|
N100 Plan
The N100 Plan was the corporate code name for the top secret concept, engineering, and development of an entirely new motorcycle engine by Kawasaki Motorcycle Corporation, a division of Kawasaki Heavy Industries in 1966. Goal The goal of Kawasaki engineering in the N100 Plan was to create a large bore, fast motorcycle engine for entry into the American market, the largest market for motorcycles. Honda had already introduced its successful Honda CB450 in 1965 and Kawasaki desired to enter that larger bore niche. Kawasaki directive The N100 Plan called for an air-cooled standard motorcycle with an engine capacity of 500 cubic centimeters. The power output was set at no less than 60ps (equivalent to a per liter horsepower of 120ps). The performance minimum was to make a 13-second standing start 1/4 mile run (0–400 meters). Development Three cylinder development The Kawasaki engineers approached the N100 Plan in two ways. (1) Use an existing, tried and true Kawasaki A7 350 "Aveng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corporate
A corporation is an organization—usually a group of people or a company—authorized by the state to act as a single entity (a legal entity recognized by private and public law "born out of statute"; a legal person in legal context) and recognized as such in law for certain purposes. Early incorporated entities were established by charter (i.e. by an ''ad hoc'' act granted by a monarch or passed by a parliament or legislature). Most jurisdictions now allow the creation of new corporations through registration. Corporations come in many different types but are usually divided by the law of the jurisdiction where they are chartered based on two aspects: by whether they can issue stock, or by whether they are formed to make a profit. Depending on the number of owners, a corporation can be classified as ''aggregate'' (the subject of this article) or '' sole'' (a legal entity consisting of a single incorporated office occupied by a single natural person). One of the most attrac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-stroke
A two-stroke (or two-stroke cycle) engine is a type of internal combustion engine that completes a Thermodynamic power cycle, power cycle with two strokes (up and down movements) of the piston during one power cycle, this power cycle being completed in one revolution of the crankshaft. A four-stroke engine requires four strokes of the piston to complete a power cycle during two crankshaft revolutions. In a two-stroke engine, the end of the combustion stroke and the beginning of the compression stroke happen simultaneously, with the intake and exhaust (or Scavenging (automotive), scavenging) functions occurring at the same time. Two-stroke engines often have a high power-to-weight ratio, power being available in a narrow range of rotational speeds called the power band. Two-stroke engines have fewer moving parts than four-stroke engines. History The first commercial two-stroke engine involving cylinder compression is attributed to Scotland, Scottish engineer Dugald Clerk, who pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
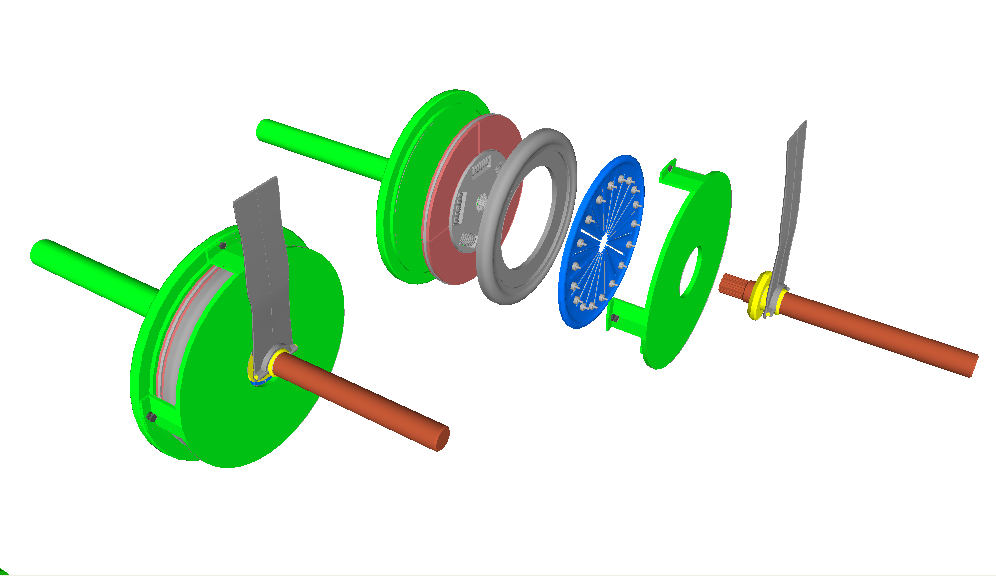
Kawasaki H2 Mach IV
The Kawasaki H2 Mach IV was a 750 cc Straight-three engine, 3-cylinder Two-stroke engine, two-stroke production motorcycle manufactured by Kawasaki motorcycles, Kawasaki. The H2 was a Kawasaki triple sold from September 1971 through 1975. A standard, factory produced H2 was able to travel a quarter mile from a standing start in 12.0 seconds. It handled better than the Mach III that preceded it. By the standards of its time, its handling was sufficient to make it the production bike to beat on the race track. Nonetheless, its tendency to pull wheelies and a less than solid feel through high speed corners led to adjustments to the design as it evolved. More than any other model, it created Kawasaki's reputation for building what motorcycle journalist Alastair Walker called, "scarily fast, good-looking, no holds barred motorcycles", and led to a further decline in the market place of the British motorcycle industry. History In September 1971 the H2 was a direct result of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kawasaki S1 Mach I
The Kawasaki Mach I (model designation S1) was a Kawasaki motorcycle made 1972 through 1975. History The Mach I was a direct result of the widespread success of the Kawasaki H1 Mach III 500 cc introduced in 1969. The Mach I's engine was a three-cylinder two-stroke with an engine displacement of 249 cc (15.1 cubic inches) which produced 32 bhp at 8,000 rpm, a power-to-weight ratio of to every 11.8 pounds. The S1 Mach I replaced the twin Kawasaki A1 Samurai 250 with its twin-cylinder, Kawasaki rotary disc valve engine which produced at 8,000 rpm. The S1 Mach I emerged nearly one year after its bigger brother, the S2 Mach II 350, and from the development success of the Kawasaki H1 Mach III The Kawasaki H1 Mach III was a two-stroke 500 cc sport bike made by Kawasaki from 1969 through to 1975. History By mid-1960s, the US had become the largest motorcycle market. American riders were demanding bikes with more horsepower and hig .... It was essential ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kawasaki S2 Mach II
The S2 Mach II is a 350 cc Kawasaki motorcycle introduced for the 1972 model year and discontinued at the end of the 1974 model year. It has a 3-cylinder two-stroke engine with a displacement Displacement may refer to: Physical sciences Mathematics and Physics * Displacement (geometry), is the difference between the final and initial position of a point trajectory (for instance, the center of mass of a moving object). The actual path ... of , and superseded the rotary disc valve twin-cylinder Kawasaki A7 Avenger. , Ride Magazine, 2012-12-4. References {{Reflist, 30em Standar ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kawasaki H1 Mach III
The Kawasaki H1 Mach III was a two-stroke 500 cc sport bike made by Kawasaki from 1969 through to 1975. History By mid-1960s, the US had become the largest motorcycle market. American riders were demanding bikes with more horsepower and higher maximum speeds. Kawasaki already had the largest-displacement Japanese machine with their 650 cc four-stroke W series, but it did not fit the niche Kawasaki was aiming for. Honda had introduced its Honda CB450 in 1965 and in 1969, the Suzuki T500 Titan/Cobra appeared. Also in development was the Yamaha XS 650. Already familiar with the Honda CB450, Kawasaki development began work on the top secret N100 Plan in 1967. The goal was to produce a motorcycle with 500 cc displacement that was able to develop 60 hp and have 13-second quarter-mile times, then considered over the achievable limit for a road bike. When announced, the H1 was critiqued in UK motorcycling press for their "own ambitious claim" of "the fastest and b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clutch
A clutch is a mechanical device that engages and disengages power transmission, especially from a drive shaft to a driven shaft. In the simplest application, clutches connect and disconnect two rotating shafts (drive shafts or line shafts). In these devices, one shaft is typically attached to an engine or other power unit (the driving member), while the other shaft (the driven member) provides output power for work. Typically the motions involved are rotary, but linear clutches also exist. In a motor vehicle, the clutch acts as a mechanical linkage between the engine and transmission, and briefly disconnects, or separates the engine from the transmission system. This disconnects the drive wheels whenever the clutch pedal is depressed, allowing the driver to smoothly change gears. In a torque-controlled drill, for instance, one shaft is driven by a motor, and the other drives a drill chuck. The clutch connects the two shafts so they may be locked together and spin at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuma, Arizona
Yuma ( coc, Yuum) is a city in and the county seat of Yuma County, Arizona, United States. The city's population was 93,064 at the 2010 census, up from the 2000 census population of 77,515. Yuma is the principal city of the Yuma, Arizona, Metropolitan Statistical Area, which consists of Yuma County. According to the United States Census Bureau, the 2020 estimated population of the Yuma MSA is 203,247. According to Guinness World Records, Yuma is the "Sunniest City on Earth," promising "sunshine and warm weather at least 91% of the year." Anywhere from 70,000 to over 85,000 out-of-state visitors make Yuma their winter residence. Yuma's weather also makes it an agricultural powerhouse, growing over 175 types of crops, the largest of which is lettuce. Yuma County provides 90% of all leafy vegetables grown from November to March in the United States. Yuma is also known for its large military population due to several military bases, including the Marine Corps Air Station. Yum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
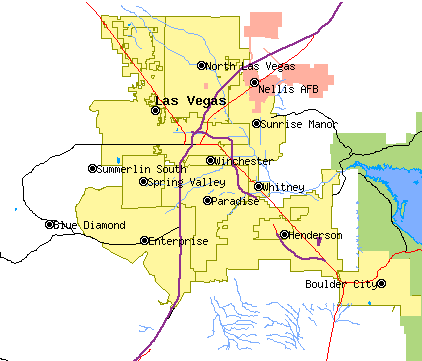
Las Vegas Valley
The Las Vegas Valley is a major metropolitan area in the Southern Nevada, southern part of the U.S. state of Nevada, and the second largest in the Southwestern United States. The state's largest urban agglomeration, the Las Vegas Metropolitan Statistical Area is coextensive since 2003 with Clark County, Nevada, Clark County, Nevada. The Valley is largely defined by the Las Vegas Valley landform, a Depression (geology), basin area surrounded by mountains to the north, south, east and west of the metropolitan area. The Valley is home to the three largest incorporated cities in Nevada: Las Vegas, Henderson, Nevada, Henderson and North Las Vegas, Nevada, North Las Vegas. Eleven unincorporated towns governed by the Clark County government are part of the Las Vegas Township and constitute the largest community in the state of Nevada. The names Las Vegas and Vegas are interchangeably used to indicate the Valley, Las Vegas Strip, the Strip, and the city, and as a brand by the Las Vegas Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Los Angeles
Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ángeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the largest city in the state of California and the second most populous city in the United States after New York City, as well as one of the world's most populous megacities. Los Angeles is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Southern California. With a population of roughly 3.9 million residents within the city limits , Los Angeles is known for its Mediterranean climate, ethnic and cultural diversity, being the home of the Hollywood film industry, and its sprawling metropolitan area. The city of Los Angeles lies in a basin in Southern California adjacent to the Pacific Ocean in the west and extending through the Santa Monica Mountains and north into the San Fernando Valley, with the city bordering the San Gabriel Valley to it's east. It covers about , and is the county seat of Los Angeles County, which is the most populous county in the United States with an estim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osaka University
, abbreviated as , is a public research university located in Osaka Prefecture, Japan. It is one of Japan's former Imperial Universities and a Designated National University listed as a "Top Type" university in the Top Global University Project. The university is often ranked among the top three public universities in Japan, along with the University of Tokyo and Kyoto University. It is ranked third overall among Japanese universities and 75th worldwide in the 2022 QS World University Rankings. Osaka University was one of the earliest modern universities in Japan at its founding in 1931. The history of the institution includes much older predecessors in Osaka such as the Kaitokudō founded in 1724 and the Tekijuku founded in 1838. In 2007, it merged with Osaka University of Foreign Studies and became the largest national university in Japan. Osaka University is one of the most productive research institutions in Japan. Numerous prominent scholars and scientists have attended or w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Straight-three Engine
A straight-three engine (also called an inline-triple or inline-three) is a three-cylinder piston engine where cylinders are arranged in a line along a common crankshaft. Less common than straight-four engines, straight-three engines have nonetheless been used in various motorcycles, cars and agricultural machinery. Design A crankshaft angle of 120 degrees is typically used by straight-three engines, since this results in an evenly spaced firing interval. Another benefit of this configuration is perfect primary balance and secondary balance, however an end-to-end rocking couple is induced because there is no symmetry in the piston velocities about the middle piston. A balance shaft is sometimes used to reduce the vibrations caused by the rocking couple. Other crankshaft angles have been used occasionally. The 1976-1981 Laverda Jota motorcycle used a 180 degree crankshaft, where the outer pistons rise and fall together and inner cylinder is offset from them by 180 degrees. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |