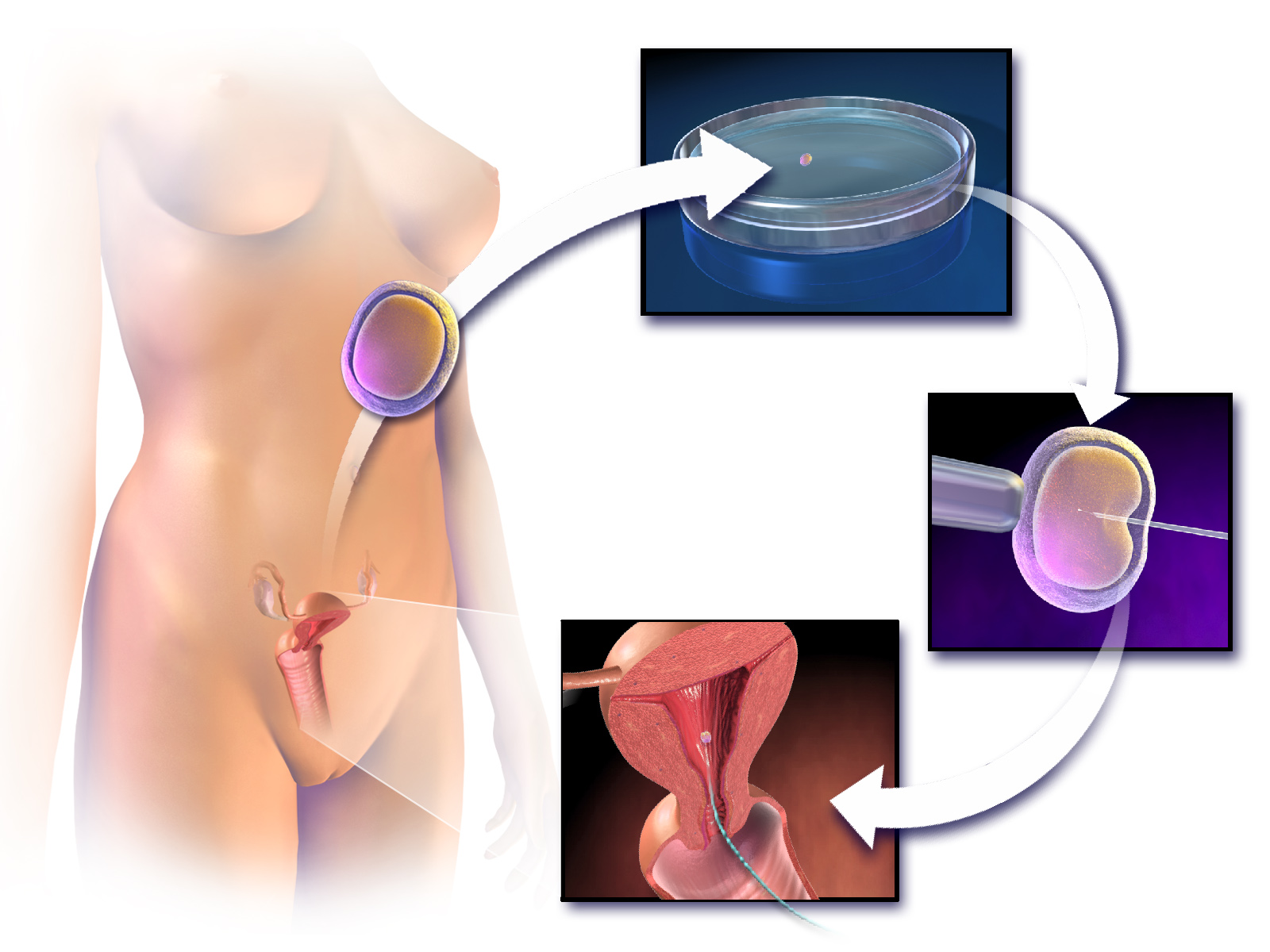
Assisted Reproductive Technology
Assisted reproductive technology (ART) includes medical procedures used primarily to address infertility. This subject involves procedures such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), cryopreservation of gametes or embryos, and/or the use of fertility medication. When used to address infertility, ART may also be referred to as fertility treatment. ART mainly belongs to the field of reproductive endocrinology and infertility. Some forms of ART may be used with regard to fertile couples for genetic purpose (see preimplantation genetic diagnosis). ART may also be used in surrogacy arrangements, although not all surrogacy arrangements involve ART. The existence of sterility will not always require ART to be the first option to consider, as there are occasions when its cause is a mild disorder that can be solved with more conventional treatments or with behaviors based on promoting health and reproductive habits. Procedures General With ART, the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection
Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI ) is an in vitro fertilization (IVF) procedure in which a single sperm cell is injected directly into the cytoplasm of an egg. This technique is used in order to prepare the gametes for the obtention of embryos that may be transferred to a maternal uterus. With this method, the acrosome reaction is skipped. There are several differences between classic IVF and ICSI. However, the steps to be followed before and after insemination are the same. In terms of insemination, ICSI needs only one sperm cell per oocyte, while IVF needs 50,000–100,000. This is because the acrosome reaction has to take place and thousands of sperm cells have to be involved in IVF. Once fertilized, the egg is transformed into a pre-embryo and it has to be transferred to the uterus to continue its development. The first human pregnancy generated by ICSI was carried out in 1991 by Gianpiero Palermo and his team. Round spermatid injection (ROSI) Round spermatid inject ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vitro Fertilization
In vitro fertilisation (IVF) is a process of fertilisation where an egg is combined with sperm in vitro ("in glass"). The process involves monitoring and stimulating an individual's ovulatory process, removing an ovum or ova (egg or eggs) from their ovaries and letting sperm fertilise them in a culture medium in a laboratory. After the fertilised egg (zygote) undergoes embryo culture for 2–6 days, it is transferred by catheter into the uterus, with the intention of establishing a successful pregnancy. IVF is a type of assisted reproductive technology used for infertility treatment, gestational surrogacy, and, in combination with pre-implantation genetic testing, avoiding transmission of genetic conditions. A fertilised egg from a donor may implant into a surrogate's uterus, and the resulting child is genetically unrelated to the surrogate. Some countries have banned or otherwise regulate the availability of IVF treatment, giving rise to fertility tourism. Restrictions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syntaxin-2
Syntaxin-2, also known as epimorphin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''STX2'' gene. The product of this gene belongs to the syntaxin/epimorphin family of proteins. The syntaxins are a large protein family implicated in the targeting and fusion of intracellular transport vesicles. The product of this gene regulates epithelial-mesenchymal interactions and epithelial cell morphogenesis and activation. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. When the N terminus is on the cytosolic face it acts as a t-SNARE involved in intracellular vesicle docking and is called Syntaxin-2. When flipped inside out, i.e. N terminus hangs out on the extracellular surface (by some nonclassical secretion pathway) it acts as a versatile morphogen and is called epimorphin. This membrane protein enjoys the double choice of another form of topological alternatives of being targeted to either apical or basolateral surface of an epithelial cell i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SNARE
SNARE proteins – " SNAP REceptor" – are a large protein family consisting of at least 24 members in yeasts, more than 60 members in mammalian cells, and some numbers in plants. The primary role of SNARE proteins is to mediate vesicle fusion – the fusion of vesicles with the target membrane; this notably mediates exocytosis, but can also mediate the fusion of vesicles with membrane-bound compartments (such as a lysosome). The best studied SNAREs are those that mediate the neurotransmitter release of synaptic vesicles in neurons. These neuronal SNAREs are the targets of the neurotoxins responsible for botulism and tetanus produced by certain bacteria. Types SNAREs can be divided into two categories: ''vesicle'' or ''v-SNAREs'', which are incorporated into the membranes of transport vesicles during budding, and ''target'' or ''t-SNAREs'', which are associated with nerve terminal membranes. Evidence suggests that t-SNAREs form stable subcomplexes which serve as guides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |