|
Mutase
A mutase is an enzyme of the isomerase class that catalyzes the movement of a functional group from one position to another within the same molecule. In other words, mutases catalyze intramolecular group transfers. Examples of mutases include ''bisphosphoglycerate mutase'', which appears in red blood cells and ''phosphoglycerate mutase'', which is an enzyme integral to glycolysis. In glycolysis, it changes 3-phosphoglycerate to 2-phosphoglycerate by moving a single phosphate group within a single molecule. See also * Phosphoglucomutase * Methylmalonyl-CoA mutase * Phosphoglycerate mutase :''This enzyme is not to be confused with Bisphosphoglycerate mutase which catalyzes the conversion of 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate.'' Phosphoglycerate mutase (PGM) is any enzyme that catalyzes step 8 of glycolysis - ... References {{Enzyme-stub Isomerases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylmalonyl-CoA Mutase
Methylmalonyl-CoA mutase (, MCM), mitochondrial, also known as methylmalonyl-CoA isomerase, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MUT'' gene. This vitamin B12-dependent enzyme catalyzes the isomerization of methylmalonyl-CoA to succinyl-CoA in humans. Mutations in ''MUT'' gene may lead to various types of methylmalonic aciduria. MCM was first identified in rat liver and sheep kidney in 1955. In its latent form, it is 750 amino acids in length. Upon entry to the mitochondria, the 32 amino acid mitochondrial leader sequence at the N-terminus of the protein is cleaved, forming the fully processed monomer. The monomers then associate into homodimers, and bind AdoCbl (one for each monomer active site) to form the final, active holoenzyme form. Structure Gene The ''MUT'' gene lies on the chromosome location of 6p12.3 and consists of 13 exons, spanning over 35kb. Protein The mature enzyme is a homodimer with the N-terminal CoA binding domain and the C- terminal cobalam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
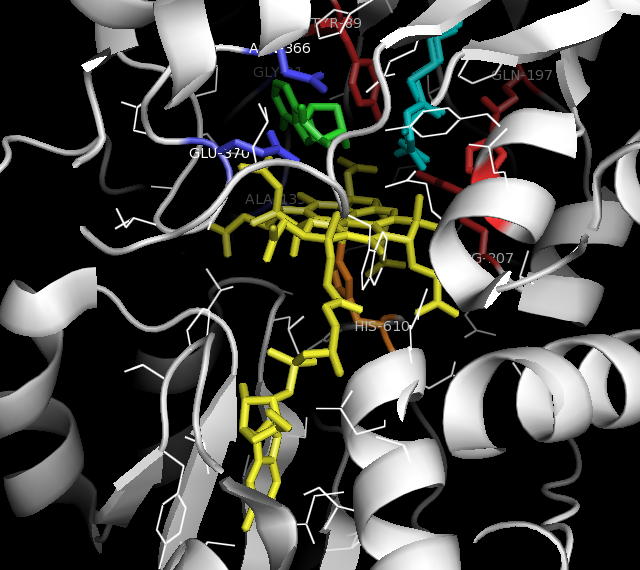
Phosphoglycerate Mutase
:''This enzyme is not to be confused with Bisphosphoglycerate mutase which catalyzes the conversion of 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate.'' Phosphoglycerate mutase (PGM) is any enzyme that catalyzes step 8 of glycolysis - the internal transfer of a phosphate group from C-3 to C-2 which results in the conversion of 3-phosphoglycerate (3PG) to 2-phosphoglycerate (2PG) through a 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate intermediate. These enzymes are categorized into the two distinct classes of either cofactor-dependent (dPGM) or cofactor-independent (iPGM). The dPGM enzyme () is composed of approximately 250 amino acids and is found in all vertebrates as well as in some invertebrates, fungi, and bacteria. The iPGM () class is found in all plants and algae as well as in some invertebrate, fungi, and Gram-positive bacteria. This class of PGM enzyme shares the same superfamily as alkaline phosphatase. Mechanism PGM is an isomerase enzyme, effectively transferring a phosph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphoglycerate Mutase
:''This enzyme is not to be confused with Bisphosphoglycerate mutase which catalyzes the conversion of 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate.'' Phosphoglycerate mutase (PGM) is any enzyme that catalyzes step 8 of glycolysis - the internal transfer of a phosphate group from C-3 to C-2 which results in the conversion of 3-phosphoglycerate (3PG) to 2-phosphoglycerate (2PG) through a 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate intermediate. These enzymes are categorized into the two distinct classes of either cofactor-dependent (dPGM) or cofactor-independent (iPGM). The dPGM enzyme () is composed of approximately 250 amino acids and is found in all vertebrates as well as in some invertebrates, fungi, and bacteria. The iPGM () class is found in all plants and algae as well as in some invertebrate, fungi, and Gram-positive bacteria. This class of PGM enzyme shares the same superfamily as alkaline phosphatase. Mechanism PGM is an isomerase enzyme, effectively transferring a phosph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphoglucomutase
Phosphoglucomutase () is an enzyme that transfers a phosphate group on an α-D-glucose monomer from the 1 to the 6 position in the forward direction or the 6 to the 1 position in the reverse direction. More precisely, it facilitates the interconversion of glucose 1-phosphate and glucose 6-phosphate. Biological Function Role in glycogenolysis After glycogen phosphorylase catalyzes the phosphorolytic cleavage of a glucosyl residue from the glycogen polymer, the freed glucose has a phosphate group on its 1-carbon. This glucose 1-phosphate molecule is not itself a useful metabolic intermediate, but phosphoglucomutase catalyzes the conversion of this glucose 1-phosphate to glucose 6-phosphate (see below for the mechanism of this reaction). Glucose 6-phosphate’s metabolic fate depends on the needs of the cell at the time it is generated. If the cell is low on energy, then glucose 6-phosphate will travel down the glycolytic pathway, eventually yielding two molecules of adenosine trip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isomerase
Isomerases are a general class of enzymes that convert a molecule from one isomer to another. Isomerases facilitate intramolecular rearrangements in which bonds are broken and formed. The general form of such a reaction is as follows: A–B → B–A There is only one substrate yielding one product. This product has the same molecular formula as the substrate but differs in bond connectivity or spatial arrangement. Isomerases catalyze reactions across many biological processes, such as in glycolysis and carbohydrate metabolism. Isomerization Isomerases catalyze changes within one molecule. They convert one isomer to another, meaning that the end product has the same molecular formula but a different physical structure. Isomers themselves exist in many varieties but can generally be classified as structural isomers or stereoisomers. Structural isomers have a different ordering of bonds and/or different bond connectivity from one another, as in the case of hexane and it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bisphosphoglycerate Mutase
Bisphosphoglycerate mutase (, BPGM) is an enzyme unique to erythrocytes and placental cells. It is responsible for the catalytic synthesis of 2,3-Bisphosphoglycerate (2,3-BPG) from 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate. BPGM also has a mutase and a phosphatase function, but these are much less active, in contrast to its glycolytic cousin, phosphoglycerate mutase (PGM), which favors these two functions, but can also catalyze the synthesis of 2,3-BPG to a lesser extent. Tissue distribution Because the main function of bisphosphoglycerate mutase is the synthesis of 2,3-BPG, this enzyme is found only in erythrocytes and placental cells. In glycolysis, converting 1,3-BPG to 2,3-BPG would be very inefficient, as it just adds another unnecessary step. Since the main role of 2,3-BPG is to shift the equilibrium of hemoglobin toward the deoxy-state, its production is really only useful in the cells which contain hemoglobin- erythrocytes and placental cells. Function 1,3-BPG is formed as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose () into pyruvate (). The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH). Glycolysis is a sequence of ten reactions catalyzed by enzymes. Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that does not require oxygen (In anaerobic conditions pyruvate is converted to lactic acid). The wide occurrence of glycolysis in other species indicates that it is an ancient metabolic pathway. Indeed, the reactions that make up glycolysis and its parallel pathway, the pentose phosphate pathway, occur in the oxygen-free conditions of the Archean oceans, also in the absence of enzymes, catalyzed by metal. In most organisms, glycolysis occurs in the liquid part of cells, the cytosol. The most common type of glycolysis is the ''Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas (EMP) pathway'', which was discovered by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |