|
Mozart And Dance
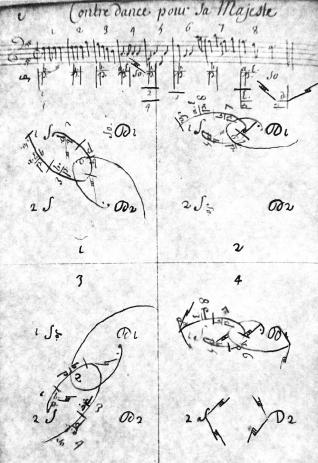
The composer Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart wrote a great deal of dance music, both for public use and as elements of larger works such as operas, quartets, and symphonies. According to the reminiscences of those who knew him, the composer himself enjoyed dancing very much; he was skillful and danced often. Dance music composed by Mozart About 200 dances by Mozart are still preserved. The modern edition of the dances as published by the ''Neue Mozart-Ausgabe'' runs to about 300 total pages in score. For a complete listing of Mozart's dances, see this list. History Mozart began writing dances when he was five years old; see ''Nannerl Notenbuch''. In 1768, when Mozart was 12, his father Leopold reported that Wolfgang had composed "many minuets for all types of instrument".Lindmayr-Brandl (2006, 135) Mozart continued to write dance music for various occasions during the Salzburg period of his life (up to 1781).Lindmayr-Brandl (2006, 134) Following his move to Vienna, the pace of dance m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
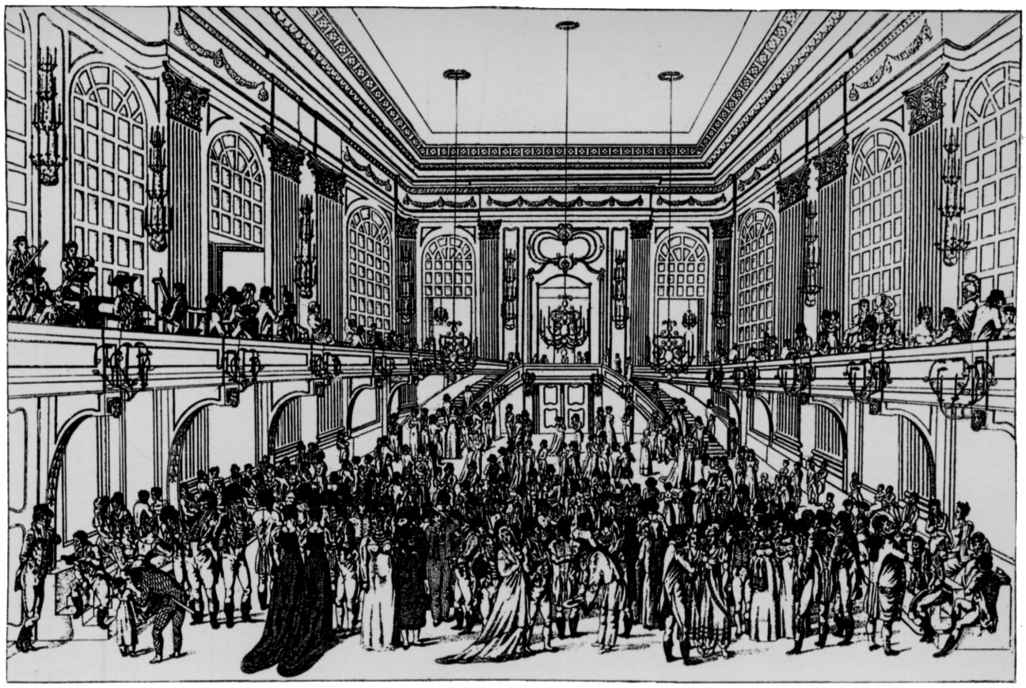
English Country Dance
A country dance is any of a very large number of social dances of a type that originated in the British Isles; it is the repeated execution of a predefined sequence of figures, carefully designed to fit a fixed length of music, performed by a group of people, usually in couples, in one or more sets. The figures involve interaction with your partner and/or with other dancers, usually with a progression so that you dance with everyone in your set. It is common in modern times to have a "caller" who teaches the dance and then calls the figures as you dance. Country dances are done in many different styles. As a musical form written in or time, the contredanse was used by Beethoven and Mozart. Introduced to South America by French immigrants, Country Dance had great influence upon Latin American music as contradanza. The ''Anglais'' (from the French word meaning "English") or ''Angloise'' is another term for the English country dance. A Scottish country dance may be termed an . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mozart's Compositional Method
Scholars have long studied how Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart created his works. Nineteenth-century views on this topic were often based on a romantic, mythologizing conception of the process of composition. More recent scholarship addresses this issue by systematically examining authenticated letters and documents, and has arrived at rather different conclusions. Mozart's approach to composition A surviving letter of Mozart's to his father Leopold (31 July 1778) indicates that he considered composition an active process:You know that I plunge myself into music, so to speak—that I think about it all day long—that I like experimenting—studying—reflecting.One cannot quite determine from these words alone whether Mozart's approach to composition was a conscious method, or more inspired and intuitive. Sketches Mozart often wrote sketches, from small snippets to extensive drafts, for his compositions. Though many of these were destroyed by Mozart's widow Constanze, about 320 sketc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolfgang Plath
Wolfgang Plath (27 December 1930 – 19 March 1995) was a German musicologist specialising in research on Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart. Life Born in Riga, Plath studied musicology under Walter Gerstenberg, first at the Free University of Berlin, then at University of Tübingen. His PhD thesis in 1958 dealt with the ''Klavierbüchlein für Wilhelm Friedemann Bach''. In 1959, he became the assistant of Ernst Fritz Schmid in Augsburg and the International Mozarteum Foundation appointed him, together with Wolfgang Rehm, editor of the ''Neue Mozart-Ausgabe''; Plath held this position until his death. |
Georg Nikolaus Von Nissen
Georg Nikolaus von Nissen (sometimes Nicolaus or Nicolai; 22 January 1761 – 24 March 1826) was a Danish diplomat and music historian. He is the author of one of the first biographies of composer Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, still used today as a scholarly source. Life Nissen was born in Haderslev, Denmark. He completed his schooling in 1781 and became "authorized agent of the General Post Office" in Copenhagen in 1781. In 1792 he became a diplomat in the Danish foreign service. As of 1793, he worked in Vienna as chargé d'affaires. In 1797, while serving in this post, Nissen first met Mozart's widow, Constanze, whose husband had died six years earlier in 1791. He was initially her tenant. The two began living together in September 1798. Constanze had been through an arduous period following Mozart's death, trying to ward off poverty for herself and her two sons. In this she was successful, obtaining a pension from the Emperor, and making considerable money from concerts o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piccolo
The piccolo ( ; Italian for 'small') is a half-size flute and a member of the woodwind family of musical instruments. Sometimes referred to as a "baby flute" the modern piccolo has similar fingerings as the standard transverse flute, but the sound it produces is an octave higher. This has given rise to the name ottavino (), by which the instrument is called in Italian and thus also in scores of Italian composers. Piccolos are often orchestrated to double the violins or the flutes, adding sparkle and brilliance to the overall sound because of the aforementioned one-octave transposition upwards. The piccolo is a standard member in orchestras, marching bands, and wind ensembles. History Since the Middle Ages, evidence indicates the use of octave transverse flutes as military instruments, as their penetrating sound was audible above battles. In cultured music, however, the first piccolos were used in some of Jean Philippe Rameau's works in the first half of the 18th century. Sti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flageolet
The flageolet is a woodwind instrument and a member of the fipple flute family which includes recorders and tin whistles. Its invention was erroneously ascribed to the 16th-century Sieur Juvigny in 1581. There are two basic forms of the instrument: the French, having four finger holes on the front and two thumb holes on the back; and the English, having six finger holes on the front and sometimes a single thumb hole on the back. The latter was developed by English instrument maker William Bainbridge, resulting in the "improved English flageolet" in 1803. There are also double and triple flageolets, having two or three bodies that allowed for a drone and countermelody. Flageolets were made until the 19th century. Flageolets have varied greatly during the last 400 years. The first flageolets were called "French flageolets", and have four tone-holes on the front and two on the back. This instrument was played by Hector Berlioz, Frédéric Chalon, Samuel Pepys, and Robert Louis Steve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post Horn
The post horn (''also'' post-horn) is a valveless cylindrical brass instrument with a cupped mouthpiece. The instrument was used to signal the arrival or departure of a post rider or mail coach. It was used especially by postilions of the 18th and 19th centuries. Use and construction The post horn is sometimes confused with the coach horn, and even though the two types of horn served the same principal purpose, they differ in their physical appearance. The post horn has a cylindrical bore and was generally used on a coach pulled by two horses (technically referred to as "Tonga"); hence, it is sometimes also called the Tonga horn. The coach horn, on the other hand, has a conical bore and was used on a coach pulled by four horses (referred to as a "four-in-hand"). The post horn is no more than in length, whereas the coach horn can be up to long. The latter has more of a funnel-shaped bell, while the former's bell is trumpet-shaped. Post horns need not be straight but can be coil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurdy-gurdy
The hurdy-gurdy is a string instrument that produces sound by a hand-crank-turned, rosined wheel rubbing against the strings. The wheel functions much like a violin bow, and single notes played on the instrument sound similar to those of a violin. Melodies are played on a keyboard that presses ''tangents''—small wedges, typically made of wood—against one or more of the strings to change their pitch. Like most other acoustic stringed instruments, it has a sound board and hollow cavity to make the vibration of the strings audible. Most hurdy-gurdies have multiple drone strings, which give a constant pitch accompaniment to the melody, resulting in a sound similar to that of bagpipes. For this reason, the hurdy-gurdy is often used interchangeably or along with bagpipes. It is mostly used in Occitan, Aragonese, Cajun French, Asturian, Cantabrian, Galician, Hungarian, and Slavic folk music. One or more of the drone strings usually passes over a loose bridge that can be made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jingle Bell
A jingle bell or sleigh bell is a type of bell which produces a distinctive 'jingle' sound, especially in large numbers. They find use in many areas as a percussion instrument, including the classic sleigh bell sound and morris dancing. They are typically used as a cheaper alternative to small 'classic' bells. The simplest jingle bells are produced from a single piece of sheet metal bent into a roughly spherical shape to contain a small ball bearing or short piece of metal rod. This method of production results in the classic two- or four-leaved shape. Two halves may also be crimped together, resulting in a ridge around the middle. A glass marble may also be used as the ringer on larger bells. History Bells of this type were developed centuries ago from the European crotal bell for fastening to harnesses used with horses or teams of horses. Typically they were used for horse-drawn vehicles, such as carriages and sleighs. The bell was designed to make a jingly sound whenev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tambourine
The tambourine is a musical instrument in the percussion family consisting of a frame, often of wood or plastic, with pairs of small metal jingles, called "zills". Classically the term tambourine denotes an instrument with a drumhead, though some variants may not have a head. Tambourines are often used with regular percussion sets. They can be mounted, for example on a stand as part of a drum kit (and played with drum sticks), or they can be held in the hand and played by tapping or hitting the instrument. Tambourines come in many shapes with the most common being circular. It is found in many forms of music: Turkish folk music, Greek folk music, Italian folk music, French folk music, classical music, Persian music, samba, gospel music, pop music, country music, and rock music. History The origin of the tambourine is unknown, but it appears in historical writings as early as 1700 BC and was used by ancient musicians in West Africa, the Middle East, Greece and India. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drum
The drum is a member of the percussion group of musical instruments. In the Hornbostel-Sachs classification system, it is a membranophone. Drums consist of at least one membrane, called a drumhead or drum skin, that is stretched over a shell and struck, either directly with the player's hands, or with a percussion mallet, to produce sound. There is usually a resonant head on the underside of the drum. Other techniques have been used to cause drums to make sound, such as the thumb roll. Drums are the world's oldest and most ubiquitous musical instruments, and the basic design has remained virtually unchanged for thousands of years. Drums may be played individually, with the player using a single drum, and some drums such as the djembe are almost always played in this way. Others are normally played in a set of two or more, all played by the one player, such as bongo drums and timpani. A number of different drums together with cymbals form the basic modern drum kit. Uses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_by_Lange_1782.jpg)




