|
Much Ado About Nothing (opera)
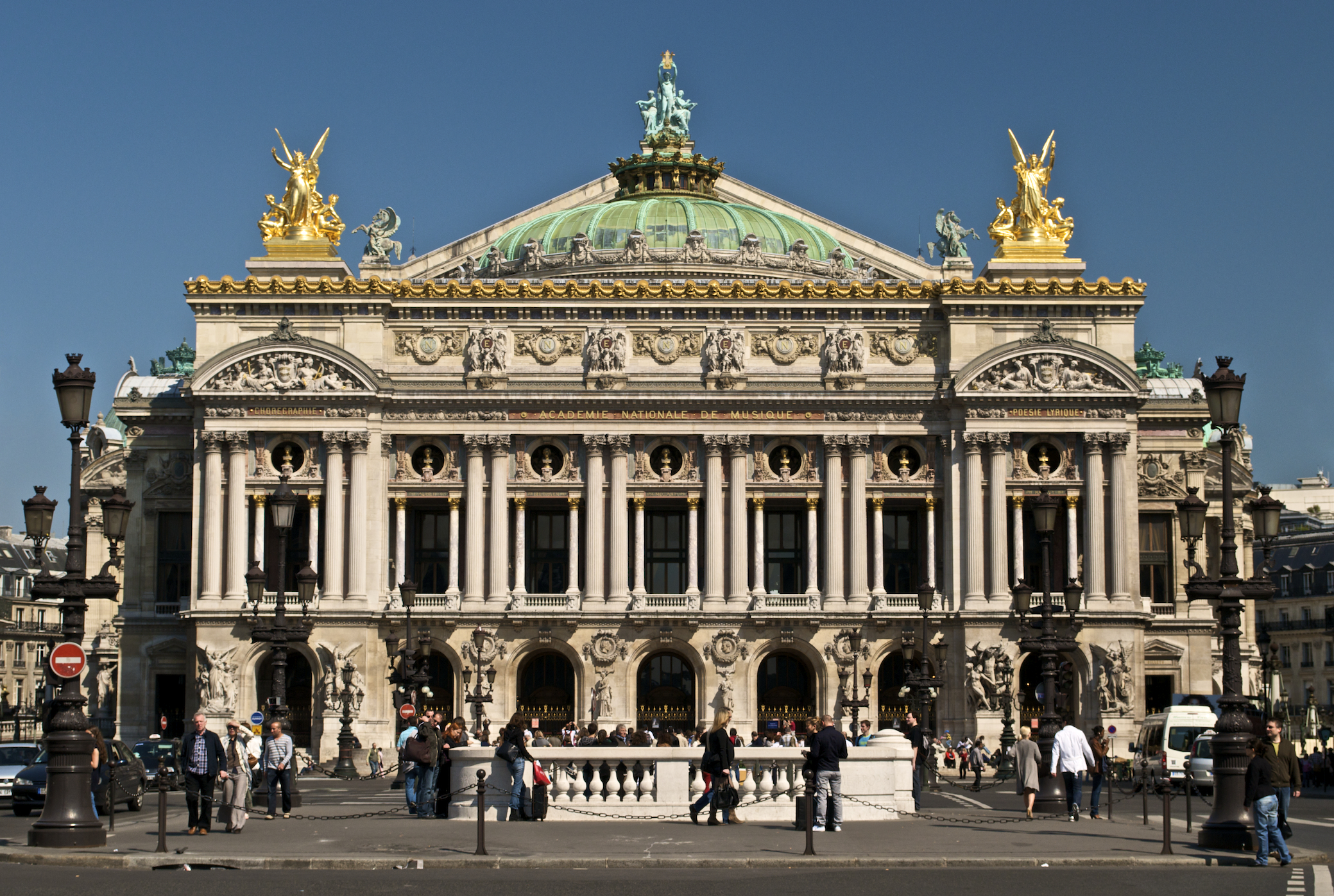
''Much Ado About Nothing'' is an opera in four acts by Charles Villiers Stanford (his Op. 76a), to a libretto by Julian Sturgis based on Shakespeare's play ''Much Ado About Nothing''. It was the composer's seventh completed opera. Performance history It premiered at the Royal Opera House, Covent Garden on 30 May 1901, conducted by Luigi Mancinelli, when it was "well, but not rapturously received by the public", and given one further performance four days later. ''The Manchester Guardian'' commented, "Not even in the ''Falstaff'' of Arrigo Boito Arrigo Boito (; 24 February 1842 10 June 1918) (whose original name was Enrico Giuseppe Giovanni Boito and who wrote essays under the anagrammatic pseudonym of Tobia Gorrio) was an Italian poet, journalist, novelist, librettist and composer, best ... and Giuseppe Verdi have the characteristic charm, the ripe and pungent individuality of the original comedy been more sedulously preserved." The opera was performed in German translat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Villiers Stanford
Sir Charles Villiers Stanford (30 September 1852 – 29 March 1924) was an Anglo-Irish composer, music teacher, and conductor of the late Romantic music, Romantic era. Born to a well-off and highly musical family in Dublin, Stanford was educated at the University of Cambridge before studying music in University of Music and Theatre Leipzig, Leipzig and Berlin. He was instrumental in raising the status of the Cambridge University Musical Society, attracting international stars to perform with it. While still an undergraduate, Stanford was appointed organist of Trinity College, Cambridge. In 1882, aged 29, he was one of the founding professors of the Royal College of Music, where he taught composition for the rest of his life. From 1887 he was also Professor of Music (Cambridge), Professor of Music at Cambridge. As a teacher, Stanford was sceptical about modernism, and based his instruction chiefly on classical principles as exemplified in the music of Johannes Brahms, Brahms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baritone
A baritone is a type of classical male singing voice whose vocal range lies between the bass and the tenor voice-types. The term originates from the Greek (), meaning "heavy sounding". Composers typically write music for this voice in the range from the second F below middle C to the F above middle C (i.e. F2–F4) in choral music, and from the second A below middle C to the A above middle C (A2 to A4) in operatic music, but the range can extend at either end. Subtypes of baritone include the baryton-Martin baritone (light baritone), lyric baritone, ''Kavalierbariton'', Verdi baritone, dramatic baritone, ''baryton-noble'' baritone, and the bass-baritone. History The first use of the term "baritone" emerged as ''baritonans'', late in the 15th century, usually in French sacred polyphonic music. At this early stage it was frequently used as the lowest of the voices (including the bass), but in 17th-century Italy the term was all-encompassing and used to describe the averag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operas Based On Works By William Shakespeare
Opera is a form of theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by singers. Such a "work" (the literal translation of the Italian word "opera") is typically a collaboration between a composer and a librettist and incorporates a number of the performing arts, such as acting, scenery, costume, and sometimes dance or ballet. The performance is typically given in an opera house, accompanied by an orchestra or smaller musical ensemble, which since the early 19th century has been led by a conductor. Although musical theatre is closely related to opera, the two are considered to be distinct from one another. Opera is a key part of the Western classical music tradition. Originally understood as an entirely sung piece, in contrast to a play with songs, opera has come to include numerous genres, including some that include spoken dialogue such as ''Singspiel'' and ''Opéra comique''. In traditional number opera, singers employ two styles of singing: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English-language Operas
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the island of Great Britain. Existing on a dialect continuum with Scots, and then closest related to the Low Saxon and Frisian languages, English is genealogically West Germanic. However, its vocabulary is also distinctively influenced by dialects of France (about 29% of Modern English words) and Latin (also about 29%), plus some grammar and a small amount of core vocabulary influenced by Old Norse (a North Germanic language). Speakers of English are called Anglophones. The earliest forms of English, collectively known as Old English, evolved from a group of West Germanic (Ingvaeonic) dialects brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the 5th century and further mutated by Norse-speaking Viking settlers starting in the 8th and 9th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compositions By Charles Villiers Stanford
Composition or Compositions may refer to: Arts and literature *Composition (dance), practice and teaching of choreography *Composition (language), in literature and rhetoric, producing a work in spoken tradition and written discourse, to include visuals and digital space *Composition (music), an original piece of music and its creation *Composition (visual arts), the plan, placement or arrangement of the elements of art in a work * ''Composition'' (Peeters), a 1921 painting by Jozef Peeters *Composition studies, the professional field of writing instruction * ''Compositions'' (album), an album by Anita Baker *Digital compositing, the practice of digitally piecing together a video Computer science *Function composition (computer science), an act or mechanism to combine simple functions to build more complicated ones *Object composition, combining simpler data types into more complex data types, or function calls into calling functions History *Composition of 1867, Austro-Hungarian/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1901 Operas
Nineteen or 19 may refer to: * 19 (number), the natural number following 18 and preceding 20 * one of the years 19 BC, AD 19, 1919, 2019 Films * 19 (film), ''19'' (film), a 2001 Japanese film * Nineteen (film), ''Nineteen'' (film), a 1987 science fiction film Music * 19 (band), a Japanese pop music duo Albums * 19 (Adele album), ''19'' (Adele album), 2008 * ''19'', a 2003 album by Alsou * ''19'', a 2006 album by Evan Yo * ''19'', a 2018 album by MHD (rapper), MHD * ''19'', one half of the double album ''63/19'' by Kool A.D. * ''Number Nineteen'', a 1971 album by American jazz pianist Mal Waldron * XIX (EP), ''XIX'' (EP), a 2019 EP by 1the9 Songs * 19 (song), "19" (song), a 1985 song by British musician Paul Hardcastle. * "Nineteen", a song by Bad4Good from the 1992 album ''Refugee (Bad4Good album), Refugee'' * "Nineteen", a song by Karma to Burn from the 2001 album ''Almost Heathen''. * Nineteen (song), "Nineteen" (song), a 2007 song by American singer Billy Ray Cyrus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operas
Opera is a form of theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by singers. Such a "work" (the literal translation of the Italian word "opera") is typically a collaboration between a composer and a librettist and incorporates a number of the performing arts, such as acting, scenery, costume, and sometimes dance or ballet. The performance is typically given in an opera house, accompanied by an orchestra or smaller musical ensemble, which since the early 19th century has been led by a conductor. Although musical theatre is closely related to opera, the two are considered to be distinct from one another. Opera is a key part of the Western classical music tradition. Originally understood as an entirely sung piece, in contrast to a play with songs, opera has come to include numerous genres, including some that include spoken dialogue such as ''Singspiel'' and ''Opéra comique''. In traditional number opera, singers employ two styles of singing: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Musical Times
''The Musical Times'' is an academic journal of classical music edited and produced in the United Kingdom and currently the oldest such journal still being published in the country. It was originally created by Joseph Mainzer in 1842 as ''Mainzer's Musical Times and Singing Circular'', but in 1844 he sold it to Joseph Alfred Novello (who also founded ''The Musical World'' in 1836), and it was published monthly by the Novello and Co. (also owned by Alfred Novello at the time).. It first appeared as ''The Musical Times and Singing Class Circular'', a name which was retained until 1903. From the very beginning, every issue - initially just eight pages - contained a simple piece of choral music (alternating secular and sacred), which choral society members subscribed to collectively for the sake of the music. Its title was shortened to its present name from January 1904. Even during World War II it continued to be published regularly, making it the world's oldest continuously publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Hyde
Walter Hyde (6 February 1875 – 11 November 1951) was a British tenor, actor and teacher of voice whose career spanned genres from musical theatre to grand opera. In 1901 he sang Borrachio in the premiere of Stanford's ''Much Ado About Nothing'' and soon appeared in London's West End in light opera and Edwardian musical comedy. He appeared regularly at the Royal Opera House in Covent Garden between 1908 and 1924, becoming known for roles in Wagner operas, among others, both in Britain and America. He was also in demand as a concert artist. In his later years he was Professor of Voice at the Guildhall School of Music where his students included Geraint Evans and Owen Brannigan. Early life Hyde was born in the Kings Norton area of Birmingham in 1875, the third son of Henry Michael Hyde (1848–1920), a carpenter, and Elizabeth ''née'' Hiley (1851–1932). His twin brothers, Harry and Charles, were two years older. The family had musical inclinations. Hyde later recalled: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Putnam Griswold
Putnam Griswold (1875 – February 26, 1914) was an American opera bass singer. Biography Born in Minneapolis, Minnesota, in 1875, Griswold originally followed a business career. At the age of 22 he discovered his voice and began to study with a local teacher in California. In 1900 he went to London, where he was for two years a pupil of Alberto Randegger at the Royal College of Music. During the winter of 1902/03 he studied under Bouhy at Paris, the next winter under Julius Stockhausen at Frankfurt; and finally he completed his studies with Emerich at Berlin in 1905. His operatic début took place at the Royal Opera House, Covent Garden, London, in 1901. During the summer of 1904 he sang at the Royal Opera in Berlin. After having sung the role of Gurnemanz in Savage's production of ''Parsifal'' in America (1904–1905), he became in 1906 a regular member of the Berlin Opera. There he remained, appearing also as guest in various German cities, until he came to the Metropoli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pol Plançon
Pol Henri Plançon (; 12 June 1851 – 11 August 1914) was a distinguished French operatic bass (''basse chantante''). He was one of the most acclaimed singers active during the 1880s, 1890s and early 20th century—a period often referred to as the "Golden Age of Opera". In addition to being among the earliest international opera stars to have made recordings, he was a versatile singer who performed roles ranging from Sarastro in Mozart's ''The Magic Flute'' to the core bass roles by Meyerbeer, Gounod, Verdi and Wagner, among others. He was renowned for his legato singing as well as for his diction, tone, intonation, and mastery of ornaments and fioriture. Biography Pol Plançon was born in Fumay, in the Ardennes ''département'' of France, near the Belgian border. "Pol" is a pet form of Paul. Training Blessed with a fine natural voice, he commenced learning to sing with the pivotal French tenor Gilbert Duprez (the originator of the "chest voice high C"), who had turned to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
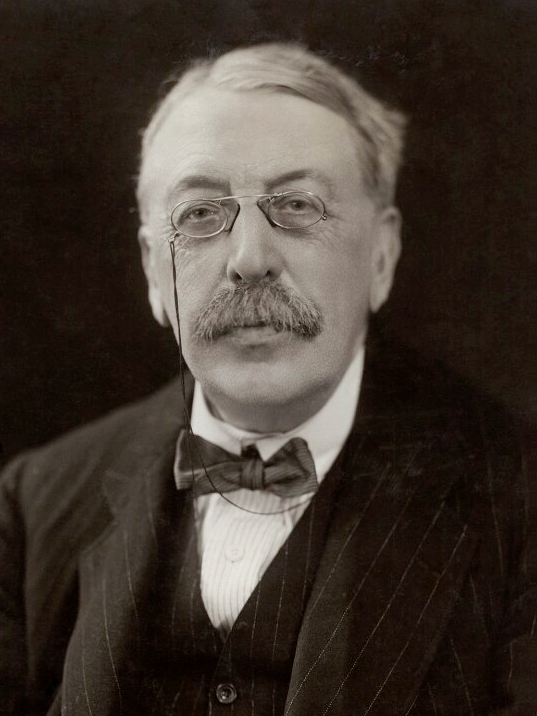
David Bispham
David Scull Bispham (January 5, 1857 – October 2, 1921) was an American operatic baritone. Biography Bispham was born on January 5, 1857 in Philadelphia, the only child of William Danforth Bispham and Jane Lippincott Scull.W. Bispham, 274 Both of Bispham's parents were members of the Society of Friends. In 1867, the family relocated to Moorestown Township, New Jersey. In 1872, Bispham entered Haverford College, from which he was graduated in 1876. After graduation, Bispham entered the wool business with his mother's brothers, all the while continuing to develop his musical talents as an amateur. Bispham appeared in numerous musical performances in his childhood despite having no formal musical training. In 1885, Bispham married Caroline Russell, the daughter of General Charles Sawyer Russell. They would go on to have four children: Jeanette, Vida, Leonie, and David. The Bisphams honeymooned in Europe, and when they returned to Philadelphia, Bispham found work with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |