|
Myrothamnaceae
''Myrothamnus'' is a genus of flowering plants, consisting of two species of small xerophytic shrubs, in the southern parts of tropical Africa and in Madagascar. ''Myrothamnus'' is recognized as the only genus in the family Myrothamnaceae. Myrothamnaceae was included in order Hamamelidales in the Cronquist system. Molecular systematic studies have suggested that ''Myrothamnus'' is not closely related to Hamamelidaceae nor any other family included in that order, but rather is closely related to ''Gunnera''. In the APG II system (2003) the genus is assigned to family Gunneraceae or to the optionally recognized segregate family Myrothamnaceae. In the APG III system (2009) and APG IV system (2016) the narrower circumscription is preferred, and these two families are considered distinct Species Species of ''Myrothamnus'' are dioecious shrubs. # ''Myrothamnus flabellifolius'' Welw. - Angola, Southern Africa, Zimbabwe # ''Myrothamnus moschata ''Myrothamnus moschata'' is a plant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myrothamnus Flabellifolius Myrothamanaceae
''Myrothamnus'' is a genus of flowering plants, consisting of two species of small xerophytic shrubs, in the southern parts of tropical Africa and in Madagascar. ''Myrothamnus'' is recognized as the only genus in the family Myrothamnaceae. Myrothamnaceae was included in order Hamamelidales in the Cronquist system. Molecular systematic studies have suggested that ''Myrothamnus'' is not closely related to Hamamelidaceae nor any other family included in that order, but rather is closely related to ''Gunnera''. In the APG II system (2003) the genus is assigned to family Gunneraceae or to the optionally recognized segregate family Myrothamnaceae. In the APG III system (2009) and APG IV system (2016) the narrower circumscription is preferred, and these two families are considered distinct Species Species of ''Myrothamnus'' are dioecious shrubs. # ''Myrothamnus flabellifolius'' Welw. - Angola, Southern Africa, Zimbabwe # ''Myrothamnus moschata ''Myrothamnus moschata'' is a plant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gunnerales
The Gunnerales are an order of flowering plants. In the APG III system (2009) and APG IV system (2016) it contains two genera: ''Gunnera'' (in family Gunneraceae) and ''Myrothamnus'' (in family Myrothamnaceae). In the Cronquist system (1981), the Gunneraceae were in the Haloragales and Myrothamnaceae in the Hamamelidales. DNA analysis was definitive, but the grouping of the two families was a surprise, given their very dissimilar morphologies. In Cronquist's old system (1981, 1988), and Takhtajan's (1997), the Gunneraceae were in the Rosidae, and the Myrothamnaceae were in the Hamamelids. In modern classification systems such as APG III and APG IV this order was the first to derive from the core eudicots. Description Both families contain ellagic acid. Phloem cells contain a large number of plastids and the leaves have dented borders. The plants are dioecious, have small flowers without perianth, and the stigma is at least weakly secretory. Gunnerales characters shared with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gunnera
''Gunnera'' is the sole genus of herbaceous flowering plants in the family Gunneraceae, which contains 63 species. Some species in this genus, namely those in the subgenus ''Panke'', have extremely large leaves. Species in the genus are variously native to Latin America, Australia, New Zealand, Papuasia, Hawaii, insular Southeast Asia, Africa, and Madagascar. The stalks of many species are edible. Taxonomy ''Gunnera'' is the only genus in the family Gunneraceae. The APG II system, of 2003, also recognizes this family and assigns it to the order Gunnerales in the clade core eudicots. The family then consisted of one or two genera, ''Gunnera'' and, optionally, ''Myrothamnus'', the latter optionally segregated as a separate family, Myrothamnaceae. This represents a change from the APG system, of 1998, which firmly recognized two separate families, unplaced as to order. The APG III system and APG IV system recognizes the family Gunneraceae and places ''Myrothamnus'' in Myrothamna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamamelidales
Hamamelidales is an order of flowering plants formerly accepted in a number of systems of plant taxonomy, including the Cronquist system published in 1968 and 1988. The order is not currently accepted in the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group III system of plant taxonomy, the most widely accepted system as molecular systematic studies have suggested that these families are not closely related to each other. The APG II system (2003) assigns them to several different orders: Hamamelidaceae and Cercidiphyllaceae to Saxifragales, Eupteleaceae to Ranunculales, Platanaceae to Proteales, and Myrothamnaceae to Gunnerales. Additional studies of the chloroplast genome have since confirmed that the families moved into the Saxigragales are closely related. The Cronquist system (1981) included the order in subclass Hamamelidae with the circumscription: * order Hamamelidales *: family Hamamelidaceae, now in order Saxifragales *: family Cercidiphyllaceae, now in order Saxifragales *: family Eupteleace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cronquist System
The Cronquist system is a taxonomic classification system of flowering plants. It was developed by Arthur Cronquist in a series of monographs and texts, including ''The Evolution and Classification of Flowering Plants'' (1968; 2nd edition, 1988) and ''An Integrated System of Classification of Flowering Plants'' (1981) (''see'' Bibliography). Cronquist's system places flowering plants into two broad classes, Magnoliopsida ( dicotyledons) and Liliopsida (monocotyledons). Within these classes, related orders are grouped into subclasses. While the scheme was widely used, in either the original form or in adapted versions, many botanists now use the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group classification for the orders and families of flowering plants, first developed in 1998. The system as laid out in Cronquist's ''An Integrated System of Classification of Flowering Plants'' (1981) counts 64 orders and 321 families in class Magnoliopsida and 19 orders and 65 families in class Liliopsida. ''The Evo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
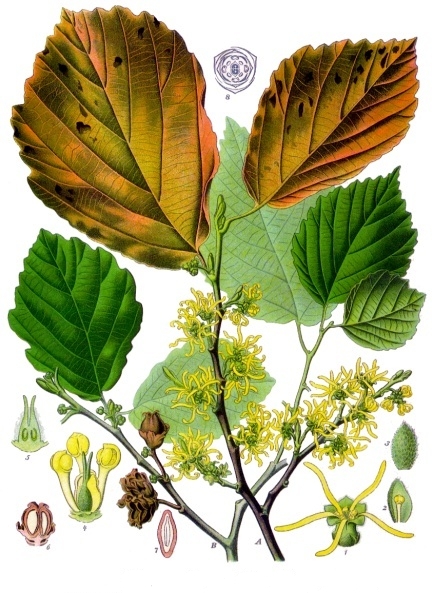
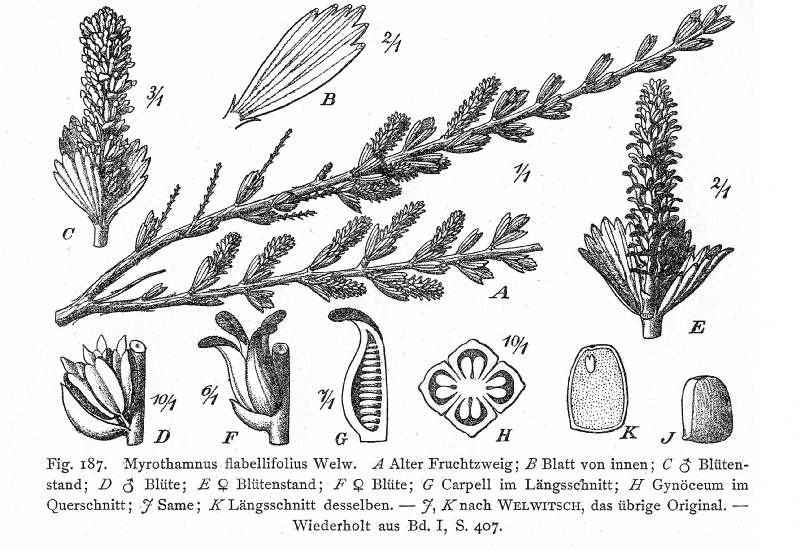
Myrothamnus Flabellifolius
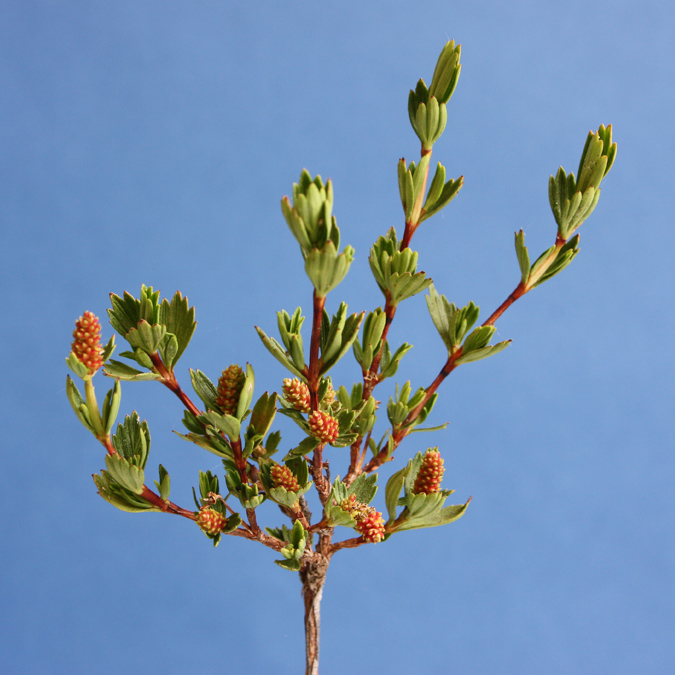
''Myrothamnus flabellifolius'' is a plant species in the genus ''Myrothamnus'' found in Southern Africa. It is also called the resurrection plant, for the speed with which apparently dead leaves revive when the rains come. (see Poikilohydry Poikilohydry is the lack of ability (structural or functional mechanism) to maintain and/or regulate water content to achieve homeostasis In biology, homeostasis (British English, British also homoeostasis) Help:IPA/English, (/hɒmɪə(ʊ)ˈste ...) 3,4,5-Tri-O-galloylquinic acid is a tannin found in ''M. flabellifolius''. Description ''Myrothamnus flabellifolius'' is a small resinous shoot that reaches 200 - 1200mm in height. It can be found in either single bundles or colonies. These colonies are commonly found to have extensive root systems. During the winter these plants are known to lose all of their leaves. It will stay in this state for approximately half of the year. After first rainfall, it can grow back its leaves very quickl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myrothamnus Moschata
''Myrothamnus moschata'' is a plant species in the genus ''Myrothamnus ''Myrothamnus'' is a genus of flowering plants, consisting of two species of small xerophytic shrubs, in the southern parts of tropical Africa and in Madagascar. ''Myrothamnus'' is recognized as the only genus in the family Myrothamnaceae. My ...''. References Gunnerales {{Eudicot-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
APG IV System
The APG IV system of flowering plant classification is the fourth version of a modern, mostly molecular-based, system of plant taxonomy for flowering plants (angiosperms) being developed by the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group (APG). It was published in 2016, seven years after its predecessor the APG III system was published in 2009, and 18 years after the first APG system was published in 1998. In 2009, a linear arrangement of the system was published separately; the APG IV paper includes such an arrangement, cross-referenced to the 2009 one. Compared to the APG III system, the APG IV system recognizes five new orders (Boraginales, Dilleniales, Icacinales, Metteniusales and Vahliales), along with some new families, making a total of 64 angiosperm orders and 416 families. In general, the authors describe their philosophy as "conservative", based on making changes from APG III only where "a well-supported need" has been demonstrated. This has sometimes resulted in placements that a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
APG III System
The APG III system of flowering plant classification is the third version of a modern, mostly molecular-based, system of plant taxonomy being developed by the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group (APG). Published in 2009, it was superseded in 2016 by a further revision, the APG IV system. Along with the publication outlining the new system, there were two accompanying publications in the same issue of the Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society: * The first, by Chase & Reveal, was a formal phylogenetic classification of all land plants (embryophytes), compatible with the APG III classification. As the APG have chosen to eschew ranks above order, this paper was meant to fit the system into the existing Linnaean hierarchy for those that prefer such a classification. The result was that all land plants were placed in the class Equisetopsida, which was then divided into 16 subclasses and a multitude of superorders. * The second, by Haston ''et al.'', was a linear sequence of families followi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eudicot Genera
The eudicots, Eudicotidae, or eudicotyledons are a clade of flowering plants mainly characterized by having two seed leaves upon germination. The term derives from Dicotyledons. Traditionally they were called tricolpates or non-magnoliid dicots by previous authors. The botanical terms were introduced in 1991 by evolutionary botanist James A. Doyle and paleobotanist Carol L. Hotton to emphasize the later evolutionary divergence of tricolpate dicots from earlier, less specialized, dicots. Numerous familiar plants are eudicots, including many common food plants, trees, and ornamentals. Some common and familiar eudicots include sunflower, dandelion, forget-me-not, cabbage, apple, buttercup, maple, and macadamia. Most leafy trees of midlatitudes also belong to eudicots, with notable exceptions being magnolias and tulip trees which belong to magnoliids, and ''Ginkgo biloba'', which is not an angiosperm. Description The close relationships among flowering plants with tricolpate pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botanical Journal Of The Linnean Society
The ''Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society'' is a scientific journal publishing original papers relating to the taxonomy of all plant groups and fungi, including anatomy, biosystematics, cytology, ecology, ethnobotany, electron microscopy, morphogenesis, palaeobotany, palynology and phytochemistry.Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society The journal is published by the and is available in both print and searchable online formats. Like the '' |