|
Multiscopy
A 3D display is multiscopic if it projects more than two images out into the world, unlike conventional 3D stereoscopy, which simulates a 3D scene by displaying only two different views of it, each visible to only one of the viewer's eyes. Multiscopic displays can represent the subject as viewed from a series of locations, and allow each image to be visible only from a range of eye locations narrower than the average human interocular distance of 63 mm. As a result, not only does each eye see a different image, but different pairs of images are seen from different viewing locations. This allows the observer to view the 3D subject from different angles as they move their head, simulating the real-world depth cue of motion parallax. It also reduces or eliminates the complication of pseudoscopic viewing zones typical of "no glasses" 3D displays that use only two images, making it possible for several randomly located observers to all see the subject in correct 3D at the same time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Volumetric Display
A volumetric display device is a display device that forms a visual representation of an object in Three-dimensional space, three physical dimensions, as opposed to the planar image of traditional screens that simulate depth through a number of different visual effects. One definition offered by pioneers in the field is that volumetric displays create 3D imagery via the emission, scattering, or relaying of illumination from well-defined regions in (x,y,z) space. A true volumetric display produces in the observer a visual experience of a material object in three-dimensional space, even though no such object is present. The perceived object displays characteristics similar to an actual material object by allowing the observer to view it from any direction, to focus a camera on a specific detail, and to see perspective – meaning that the parts of the image closer to the viewer appear larger than those further away. Volumetric 3D displays are a type of autostereoscopic display, in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Stereoscopy
Stereoscopy, also called stereoscopics or stereo imaging, is a technique for creating or enhancing the depth perception, illusion of depth in an image by means of stereopsis for binocular vision. The word ''stereoscopy'' derives . Any stereoscopic image is called a stereogram. Originally, stereogram referred to a pair of stereo images which could be viewed using a stereoscope. Most stereoscopic methods present a pair of two-dimensional images to the viewer. The left image is presented to the left eye and the right image is presented to the right eye. When viewed, the human brain perceives the images as a single 3D view, giving the viewer the perception of Three-dimensional space, 3D depth. However, the 3D effect lacks proper focal depth, which gives rise to the Vergence-accommodation conflict. Stereoscopy is distinguished from other types of 3d display#3D displays, 3D displays that display an image in Three-dimensional space, three full dimensions, allowing the observer to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Motion Parallax
Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different lines of sight and is measured by the angle or half-angle of inclination between those two lines. Due to foreshortening, nearby objects show a larger parallax than farther objects, so parallax can be used to determine distances. To measure large distances, such as the distance of a planet or a star from Earth, astronomers use the principle of parallax. Here, the term ''parallax'' is the semi-angle of inclination between two sight-lines to the star, as observed when Earth is on opposite sides of the Sun in its orbit. These distances form the lowest rung of what is called "the cosmic distance ladder", the first in a succession of methods by which astronomers determine the distances to celestial objects, serving as a basis for other distance measurements in astronomy forming the higher rungs of the ladder. Because parallax is weak if the triangle formed with an object under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pseudoscopic Vision
A pseudoscope is a binocular optical instrument that reverses depth perception. It is used to study human stereoscopic perception. Objects viewed through it appear inside out, for example: a box on a floor would appear as a box-shaped hole in the floor. It typically uses sets of optical prisms, or periscopically arranged mirrors to swap the view of the left eye with that of the right eye. Purpose In the 1800s Charles Wheatstone coined the name from the Greek ψευδίς σκοπειν – 'false view'. The device was used to explore his theory of stereo vision. Basically, pseudoscopic vision is three-dimensional vision in reverse. For example, in aerial photography, swimming pools appear to look like buildings and buildings appear to look like swimming pools. In red and green plotters like the Kelsh and Multiplex this is achieved by reversing the lenses on the 3D glasses. The images will be reverse order. The right image will be viewed through the left eye, and the left image wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Herbert E
Herbert may refer to: People * Herbert (musician), a pseudonym of Matthew Herbert * Herbert (given name) * Herbert (surname) Places Antarctica * Herbert Mountains, Coats Land * Herbert Sound, Graham Land Australia * Herbert, Northern Territory, a rural locality * Herbert, South Australia. former government town * Division of Herbert, an electoral district in Queensland * Herbert River, a river in Queensland * County of Herbert, a cadastral unit in South Australia Canada * Herbert, Saskatchewan, Canada, a town * Herbert Road, St. Albert, Canada New Zealand * Herbert, New Zealand, a town * Mount Herbert (New Zealand) United States * Herbert, Illinois, an unincorporated community * Herbert, Michigan, a former settlement * Herbert Creek, a stream in South Dakota * Herbert Island, Alaska Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities * Herbert (Disney character) * Herbert Pocket, a character in the Charles Dickens novel ''Great Expectations'' * Herbert West, ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Stereoscopic
Stereoscopy, also called stereoscopics or stereo imaging, is a technique for creating or enhancing the illusion of depth in an image by means of stereopsis for binocular vision. The word ''stereoscopy'' derives . Any stereoscopic image is called a stereogram. Originally, stereogram referred to a pair of stereo images which could be viewed using a stereoscope. Most stereoscopic methods present a pair of two-dimensional images to the viewer. The left image is presented to the left eye and the right image is presented to the right eye. When viewed, the human brain perceives the images as a single 3D view, giving the viewer the perception of 3D depth. However, the 3D effect lacks proper focal depth, which gives rise to the Vergence-accommodation conflict. Stereoscopy is distinguished from other types of 3D displays that display an image in three full dimensions, allowing the observer to increase information about the 3-dimensional objects being displayed by head and eye m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Parallax
Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different sightline, lines of sight and is measured by the angle or half-angle of inclination between those two lines. Due to perspective (graphical), foreshortening, nearby objects show a larger parallax than farther objects, so parallax can be used to determine distances. To measure large distances, such as the distance of a planet or a star from Earth, astronomers use the principle of parallax. Here, the term ''Stellar parallax, parallax'' is the semi-angle of inclination between two sight-lines to the star, as observed when Earth is on opposite sides of the Sun in its orbit. These distances form the lowest rung of what is called "the cosmic distance ladder", the first in a succession of methods by which astronomers determine the distances to celestial objects, serving as a basis for other distance measurements in astronomy forming the higher rungs of the ladder. Because parallax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Parallax Barriers
A parallax barrier is a device placed in front of an image source, such as a liquid crystal display, to allow it to show a stereoscopic or multiscopic image without the need for the viewer to wear 3D glasses. Placed in front of the normal LCD, it consists of an opaque layer with a series of precisely spaced slits, allowing each eye to see a different set of pixels, so creating a sense of depth through parallax in an effect similar to what lenticular printing produces for printed products and lenticular lenses for other displays. A disadvantage of the method in its simplest form is that the viewer must be positioned in a well-defined spot to experience the 3D effect. However, recent versions of this technology have addressed this issue by using face-tracking to adjust the relative positions of the pixels and barrier slits according to the location of the user's eyes, allowing the user to experience the 3D from a wide range of positions. Another disadvantage is that the horizontal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
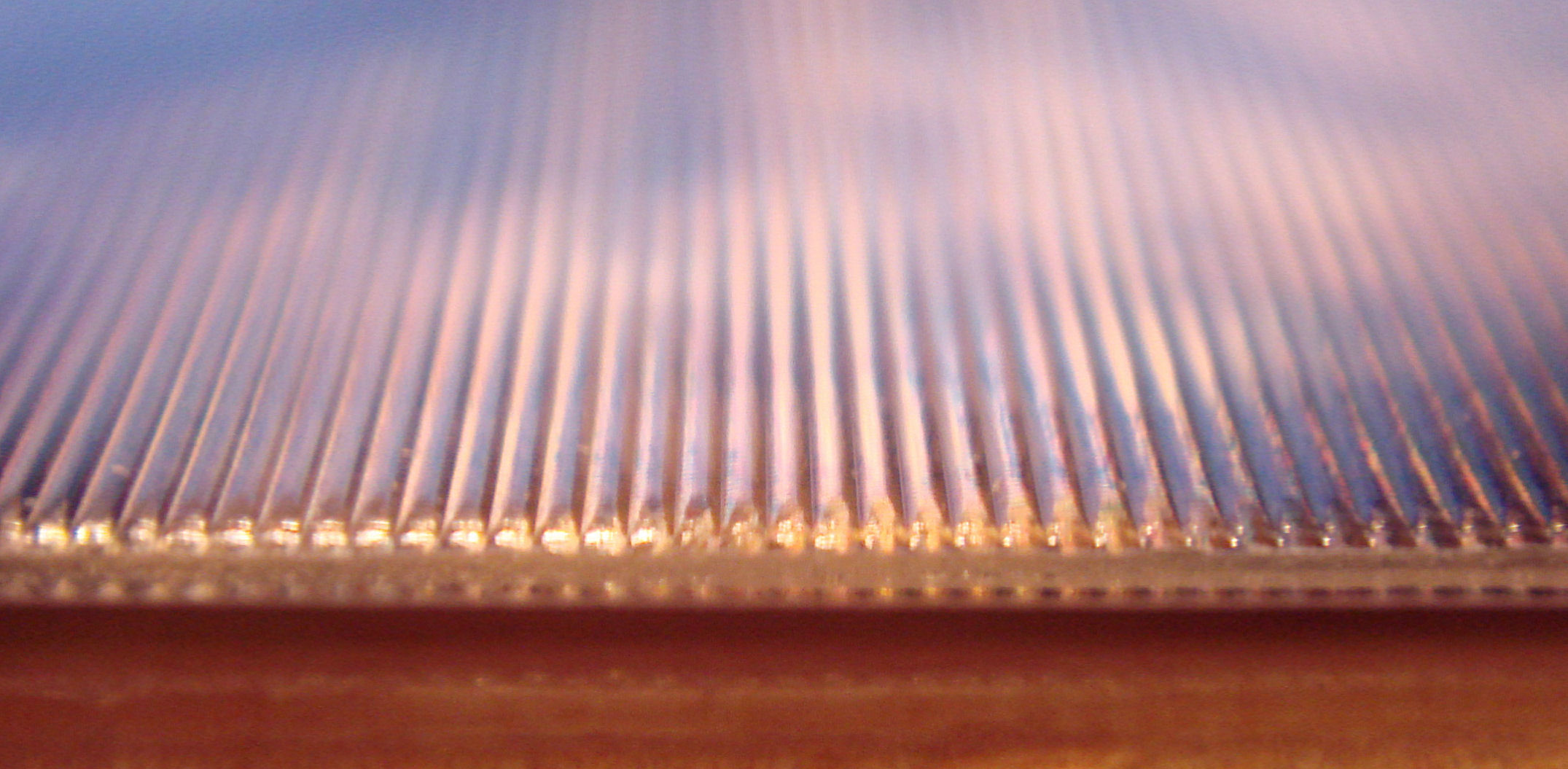
Lenticular Printing
Lenticular printing is a technology in which lenticular lenses (a technology also used for 3D displays) are used to produce printed images with an Depth perception, illusion of depth, or the ability to change or move as they are viewed from different angles. Examples include flip and animation effects such as winking eyes, and modern advertising graphics whose messages change depending on the viewing angle. It can be used to create frames of animation, for a motion effect; offsetting the various layers at different increments, for a Stereoscopy, 3D effect; or simply to show sets of alternative images that appear to transform into each other. Colloquial terms for lenticular prints include "flickers", "winkies", "wiggle pictures", and "tilt cards". The trademarks ''Vari-Vue'' and ''Magic Motion'' are often used for lenticular pictures, without regard to the actual manufacturer. Process Lenticular printing is a multi-step process that consists of creating a lenticular image fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cylindrical Lens
A cylindrical lens is a lens (optics), lens which Focus (optics), focuses light into a line instead of a point as a Lens (optics), spherical lens would. The curved face or faces of a cylindrical lens are sections of a Cylinder (geometry), cylinder, and focus the image passing through it into a line parallel to intersection of the surface of the lens and a plane tangent to it along the cylinder's axis. The lens converges or diverges the image in the direction perpendicular to this line, and leaves it unaltered in the direction parallel to its cylinder's axis (in the tangent plane). A toric lens combines the effect of a cylindrical lens with that of an ordinary spherical lens. If a thin cylindrical rod is placed on a ruled white paper with the axis of the rod making an angle θ with the ruled lines, the lines will appear broken and tilted at some angl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Integral Imaging
Integral imaging is a three-dimensional imaging technique that captures and reproduces a light field by using a two-dimensional array of microlenses (or lenslets), sometimes called a fly's-eye lens, normally without the aid of a larger overall Objective (optics), objective or viewing lens. In capture mode, in which a film or detector is coupled to the microlens array, each microlens allows an image of the subject as seen from the viewpoint of that lens's location to be acquired. In reproduction mode, in which an object or source array is coupled to the microlens array, each microlens allows each observing eye to see only the area of the associated micro-image containing the portion of the subject that would have been visible through that space from that eye's location. The optical geometry can perhaps be visualized more easily by substituting pinholes for the microlenses, as has actually been done for some demonstrations and special applications. A display using integral imaging is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lenslet
A lenslet is literally a small lens. The fact that distinguishes it from a small lens is that it is part of a lenslet array. A lenslet array consists of a set of lenslets in the same plane. Each lenslet normally has the same focal length. Lenslets have many uses. One of the key applications for lenslets is in integral imaging Integral imaging is a three-dimensional imaging technique that captures and reproduces a light field by using a two-dimensional array of microlenses (or lenslets), sometimes called a fly's-eye lens, normally without the aid of a larger overall Obje ... and light field displays. Lenslets are commonly found in Shack–Hartmann wavefront sensors and beam homogenization optics for projection systems. References Lenses {{optics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |