|
Moy House, Moray
Moy House is an 18th-century country house near Forres in Moray, Scotland. Built on the site of an older house by Collen Williamson and John Adam in the mid eighteenth century for Sir Ludovic Grant of Grant, it was the first building designed by a member of the Adam family to be built in Moray. It was designated a Category A listed building in 1971, and has been listed on the Buildings at Risk Register for Scotland since 1990; ravaged by fire in 1995, it is now a ruin. Description Moy House is a ruined mansion, built in the classical style. Its three-storey central block, which is now roofless, has two main facades, one facing east and the other west, with its principal entrance in the east front. Three-storey wings project to the east at either end of the main block, forming a U-shaped courtyard, and two-storey wings projecting beyond these to the north and south. The building is not inhabited, and has remained in a ruinous state since a fire in 1995. Its dilapidation h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoclassical Architecture
Neoclassical architecture is an architectural style produced by the Neoclassical movement that began in the mid-18th century in Italy and France. It became one of the most prominent architectural styles in the Western world. The prevailing styles of architecture in most of Europe for the previous two centuries, Renaissance architecture and Baroque architecture, already represented partial revivals of the Classical architecture of ancient Rome and (much less) ancient Greek architecture, but the Neoclassical movement aimed to strip away the excesses of Late Baroque and return to a purer and more authentic classical style, adapted to modern purposes. The development of archaeology and published accurate records of surviving classical buildings was crucial in the emergence of Neoclassical architecture. In many countries, there was an initial wave essentially drawing on Roman architecture, followed, from about the start of the 19th century, by a second wave of Greek Revival architec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
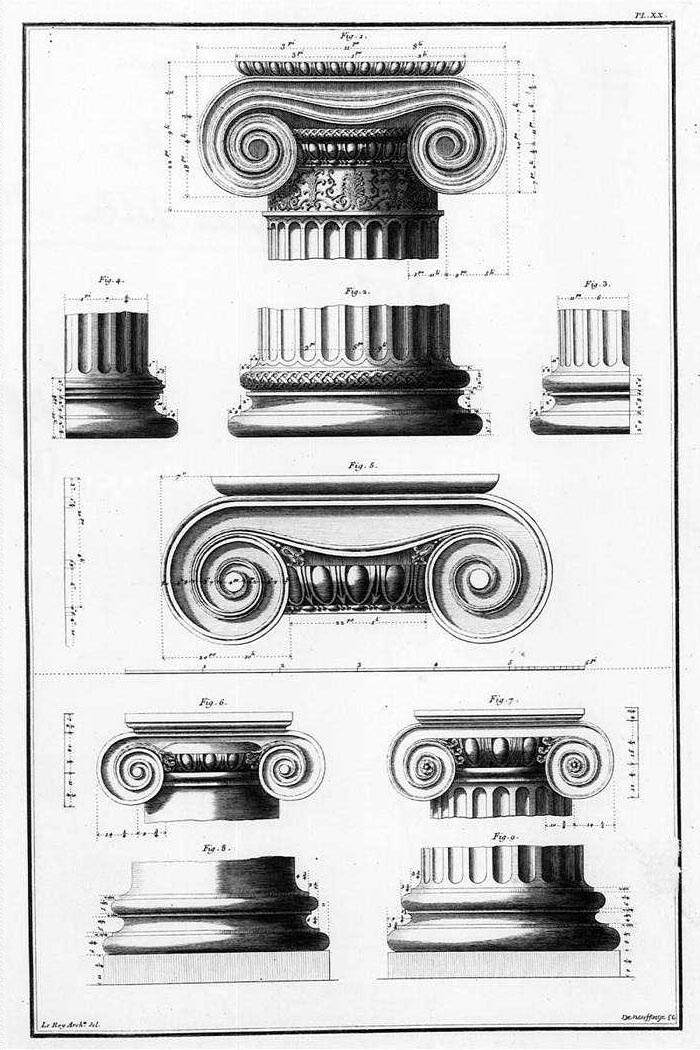
Ionic Order
The Ionic order is one of the three canonic orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric and the Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan (a plainer Doric), and the rich variant of Corinthian called the composite order. Of the three classical canonic orders, the Corinthian order has the narrowest columns, followed by the Ionic order, with the Doric order having the widest columns. The Ionic capital is characterized by the use of volutes. The Ionic columns normally stand on a base which separates the shaft of the column from the stylobate or platform while the cap is usually enriched with egg-and-dart. The ancient architect and architectural historian Vitruvius associates the Ionic with feminine proportions (the Doric representing the masculine). Description Capital The major features of the Ionic order are the volutes of its capital, which have been the subject of much theoretical and practical discourse, based on a brief and obscure passage i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Ross (architect)
Alexander Ross FRIBA LLD (9 July 1834 – 19 May 1925) was a 19th/20th century Scottish architect specialising in churches, especially for the Free Church of Scotland and the Scottish Episcopal Church. He was Provost of Inverness from 1889 to 1895. He is probably the single most important person in moulding the city of Inverness, both socially and physically. He is responsible for a very high proportion of Inverness's churches, offices, public buildings, shops, tenements and villas. Life He was born on 9 July 1834 at Huntly Hill in Stracathro near Brechin in Angus, the son of James Ross, architect. The family moved to Inverness in 1838. He was educated at Inverness Royal Academy and Dr Bell's Institution. In 1848 he was briefly apprenticed to a stonemason to gain some practical experience before being articled in his father's architects office. In 1853 his father died and he took over the office. In 1859 he took William Joass into partnership, creating Ross & Joass. In t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Adam
Robert Adam (3 July 17283 March 1792) was a British neoclassical architect, interior designer and furniture designer. He was the son of William Adam (1689–1748), Scotland's foremost architect of the time, and trained under him. With his older brother John, Robert took on the family business, which included lucrative work for the Board of Ordnance, after William's death. In 1754, he left for Rome, spending nearly five years on the continent studying architecture under Charles-Louis Clérisseau and Giovanni Battista Piranesi. On his return to Britain he established a practice in London, where he was joined by his younger brother James. Here he developed the "Adam Style", and his theory of "movement" in architecture, based on his studies of antiquity and became one of the most successful and fashionable architects in the country. Adam held the post of Architect of the King's Works from 1761 to 1769. Robert Adam was a leader of the first phase of the classical revival in En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Moray
The Bishop of Moray or Bishop of Elgin was the ecclesiastical head of the Diocese of Moray in northern Scotland, one of Scotland's 13 medieval bishoprics. If the foundation charter of the monastery at Scone is reliable, then the Bishopric of Moray was in existence as early as the reign of King Alexander I of Scotland (1107–1124), but was certainly in existence by 1127, when one Gregoir ("Gregorius") is mentioned as "Bishop of Moray" in a charter of king David I of Scotland. The bishopric had its seat ( la, Cathedra) at Elgin and Elgin Cathedral, but was severally at Birnie, Kinneddar and as late as Bishop Andreas de Moravia at Spynie, where the bishops continued to maintain a palace. The Bishopric's links with Rome ceased to exist after the Scottish Reformation, but continued, saving temporary abolition between 1638 and 1661, under the episcopal Church of Scotland until the Revolution of 1688. Episcopacy in the established church in Scotland was permanently abolished in 1689. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clan Campbell Of Cawdor
Clan Campbell of Cawdor is a highland Scottish clan and a branch of the larger Clan Campbell. While the ''clan'' is recognised by the Standing Council of Scottish Chiefs, the clan does not have a ''clan chief'' recognised by the Standing Council of Scottish Chiefs. Also, because the clan does not have a clan chief recognised by the Lord Lyon King of Arms it is considered an armigerous clan. The head of the Clan Campbell of Cawdor is the Earl Cawdor, currently held by Colin Campbell. History In 1499, Muriel Caddell, daughter and heiress of John Caddell, 7th Thane of Caddell was kidnapped by the Campbells. The battle of Daltullich was fought between her uncles and the Campbells, with several deaths, but the child was whisked away to the Campbells castle. In 1510, at 12 years old, Muriel married Sir John Campbell, third son of the 2nd Earl of Argyll. From 1524 to 1546, Sir John Campbell of Caddell lived at Caddell (now Cawdor) Castle, until his death. After Muriel's death in 157 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George IV Of The United Kingdom
George IV (George Augustus Frederick; 12 August 1762 – 26 June 1830) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and King of Hanover from the death of his father, King George III, on 29 January 1820, until his own death ten years later. At the time of his accession to the throne, he was acting as Prince Regent, having done so since 5 February 1811, during his father's final mental illness. George IV was the eldest child of King George III and Queen Charlotte. He led an extravagant lifestyle that contributed to the fashions of the Regency era. He was a patron of new forms of leisure, style and taste. He commissioned John Nash to build the Royal Pavilion in Brighton and remodel Buckingham Palace, and commissioned Jeffry Wyatville to rebuild Windsor Castle. George's charm and culture earned him the title "the first gentleman of England", but his dissolute way of life and poor relationships with his parents and his wife, Caroline of Brunswick, earned him t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George III Of The United Kingdom
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and of Monarchy of Ireland, Ireland from 25 October 1760 until Acts of Union 1800, the union of the two kingdoms on 1 January 1801, after which he was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland until his death in 1820. He was the longest-lived and longest-reigning king in British history. He was concurrently Duke and Prince-elector of Electorate of Brunswick-Lüneburg, Brunswick-Lüneburg ("Hanover") in the Holy Roman Empire before becoming King of Hanover on 12 October 1814. He was a monarch of the House of Hanover but, unlike his two predecessors, he was born in Great Britain, spoke English as his first language and never visited Hanover. George's life and reign were marked by a series of military conflicts involving his kingdoms, much of the rest of Europe, and places farther afield in Africa, the Americas and Asia. Early in his reign, Great Britain defeated France in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drawing Room
A drawing room is a room in a house where visitors may be entertained, and an alternative name for a living room. The name is derived from the 16th-century terms withdrawing room and withdrawing chamber, which remained in use through the 17th century, and made their first written appearance in 1642. In a large 16th to early 18th century English house, a withdrawing room was a room to which the owner of the house, his wife, or a distinguished guest who was occupying one of the main apartments in the house could "withdraw" for more privacy. It was often off the great chamber (or the great chamber's descendant, the state room) and usually led to a formal, or "state" bedroom. In modern houses, it may be used as a convenient name for a second or further reception room, but no particular function is associated with the name. History and development In 18th-century London, the royal morning receptions that the French called ''levées'' were called "drawing rooms", with the sense ori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
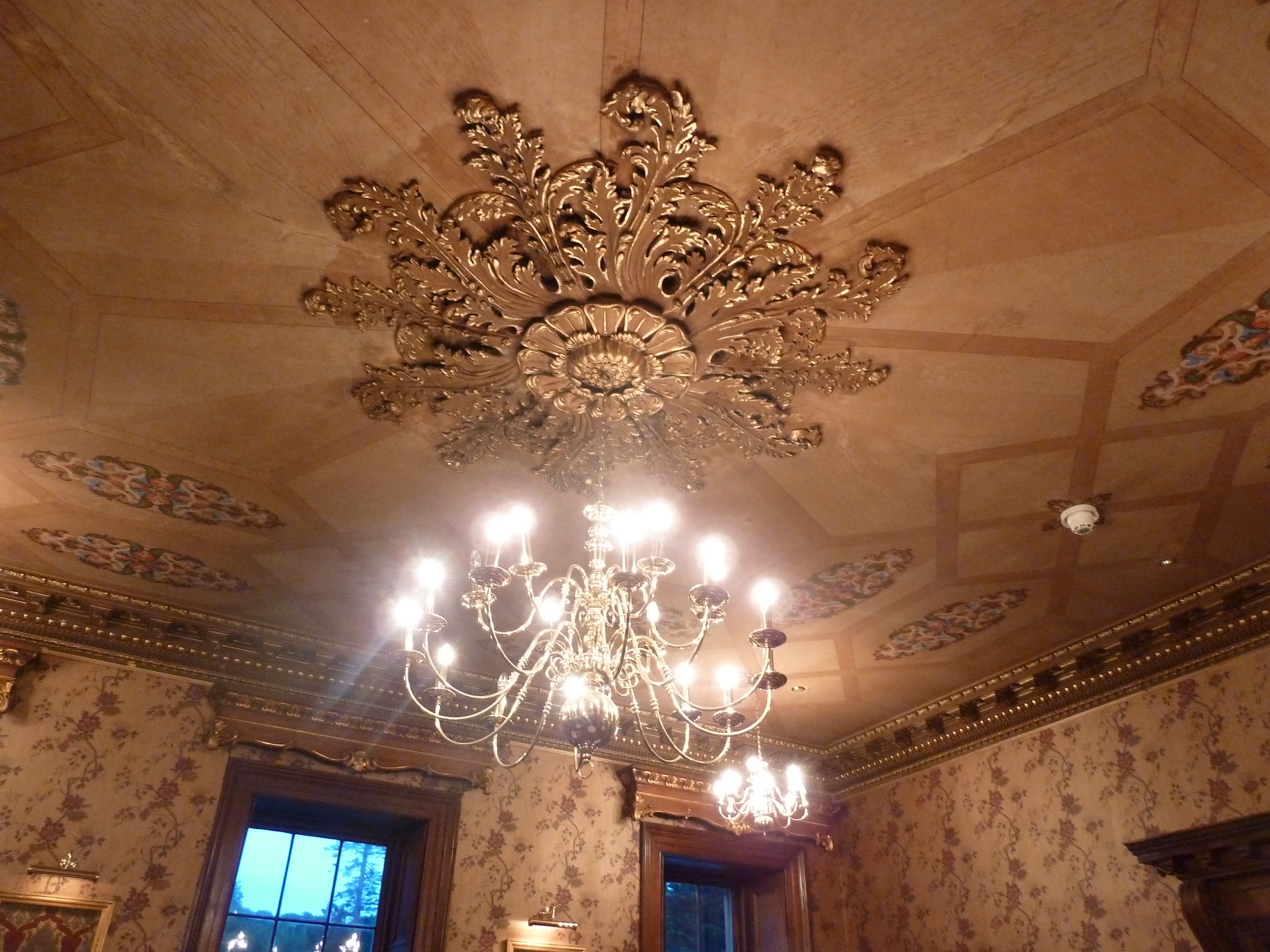
Ceiling Rose
In the United Kingdom and Australia, a ceiling rose is a decorative element affixed to the ceiling from which a chandelier or light fitting is often suspended. They are typically round in shape and display a variety of ornamental designs. In modern British wiring setups, light fittings usually use loop-in ceiling roses, which also include the functionality of a junction box. Etymology The rose has symbolised secrecy since Roman times, due to a confused association with the Egyptian god Horus. For its associations with ceilings and confidentiality, refer to the Scottish Government's Sub Rosa initiative. Through its promise of secrecy, the rose, suspended above a meeting table, symbolises the freedom to speak plainly without repercussion. The physical carving of a rose on a ceiling was used for this purpose during the rule of England's Tudor King Henry VIII and has over the centuries evolved into a standard item of domestic vernacular architecture, to such an extent that it now co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantilever
A cantilever is a rigid structural element that extends horizontally and is supported at only one end. Typically it extends from a flat vertical surface such as a wall, to which it must be firmly attached. Like other structural elements, a cantilever can be formed as a beam, plate, truss, or slab. When subjected to a structural load at its far, unsupported end, the cantilever carries the load to the support where it applies a shear stress and a bending moment. Cantilever construction allows overhanging structures without additional support. In bridges, towers, and buildings Cantilevers are widely found in construction, notably in cantilever bridges and balconies (see corbel). In cantilever bridges, the cantilevers are usually built as pairs, with each cantilever used to support one end of a central section. The Forth Bridge in Scotland is an example of a cantilever truss bridge. A cantilever in a traditionally timber framed building is called a jetty or forebay. In the southe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Architrave
In classical architecture, an architrave (; from it, architrave "chief beam", also called an epistyle; from Greek ἐπίστυλον ''epistylon'' "door frame") is the lintel or beam that rests on the capitals of columns. The term can also apply to all sides, including the vertical members, of a frame with mouldings around a door or window. The word "architrave" has come to be used to refer more generally to a style of mouldings (or other elements) framing a door, window or other rectangular opening, where the horizontal "head" casing extends across the tops of the vertical side casings where the elements join (forming a butt joint, as opposed to a miter joint). Classical architecture In an entablature in classical architecture, it is the lowest part, below the frieze and cornice. The word is derived from the Greek and Latin words ''arche'' and ''trabs'' combined to mean "main beam". The architrave is different in the different Classical orders. In the Tuscan o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_-_facade_on_Piazza_dei_signori.jpg)

.jpg)

.jpg)


