|
Mount Ellsworth (Utah)
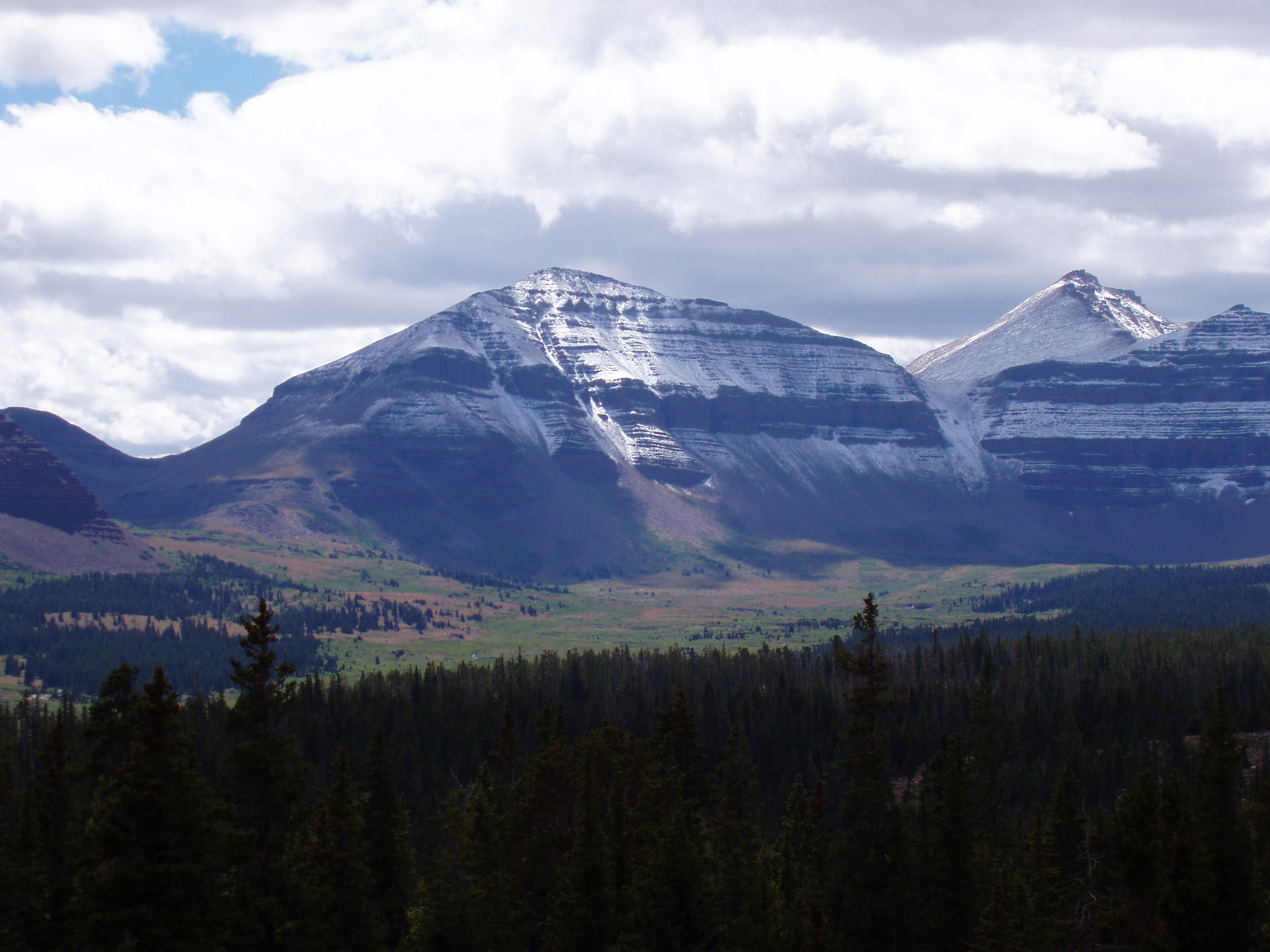
Mount Ellsworth is an 8,235-foot (2,510 m) elevation summit located in Garfield County, Utah, United States. Mount Ellsworth is part of the Henry Mountains. It is situated in a dry, rugged, and sparsely settled region west of Glen Canyon National Recreation Area, on primitive land administered by the Bureau of Land Management. Precipitation runoff from this mountain drains into tributaries of the nearby Colorado River, which here is Lake Powell eight miles to the east of this mountain. History The American geologist Grove Karl Gilbert surveyed this area in 1875 and 1876, and published his findings in 1879 as a monograph, ''The Geology of the Henry Mountains''. The term laccolith was first applied as ''laccolite'' by Gilbert after his study of intrusions of diorite in the Henry Mountains. Mount Ellsworth's name appeared on an 1875 map, but the origin is a mystery. One possibility is Elmer E. Ellsworth, (1837–1861).Pete Klocki and Tiffany Mapel, ''A Wild Redhead Tamed: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Hillers
Mount Hillers is a summit in the Henry Mountains range, in Garfield County, Utah, in the United States. Its elevation is . It was named by Almon Harris Thompson for John Karl Hillers, a government photographer. Climate Spring and fall are the most favorable seasons to visit Mount Hillers. According to the Köppen climate classification system, it is located in a Cold semi-arid climate zone, which is defined by the coldest month having an average mean temperature below 32 °F (0 °C), and at least 50% of the total annual precipitation being received during the spring and summer. This desert climate receives less than of annual rainfall, and snowfall is generally light during the winter. See also * Colorado Plateau * Laccolith * List of mountain peaks of Utah This article comprises three sortable tables of major mountain peaksThis article defines a significant summit as a summit with at least of topographic prominence, and a major summit as a summit with at least of to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geologist
A geologist is a scientist who studies the solid, liquid, and gaseous matter that constitutes Earth and other terrestrial planets, as well as the processes that shape them. Geologists usually study geology, earth science, or geophysics, although backgrounds in physics, chemistry, biology, and other sciences are also useful. Field research (field work) is an important component of geology, although many subdisciplines incorporate laboratory and digitalized work. Geologists can be classified in a larger group of scientists, called geoscientists. Geologists work in the energy and mining sectors searching for natural resources such as petroleum, natural gas, precious and base metals. They are also in the forefront of preventing and mitigating damage from natural hazards and disasters such as earthquakes, volcanoes, tsunamis and landslides. Their studies are used to warn the general public of the occurrence of these events. Geologists are also important contributors to climate ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of Utah
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Mountain Peaks Of Utah
This article comprises three sortable tables of major mountain peaksThis article defines a significant summit as a summit with at least of topographic prominence, and a major summit as a summit with at least of topographic prominence. All summits in this article have at least 500 meters of topographic prominence. An ultra-prominent summit is a summit with at least of topographic prominence. of the U.S. State of Utah. The summit of a mountain or hill may be measured in three principal ways: #The topographic elevation of a summit measures the height of the summit above a geodetic sea level.All elevations in this article include an elevation adjustment from the National Geodetic Vertical Datum of 1929 (NGVD 29) to the North American Vertical Datum of 1988 (NAVD 88). For further information, please see this United States National Geodetic Surveybr>noteIf the elevation or prominence of a summit is calculated as a range of values, the arithmetic mean is shown. The firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
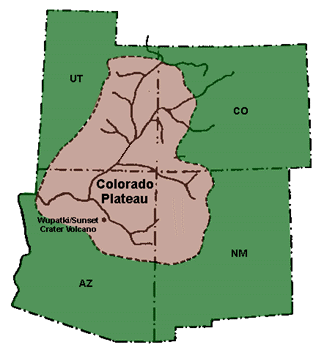
Colorado Plateau
The Colorado Plateau, also known as the Colorado Plateau Province, is a physiographic and desert region of the Intermontane Plateaus, roughly centered on the Four Corners region of the southwestern United States. This province covers an area of 336,700 km2 (130,000 mi2) within western Colorado, northwestern New Mexico, southern and eastern Utah, northern Arizona, and a tiny fraction in the extreme southeast of Nevada. About 90% of the area is drained by the Colorado River and its main tributaries: the Green, San Juan, and Little Colorado. Most of the remainder of the plateau is drained by the Rio Grande and its tributaries. The Colorado Plateau is largely made up of high desert, with scattered areas of forests. In the south-west corner of the Colorado Plateau lies the Grand Canyon of the Colorado River. Much of the Plateau's landscape is related to the Grand Canyon in both appearance and geologic history. The nickname "Red Rock Country" suggests the brightly colored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bullfrog, Utah
Bullfrog Basin is one of the National Park Service recreation sites of the Glen Canyon National Recreation Area of Kane County, Utah, United States, adjoining Lake Powell. It encompasses Bullfrog Basin Airport , the Bullfrog Resort and Marina, the Bullfrog terminus of the Charles Hall Ferry, and a campground. It is nearby the 1970s mining town Ticaboo. The National Park Lodge in the site is named Defiance House Lodge. Built on a bluff that overlooks the Bullfrog Bay part of Lake Powell, it is a stucco building with several adjoining prefabricated units. Bullfrog Basin has a USNPS visitor centre, and the Bullfrog Resort and Marina includes a restaurant, shops, and a gas station. Its development was personally championed by Calvin Rampton in the 1960s, who secured a million funds-matching grant from the Economic Development Administration in 1966 to pave an access road to the area. Although the road did not connect to a settlement at either end, the USNPS had already spent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ticaboo, Utah
Ticaboo ( ) is an unincorporated community in far southeastern Garfield County, Utah, United States. Description The community lies along State Route 276, more than east of Panguitch, the county seat of Garfield County. Its elevation is . It has a post office with the ZIP code 84533. Ticaboo gets its name from Ticaboo Creek, which was named by Cass Hite in the 1880s, from a Paiute word meaning "friendly". History The Ticaboo townsite is a master-planned community that was organized in the late 1970s to both provide housing to the then booming uranium mining industry in southeastern Garfield County, and tap into the tourism potential of nearby Lake Powell. The Ticaboo Lodge was developed to attract guests visiting the remote area as well as to encourage the development of a tourism base outside of Bullfrog in the northern Lake Powell area. The first inhabitants of Ticaboo were Kayenta Anasazi. In October 1981, the Division of Utah State History conducted an excavation of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold Semi-arid Climate
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi-arid climates, depending on variables such as temperature, and they give rise to different biomes. Defining attributes of semi-arid climates A more precise definition is given by the Köppen climate classification, which treats steppe climates (''BSk'' and ''BSh'') as intermediates between desert climates (BW) and humid climates (A, C, D) in ecological characteristics and agricultural potential. Semi-arid climates tend to support short, thorny or scrubby vegetation and are usually dominated by either grasses or shrubs as it usually can't support forests. To determine if a location has a semi-arid climate, the precipitation threshold must first be determined. The method used to find the precipitation threshold (in millimeters): *multiply ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, the climatologist Rudolf Geiger (1894–1981) introduced some changes to the classification system, which is thus sometimes called the Köppen–Geiger climate classification system. The Köppen climate classification divides climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on seasonal precipitation and temperature patterns. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Holmes (Utah)
Mount Holmes is a 7,998-foot (2,438 m) elevation summit located in eastern Garfield County, Utah, United States. Mount Holmes is part of the Henry Mountains. It is situated in a dry, rugged, and sparsely settled region west of Glen Canyon National Recreation Area, on primitive land administered by the Bureau of Land Management. Precipitation runoff from this mountain drains into tributaries of the nearby Colorado River, which here is Lake Powell six miles to the east of this mountain. History The American geologist Grove Karl Gilbert surveyed this area in 1875 and 1876, and published his findings in 1879 as a monograph, ''The Geology of the Henry Mountains''. The term laccolith was first applied as ''laccolite'' by Gilbert after his study of intrusions of diorite in the Henry Mountains. Mount Holmes was named about 1878 by Grove Karl Gilbert who would become the chief geologist of the United States Geological Survey in 1889, for William Henry Holmes (1846–1933), who provided ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elmer E
Elmer is a name of Germanic British origin. The given name originated as a surname, a medieval variant of the given name Aylmer, derived from Old English ''æþel'' (noble) and ''mær'' (famous). It was adopted as a given name in the United States, "in honor of the popularity of the brothers Ebenezer and Jonathan Elmer, leading supporters of the American Revolution." The name has declined in popularity since the first decades of the 20th century and fell out of the top 1,000 names used for American boys in 2009. However, it continues in use for newborn boys in the United States, where 154 boys born there in 2021 received the name. The name is common in the United States and Canada. Notable people with the name include: Mononym * Eilmer of Malmesbury (or Elmer), 11th-century English Benedictine monk * In the amateur radio subculture, an ''Elmer'' is a mentor to a newcoming amateur radio operatorThe term first appeared in the March, 1971 issue of ''QST'' magazine's "How's DX" c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diorite
Diorite ( ) is an intrusive igneous rock formed by the slow cooling underground of magma (molten rock) that has a moderate content of silica and a relatively low content of alkali metals. It is intermediate in composition between low-silica (mafic) gabbro and high-silica ( felsic) granite. Diorite is found in mountain-building belts (''orogens'') on the margins of continents. It has the same composition as the fine-grained volcanic rock, andesite, which is also common in orogens. Diorite has been used since prehistoric times as decorative stone. It was used by the Akkadian Empire of Sargon of Akkad for funerary sculptures, and by many later civilizations for sculptures and building stone. Description Diorite is an intrusive igneous rock composed principally of the silicate minerals plagioclase feldspar (typically andesine), biotite, hornblende, and sometimes pyroxene. The chemical composition of diorite is intermediate, between that of mafic gabbro and felsic grani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |