|
N. Wiener
Norbert Wiener (November 26, 1894 – March 18, 1964) was an American mathematician and philosopher. He was a professor of mathematics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). A child prodigy, Wiener later became an early researcher in stochastic and mathematical noise processes, contributing work relevant to electronic engineering, electronic communication, and control systems. Wiener is considered the originator of cybernetics, the science of communication as it relates to living things and machines, with implications for engineering, systems control, computer science, biology, neuroscience, philosophy, and the organization of society. Norbert Wiener is credited as being one of the first to theorize that all intelligent behavior was the result of feedback mechanisms, that could possibly be simulated by machines and was an important early step towards the development of modern artificial intelligence. Biography Youth Wiener was born in Columbia, Missouri, the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbia, Missouri
Columbia is a city in the U.S. state of Missouri. It is the county seat of Boone County and home to the University of Missouri. Founded in 1821, it is the principal city of the five-county Columbia metropolitan area. It is Missouri's fourth most-populous and fastest growing city, with an estimated 126,254 residents in 2020. As a Midwestern college town, Columbia has a reputation for progressive politics, persuasive journalism, and public art. The tripartite establishment of Stephens College (1833), the University of Missouri (1839), and Columbia College (1851), which surround the city's Downtown to the east, south, and north, has made the city a center of learning. At its center is 8th Street (also known as the Avenue of the Columns), which connects Francis Quadrangle and Jesse Hall to the Boone County Courthouse and the City Hall. Originally an agricultural town, education is now Columbia's primary economic concern, with secondary interests in the healthcare, insurance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John P
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died c. AD 30), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (lived c. AD 30), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope Joh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosopher
A philosopher is a person who practices or investigates philosophy. The term ''philosopher'' comes from the grc, φιλόσοφος, , translit=philosophos, meaning 'lover of wisdom'. The coining of the term has been attributed to the Greek thinker Pythagoras (6th century BCE).. In the Classics, classical sense, a philosopher was someone who lived according to a certain way of life, focusing upon resolving Meaning of life, existential questions about the human condition; it was not necessary that they discoursed upon Theory, theories or commented upon authors. Those who most arduously committed themselves to this lifestyle would have been considered ''philosophers''. In a modern sense, a philosopher is an intellectual who contributes to one or more branches of philosophy, such as aesthetics, ethics, epistemology, philosophy of science, logic, metaphysics, social theory, philosophy of religion, and political philosophy. A philosopher may also be someone who has worked in the hum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematician
A mathematician is someone who uses an extensive knowledge of mathematics in their work, typically to solve mathematical problems. Mathematicians are concerned with numbers, data, quantity, structure, space, models, and change. History One of the earliest known mathematicians were Thales of Miletus (c. 624–c.546 BC); he has been hailed as the first true mathematician and the first known individual to whom a mathematical discovery has been attributed. He is credited with the first use of deductive reasoning applied to geometry, by deriving four corollaries to Thales' Theorem. The number of known mathematicians grew when Pythagoras of Samos (c. 582–c. 507 BC) established the Pythagorean School, whose doctrine it was that mathematics ruled the universe and whose motto was "All is number". It was the Pythagoreans who coined the term "mathematics", and with whom the study of mathematics for its own sake begins. The first woman mathematician recorded by history was Hypati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Medal Of Science
The National Medal of Science is an honor bestowed by the President of the United States to individuals in science and engineering who have made important contributions to the advancement of knowledge in the fields of behavioral and social sciences, biology, chemistry, engineering, mathematics and physics. The twelve member presidential Committee on the National Medal of Science is responsible for selecting award recipients and is administered by the National Science Foundation (NSF). History The National Medal of Science was established on August 25, 1959, by an act of the Congress of the United States under . The medal was originally to honor scientists in the fields of the "physical, biological, mathematical, or engineering sciences". The Committee on the National Medal of Science was established on August 23, 1961, by executive order 10961 of President John F. Kennedy. On January 7, 1979, the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) passed a resolution propo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bôcher Memorial Prize
The Bôcher Memorial Prize was founded by the American Mathematical Society in 1923 in memory of Maxime Bôcher with an initial endowment of $1,450 (contributed by members of that society). It is awarded every three years (formerly every five years) for a notable research work in analysis that has appeared during the past six years. The work must be published in a recognized, peer-reviewed venue. The current award is $5,000. There have been thirty-seven prize recipients. The first woman to win the award, Laure Saint-Raymond, did so in 2020. About eighty percent of the journal articles recognized since 2000 have been from ''Annals of Mathematics'', the '' Journal of the American Mathematical Society'', ''Inventiones Mathematicae'', and ''Acta Mathematica''. Past winners * 1923 George David Birkhoff for ::''Dynamical systems with two degrees of freedom.'' Trans. Amer. Math. Soc. 18 (1917), 119-300. * 1924 Eric Temple Bell for ::''Arithmetical paraphrases. I,II.'' Trans. Amer. Mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Things Named After Norbert Wiener
{{Short description, none In mathematics, there are a large number of topics named in honor of Norbert Wiener (1894 – 1964). * Abstract Wiener space * Classical Wiener space * Paley–Wiener integral * Paley–Wiener theorem * Wiener algebra * Wiener amalgam space * Wiener chaos expansion * Wiener criterion * Wiener deconvolution * Wiener definition * Wiener entropy * Wiener equation * Wiener filter **Generalized Wiener filter * Wiener's lemma * Wiener process ** Generalized Wiener process * Wiener sausage * Wiener series * Wiener–Hopf method * Wiener–Ikehara theorem * Wiener–Khinchin theorem * Wiener–Kolmogorov prediction * Wiener–Lévy theorem * Weiner–Rosenblueth model * Wiener–Wintner theorem * Wiener's tauberian theorem In mathematical analysis, Wiener's tauberian theorem is any of several related results proved by Norbert Wiener in 1932. They provide a necessary and sufficient condition under which any function in or can be approximated by linear com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophy Of Information
The philosophy of information (PI) is a branch of philosophy that studies topics relevant to information processing, representational system and consciousness, cognitive science, computer science, information science and information technology. It includes: # the critical investigation of the conceptual nature and basic principles of information, including its dynamics, utilisation and sciences # the elaboration and application of information-theoretic and computational methodologies to philosophical problems. History The philosophy of information (PI) has evolved from the philosophy of artificial intelligence, logic of information, cybernetics, social theory, ethics and the study of language and information. Logic of information The logic of information, also known as the ''logical theory of information'', considers the information content of logical signs and expressions along the lines initially developed by Charles Sanders Peirce. Cybernetics One source for the philosophy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Revolution
The term information revolution describes current economic, social and technological trends beyond the Industrial Revolution. Many competing terms have been proposed that focus on different aspects of this societal development. The British polymath crystallographer J. D. Bernal introduced the term "''scientific and technical revolution''" in his 1939 book ''The Social Function of Science'' to describe the new role that science and technology are coming to play within society. He asserted that science is becoming a "productive force", using the Marxist Theory of Productive Forces. After some controversy, the term was taken up by authors and institutions of the then- Soviet Bloc. Their aim was to show that socialism was a safe home for the scientific and technical ("technological" for some authors) revolution, referred to by the acronym STR. The book ''Civilization at the Crossroads'', edited by the Czech philosopher Radovan Richta (1969), became a standard reference for this top ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generalized Wiener Process
In statistics, a generalized Wiener process (named after Norbert Wiener) is a continuous time random walk with drift and random jumps at every point in time. Formally: :a(x,t) dt + b(x,t) \eta \sqrt where a and b are deterministic functions, t is a continuous index for time, x is a set of exogenous variables that may change with time, dt is a differential in time, and η is a random draw from a standard normal distribution at each instant. See also *Wiener process In mathematics, the Wiener process is a real-valued continuous-time stochastic process named in honor of American mathematician Norbert Wiener for his investigations on the mathematical properties of the one-dimensional Brownian motion. It is o ... Wiener process {{statistics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolutionary Informatics
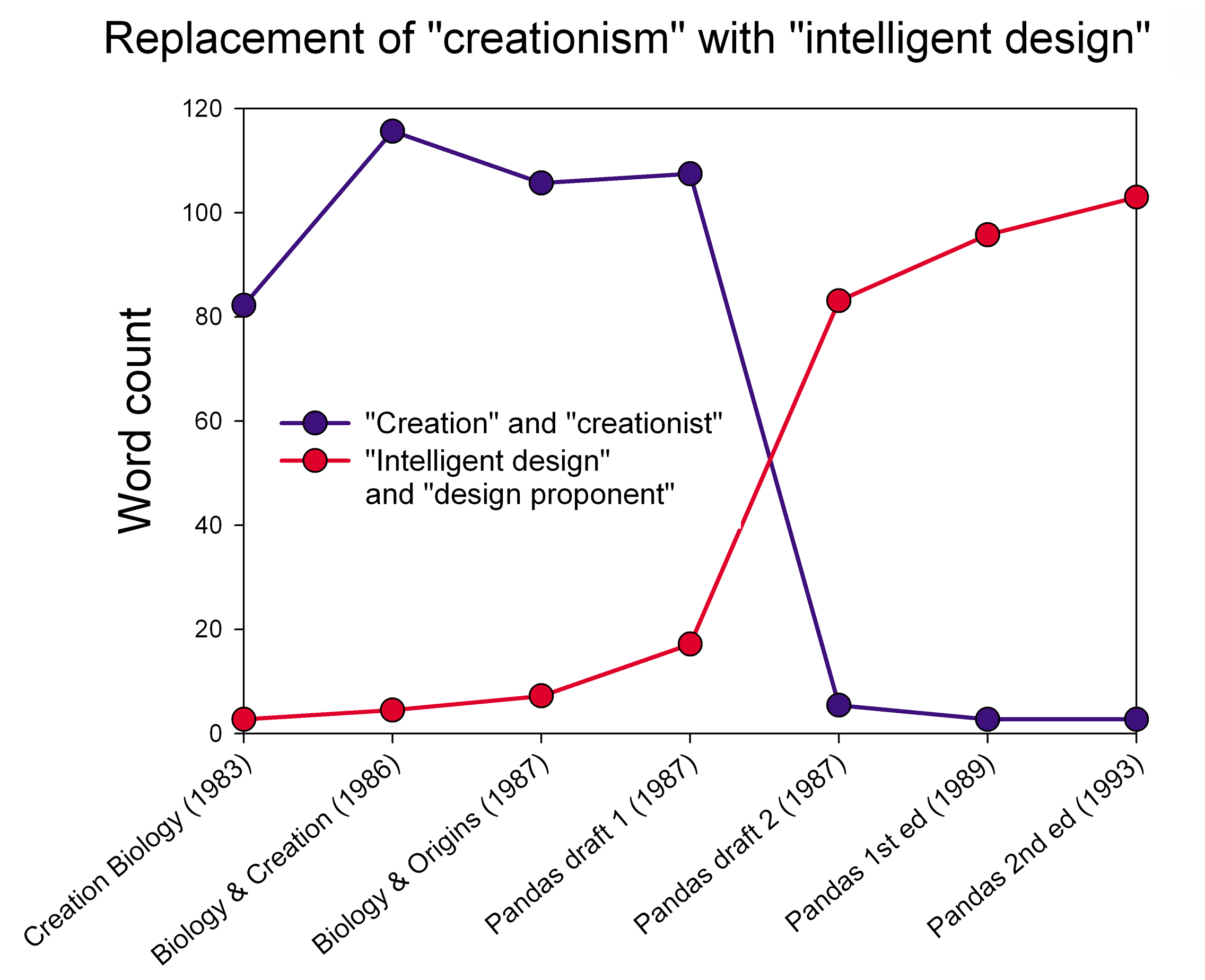
Intelligent design (ID) is a pseudoscientific argument for the existence of God, presented by its proponents as "an evidence-based scientific theory about life's origins". Numbers 2006, p. 373; " Dcaptured headlines for its bold attempt to rewrite the basic rules of science and its claim to have found indisputable evidence of a God-like being. Proponents, however, insisted it was 'not a religious-based idea, but instead an evidence-based scientific theory about life's origins – one that challenges strictly materialistic views of evolution.' Although the intellectual roots of the design argument go back centuries, its contemporary incarnation dates from the 1980s" Article available froUniversiteit Gent/ref> Proponents claim that "certain features of the universe and of living things are best explained by an intelligent cause, not an undirected process such as natural selection." * * ID is a form of creationism that lacks empirical support and offers no testable or tenable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Wiener Space
In mathematics, classical Wiener space is the collection of all continuous functions on a given domain (usually a subinterval of the real line), taking values in a metric space (usually ''n''-dimensional Euclidean space). Classical Wiener space is useful in the study of stochastic processes whose sample paths are continuous functions. It is named after the American mathematician Norbert Wiener. Definition Consider ''E'' ⊆ R''n'' and a metric space (''M'', ''d''). The classical Wiener space ''C''(''E''; ''M'') is the space of all continuous functions ''f'' : ''E'' → ''M''. I.e. for every fixed ''t'' in ''E'', :d(f(s), f(t)) \to 0 as , s - t , \to 0. In almost all applications, one takes ''E'' = , ''T'' or , +∞) and ''M'' = R''n'' for some ''n'' in N. For brevity, write ''C'' for ''C''([0, ''T'' R''n''); this is a vector space. Write ''C''0 for the linear subspace consisting only of those function (mathematics), functions that take the value ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |