|
Myxoid Tumor
A myxoid tumor is a connective tissue tumor with a "myxoid" background, composed of clear, mucoid substance. This tumoral phenotype is shared by many tumoral entities: * Myxomas ** Atrial myxoma ** Odontogenic myxoma ** Cutaneous myxoma ** Intramuscular myxoma * Myxoid hamartoma * Aggressive angiomyxoma * Myxoid leiomyoma * Chondromyxoid fibroma * Myxoid neurofibroma * Nerve sheath myxoma ( neurothekeoma) * Myxolipoma * Angiomyofibroblastoma * Myxoid leiomyosarcoma * Myxoid liposarcoma * Lipoblastoma * Myxofibrosarcoma * Myxoid cortical adenoma * Pleomorphic adenoma * Undifferentiated embryonal sarcoma * Plexiform angiomyxoid myofibroblastic tumor * Myxoid plexiform fibrohistiocytic tumor * Angiomyxolipoma (vascular myxolipoma) * Parachordoma * Acral myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcoma Acral myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcoma (AMSF), also termed myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcoma (MSF), is a rare, low-grade, soft tissue tumor that the World Health Organization ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
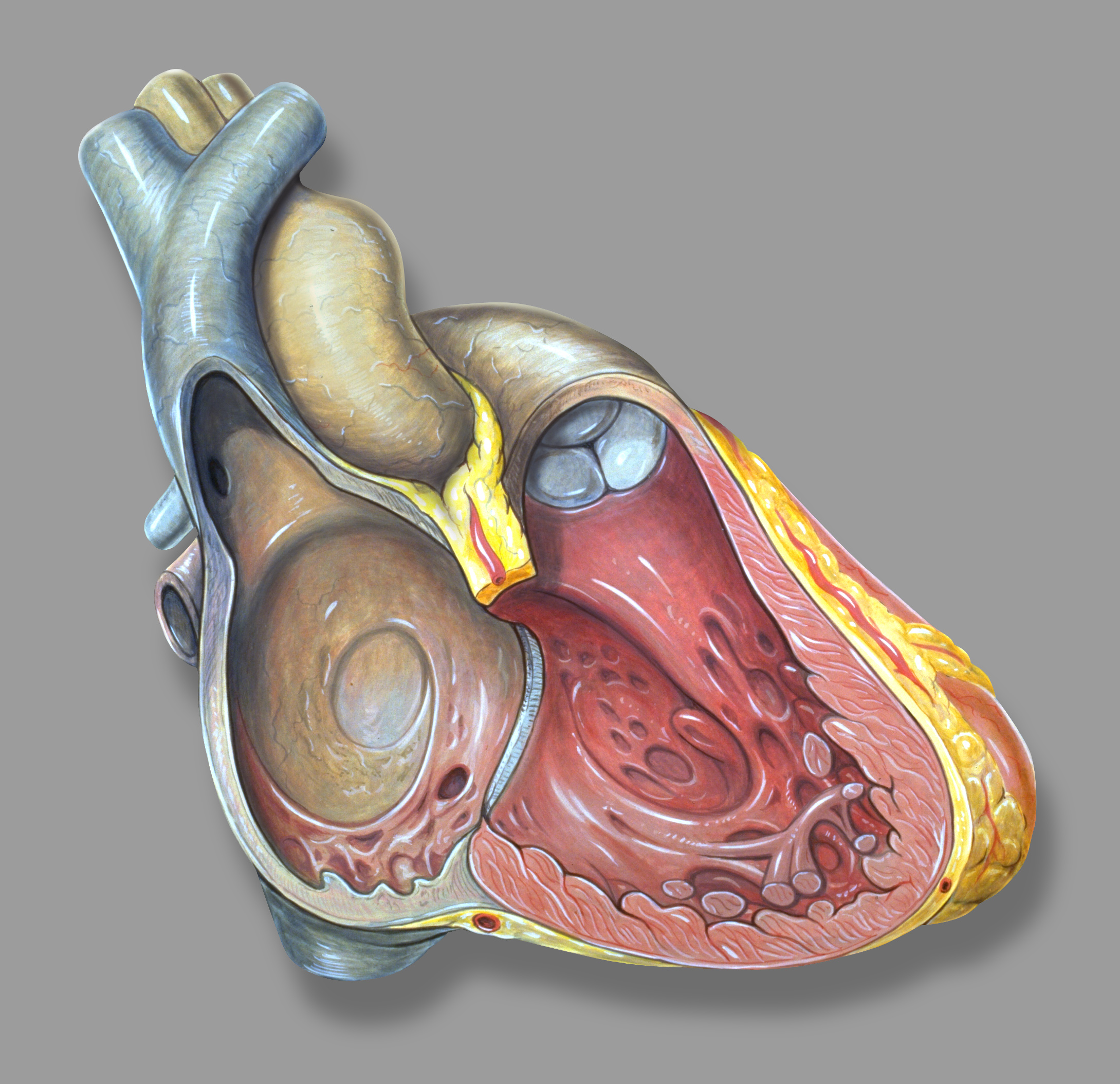
Atrial Myxoma High Mag
The atrium ( la, ātrium, , entry hall) is one of two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular valves. There are two atria in the human heart – the left atrium receives blood from the pulmonary circulation, and the right atrium receives blood from the venae cavae of the systemic circulation. During the cardiac cycle the atria receive blood while relaxed in diastole, then contract in systole to move blood to the ventricles. Each atrium is roughly cube-shaped except for an ear-shaped projection called an atrial appendage, sometimes known as an auricle. All animals with a closed circulatory system have at least one atrium. The atrium was formerly called the 'auricle'. That term is still used to describe this chamber in some other animals, such as the ''Mollusca''. They have thicker muscular walls than the atria do. Structure Humans have a four-chambered h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascular Myxolipoma
Blood vessels are the structures of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away from the tissues. Blood vessels are needed to sustain life, because all of the body's tissues rely on their functionality. There are five types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the arterioles; the capillaries, where the exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and the tissues occurs; the venules; and the veins, which carry blood from the capillaries back towards the heart. The word ''vascular'', meaning relating to the blood vessels, is derived from the Latin ''vas'', meaning vessel. Some structures – such as cartilage, the epithelium, and the lens and cornea of the eye – do not contain blood vessels and are labeled ''avascular''. Etymology * artery: late Middle English; from Latin ''ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plexiform Angiomyxoid Myofibroblastic Tumor
Plexiform angiomyxoid myofibroblastic tumor (PAMT), also called plexiform angiomyxoma, plexiform angiomyxoid tumor, or myxofibroma, is an extremely rare benign mesenchymal myxoid tumor along the gastrointestinal tract. Most of PAMTs occur in the gastric antral region, but they can be situated anywhere in the stomach. There is one recorded case of PAMT located in duodenum. Classification PAMT was first described by Takahashi et al. in 2007. Estimated frequency of PAMT is less than 1/150 compared to that of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs). The prevalence is similar in both genders and can develop at any age (7–75 years). The size of tumor ranges from 1.9 to 15.0 cm and the mean value is 6.3 cm. PAMT is considered as a benign tumor, due to its histological features such as the presence of bland tumor cells, low proliferation index, low mitotic-rate, absence of necrosis and vascular invasion and no recurrence. In one case there has been reported vascular invasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Undifferentiated Embryonal Sarcoma
Differentiation may refer to: Business * Differentiation (economics), the process of making a product different from other similar products * Product differentiation, in marketing * Differentiated service, a service that varies with the identity of the consumer or the context in which the service is used Science, technology, and mathematics Biology and medicine * Cellular differentiation, in biology * ''Differentiation'' (journal), a peer-reviewed academic journal covering cell differentiation and cell development * Developmental biology, the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop * Differentiation therapy, a cancer treatment in which malignant cells are encouraged to differentiate into more mature forms using pharmacological agents Geology * Igneous differentiation, in geology * Planetary differentiation, in planetary science and geology Social sciences * Differentiation (economics), the process of making a product different from other similar produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleomorphic Adenoma
Pleomorphic adenoma is a common benign salivary gland neoplasm characterised by neoplastic proliferation of epithelial (ductal) cells along with myoepithelial components, having a malignant potentiality. It is the most common type of salivary gland tumor and the most common tumor of the parotid gland. It derives its name from the architectural Pleomorphism (variable appearance) seen by light microscopy. It is also known as "Mixed tumor, salivary gland type", which refers to its dual origin from epithelial and myoepithelial elements as opposed to its pleomorphic appearance. Clinical presentation The tumor is usually solitary and presents as a slow growing, painless, firm single nodular mass. Isolated nodules are generally outgrowths of the main nodule rather than a multinodular presentation. It is usually mobile unless found in the palate and can cause atrophy of the mandibular ramus when located in the parotid gland. When found in the parotid tail, it may present as an eversio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myxofibrosarcoma
Myxofibrosarcoma (MFS), although a rare type of tumor, is one of the most common soft tissue sarcomas, i.e. cancerous tumors, that develop in the soft tissues of elderly individuals. Initially considered to be a type of histiocytoma termed fibrous histiocytoma or myxoid variant of malignant fibrous histiocytoma, Angervall et al. termed this tumor myxofibrosarcoma in 1977. In 2020, the World Health Organization reclassified MFS as a separate and distinct tumor in the category of malignant fibroblastic and myofibroblastic tumors. MFS tumors are often treated by surgical resection. However, these tumors have high recurrence rates at the sites of their resections. Local recurrences followed by surgical resections may be repeated multiple times but during these cycles MFS tumors often progress from a lower grade to a higher more aggressive grade, metastasize, and become life-threatening. An uncommon variant of the MFS tumors termed epithelioid myxofibrosarcoma is even more likely to fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipoblastoma
Lipoblastoma is a type of rare, subcutaneous, benign, fatty tumor, found in infants, and children, more common in males with tendency of local recurrence. Local recurrence can happen in up to 80% of incompletely resected tumours. Therefore, complete surgical resection is required to prevent recurrence. It arises from embyronic white fat that is rapidly enlarging. Most common locations are at the trunk and extremities. Types include: * Benign lipoblastomatosis, a tumor, also known as an embryonic lipoma, which usually occurs in children under three years old. This is the tumor of brown fat cells. * Myxoid lipoblastoma, a cutaneous condition characterized by excess mucin Specimen Macroscopic Grossly, it has a pale yellow, myxoid cut surface with small cystic foci. Microscopic It has lobules consists of immature adipose tissue separated by fibrous septa and lipoblasts at different stages of maturation, without atypia or mitosis. Plexiform capillary network and mature adipose tiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |