|
Myelin Gene Regulatory Factor
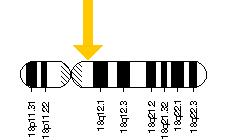
Myelin regulatory factorMyRF, also known as myelin gene regulatory factor (MRF), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MYRF'' gene. Orthologs Myelin regulatory factor is encoded by the ''Myrf/GM98'' gene in mice and by the ''MYRF'' gene in humans. The family of MyRF-like-proteins also contains the orthologues pqn-47 from ''C. elegans'' and MYRFA from ''Dictyostelium''. All orthologs have a DNA-binding domain of high homology to the ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' protein Ndt80 (a p53-like transcription factor) and therefore likely act as a transcription factor. Function MyRF is a transcription factor that promotes the expression of many genes important in the production of myelin. It is therefore of critical importance in the development and maintenance of myelin sheaths. The expression of MYRF is specific to mature, myelinating oligodendrocytes in the CNS. It has been shown to be critical for the maintenance of myelin by these cells. Following ablation of MYRF ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ablation
Ablation ( la, ablatio – removal) is removal or destruction of something from an object by vaporization, chipping, erosion, erosive processes or by other means. Examples of ablative materials are described below, and include spacecraft material for ascent and atmospheric reentry, ice and snow in glaciology, biological tissues in medicine and passive fire protection materials. Artificial intelligence In artificial intelligence (AI), especially machine learning, Ablation (artificial intelligence), ablation is the removal of a component of an AI system. The term is by analogy with biology: removal of components of an organism. Biology Biological ablation is the removal of a biological structure or functionality. Genetic ablation is another term for gene silencing, in which gene expression is abolished through the alteration or deletion of genetic sequence information. In cell ablation, individual cells in a population or culture are destroyed or removed. Both can be used as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NPC1
Niemann-Pick disease, type C1 (NPC1) is a disease of a membrane protein that mediates intracellular cholesterol trafficking in mammals. In humans the protein is encoded by the ''NPC1'' gene (chromosome location 18q11). Function NPC1 was identified as the gene that when mutated, results in Niemann-Pick disease, type C. Niemann-Pick disease, type C is a rare neurovisceral lipid storage disorder resulting from autosomal recessively inherited loss-of-function mutations in either NPC1 or NPC2. This disrupts intracellular lipid transport, leading to the accumulation of lipid products in the late endosomes and lysosomes. Approximately 95% of NPC patients are found to have mutations in the NPC1 gene. NPC1 encodes a putative integral membrane protein containing sequence motifs consistent with a role in intracellular transport of cholesterol and sphingosine to post-lysosomal destinations. Clinical significance Obesity Mutations in the NPC1 gene have been strongly linked with ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligodendrocyte
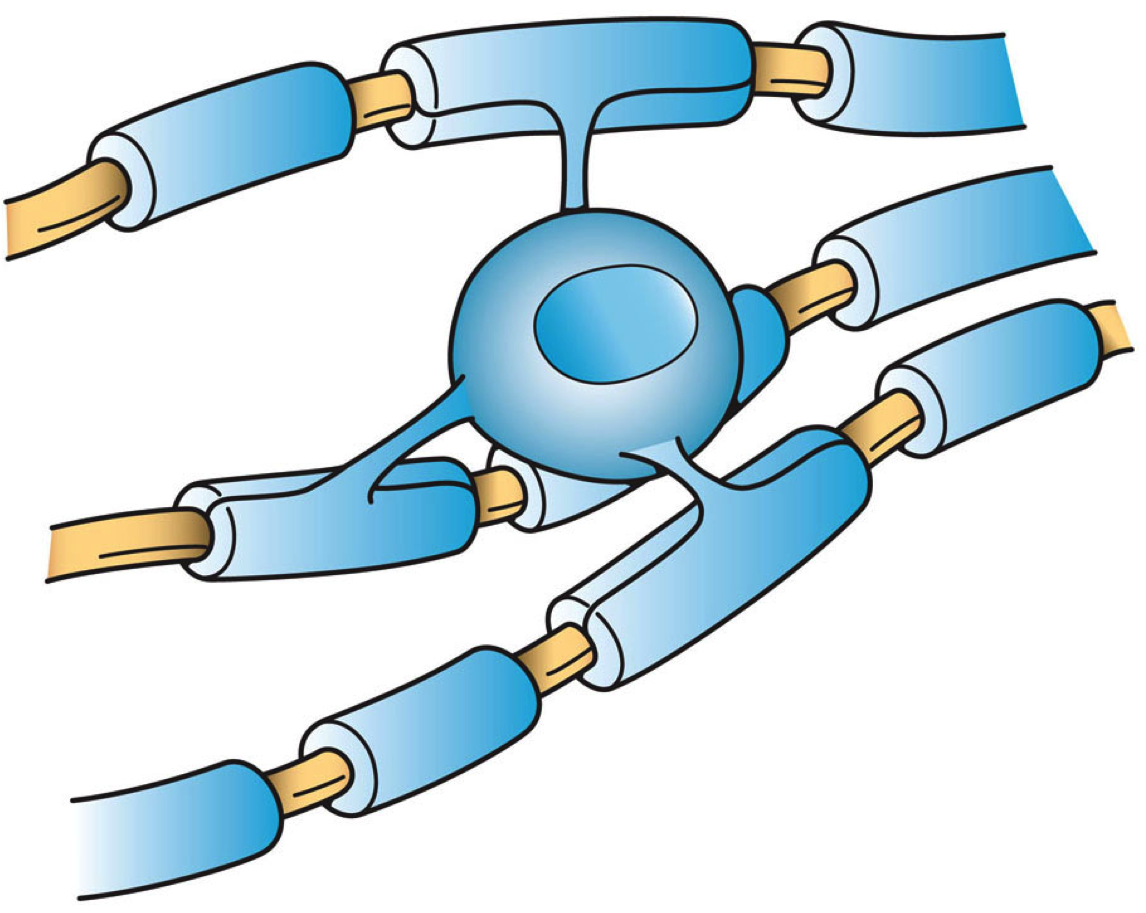
Oligodendrocytes (), or oligodendroglia, are a type of neuroglia whose main functions are to provide support and insulation to axons in the central nervous system of jawed vertebrates, equivalent to the function performed by Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system. Oligodendrocytes do this by creating the myelin sheath. A single oligodendrocyte can extend its processes to 50 axons, wrapping approximately 1 μm of myelin sheath around each axon; Schwann cells, on the other hand, can wrap around only one axon. Each oligodendrocyte forms one segment of myelin for several adjacent axons. Oligodendrocytes are found only in the central nervous system, which comprises the brain and spinal cord. These cells were originally thought to have been produced in the ventral neural tube; however, research now shows oligodendrocytes originate from the ventral ventricular zone of the embryonic spinal cord and possibly have some concentrations in the forebrain. They are the last cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myelin Sheath
Myelin is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's "wires") to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) are passed along the axon. The myelinated axon can be likened to an electrical wire (the axon) with insulating material (myelin) around it. However, unlike the plastic covering on an electrical wire, myelin does not form a single long sheath over the entire length of the axon. Rather, myelin sheaths the nerve in segments: in general, each axon is encased with multiple long myelinated sections with short gaps in between called nodes of Ranvier. Myelin is formed in the central nervous system (CNS; brain, spinal cord and optic nerve) by glial cells called oligodendrocytes and in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) by glial cells called Schwann cells. In the CNS, axons carry electrical signals from one nerve cell body to another. In the PNS, axons carry signals to muscles and glands or from sensor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple (cerebral) sclerosis (MS), also known as encephalomyelitis disseminata or disseminated sclerosis, is the most common demyelinating disease, in which the insulating covers of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord are damaged. This damage disrupts the ability of parts of the nervous system to transmit signals, resulting in a range of signs and symptoms, including physical, mental, and sometimes psychiatric problems. Specific symptoms can include double vision, blindness in one eye, muscle weakness, and trouble with sensation or coordination. MS takes several forms, with new symptoms either occurring in isolated attacks (relapsing forms) or building up over time (progressive forms). In the relapsing forms of MS, between attacks, symptoms may disappear completely, although some permanent neurological problems often remain, especially as the disease advances. While the cause is unclear, the underlying mechanism is thought to be either destruction by the immune system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein
Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) is a glycoprotein believed to be important in the myelination of nerves in the central nervous system (CNS). In humans this protein is encoded by the ''MOG'' gene. It is speculated to serve as a necessary "adhesion molecule" to provide structural integrity to the myelin sheath and is known to develop late on the oligodendrocyte. Molecular function While the primary molecular function of MOG is not yet known, its likely role with the myelin sheath is either in sheath "completion and/or maintenance". More specifically, MOG is speculated to be "necessary" as an "adhesion molecule" on the myelin sheath of the CNS to provide the structural integrity of the myelin sheath.Berger, T., Innsbruck Medical University Dept. of Neurology interviewed by S. Gillooly, Nov. 24, 2008." MOG's cDNA coding region in humans have been shown to be "highly homologous" to rats, mice, and bovine, and hence highly conserved. This suggests "an important biologica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myelin-associated Glycoprotein
Myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG, Siglec-4) is a type 1 transmembrane protein glycoprotein localized in periaxonal Schwann cell and oligodendrocyte membranes, where it plays a role in glial-axonal interactions. MAG is a member of the SIGLEC family of proteins and is a functional ligand of the NOGO-66 receptor, NgR. MAG is believed to be involved in myelination during nerve regeneration in the PNS and is vital for the long-term survival of the myelinated axons following myelinogenesis. In the CNS MAG is one of three main myelin-associated inhibitors of axonal regeneration after injury, making it an important protein for future research on neurogenesis in the CNS. Structure MAG is a 100 kDA glycoprotein. Uncleaved MAG is a complete transmembrane form, which acts as a signaling and adhesion molecule. MAG can also act as a signaling molecule as a soluble protein after it has been proteolytically shed. This form of the protein is called dMAG. Adhesion MAG has an extend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myelin Basic Protein
Myelin basic protein (MBP) is a protein believed to be important in the process of myelination of nerves in the nervous system. The myelin sheath is a multi-layered membrane, unique to the nervous system, that functions as an insulator to greatly increase the velocity of axonal impulse conduction. MBP maintains the correct structure of myelin, interacting with the lipids in the myelin membrane. MBP was initially sequenced in 1971 after isolation from bovine myelin membranes. MBP knockout mice called shiverer mice were subsequently developed and characterized in the early 1980s. ''Shiverer'' mice exhibit decreased amounts of CNS myelination and a progressive disorder characterized by tremors, seizures, and early death. The human gene for MBP is on chromosome 18; the protein localizes to the CNS and to various cells of the hematopoietic lineage. The pool of MBP in the central nervous system is very diverse, with several splice variants being expressed and a large number of pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteolipid Protein 1
Proteolipid protein 1 (PLP1) is a form of myelin proteolipid protein (PLP). Mutations in ''PLP1'' are associated with Pelizaeus–Merzbacher disease. It is a 4 transmembrane domain protein which is proposed to bind other copies of itself on the extracellular side of the membrane. In a myelin sheath, as the layers of myelin wraps come together, PLP will bind itself and tightly hold the cellular membranes together. This gene encodes a transmembrane proteolipid protein that is the predominant myelin protein present in the central nervous system (CNS). The encoded protein functions in myelination. This protein may play a role in the compaction, stabilization, and maintenance of myelin sheaths, as well as in oligodendrocyte development and axonal survival. Mutations associated with this gene cause X-linked Pelizaeus–Merzbacher disease and spastic paraplegia type 2. Two transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been identified for this gene. In melanocytic cells PLP1 gene e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the rostral (nose end) to caudal (tail end) axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain (precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets). The rest of this article exclusively discusses the vertebrate central nervous system, which is radically distinct from all other animals. Overview In vertebrates, the brain and spinal cord are both enclosed in the meninges. The meninges provide a barrier to chemicals dissolv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |