|
Mount Dickey
Mount Dickey is a peak on the west side of the Ruth Gorge in the Central Alaska Range of mountains, 12 miles (19 km) southeast of Denali and 4 miles (6 km) southwest of The Moose's Tooth. Despite its relatively low elevation, it is notable for its east face, which has around a vertical mile (1600 m) of sheer granite—it achieves this vertical gain in less than half a mile (800m) horizontal distance. This is one of the tallest rock walls in the world, and the face has seen many world-class climbs. Mount Dickey was first climbed on April 19, 1955 by David Fisher and the famous explorer, climber and cartographer Bradford Washburn, via the West Face, which is still the most popular route today. The route begins at a point in the Ruth Gorge southeast of the peak, ascends west under the formidable south face, then turns north and then east to ascend the south side of the gently sloping West Face. This route is relatively straightforward and short for an Alaskan climb (Alaska ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Barrille
Mount Barrille is a mountain summit located in the Alaska Range, in Denali National Park and Preserve, in the U.S. state of Alaska. It is situated 2,650 feet above the Ruth Glacier at the gateway to the Don Sheldon Amphitheater, or The Great Gorge, depending on direction of travel. Barrille is set southeast of Denali, west of The Mooses Tooth, east of The Rooster Comb, and north of Mount Dickey which is its nearest higher peak. The mountain was named by famed explorer Dr. Frederick Cook for Edward Barrill (1861-1946), a horse packer from Darby, Montana, who was his sole companion during his 1906 claim to be the first to climb Mount McKinley. The claim was later disproved, and in 1909 Barrill signed an affidavit stating that they had not reached the summit. Cook referred to his companion as ''Barrille'' in his accounts of the expedition, and Barrille remains as the official spelling used by the United States Geological Survey. Climbing Despite its relatively low elevation, M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, the climatologist Rudolf Geiger (1894–1981) introduced some changes to the classification system, which is thus sometimes called the Köppen–Geiger climate classification system. The Köppen climate classification divides climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on seasonal precipitation and temperature patterns. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of Matanuska-Susitna Borough, Alaska
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Alpine Journal
The ''American Alpine Journal'' is an annual magazine published by the American Alpine Club. Its mission is "to document and communicate mountain exploration." The headquarters is in Golden, Colorado. Subtitled as a compilation of "The World's Most Significant Climbs," the magazine contains feature stories about notable new routes and ascents, written by the climbers, as well as a large "Climbs and Expeditions" section containing short notes by climbers about new and noteworthy achievements. Some general articles about mountaineering, mountain medicine, the mountain environment, or other topics are also sometimes included. Each issue includes book reviews, memorials of deceased members, and club activities. History The journal was established in 1929. In 1957 and 1958, the editor was Francis P. Farquhar. From 1960 to 1995, the editor was H. Adams Carter, who brought the journal to international pre-eminence. From 1996 to 2001, the editor was Christian Beckwith. Since 2002, the ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of Alaska
The geology of Alaska includes Precambrian igneous and metamorphic rocks formed in offshore terranes and added to the western margin of North America from the Paleozoic through modern times. The region was submerged for much of the Paleozoic and Mesozoic and formed extensive oil and gas reserves due to tectonic activity in the Arctic Ocean. Alaska was largely ice free during the Pleistocene, allowing humans to migrate into the Americas. Geologic History, Stratigraphy & Tectonics Compared with other areas of the North American continent, Alaska formed in the recent geologic past. Until 200 million years ago, western North America terminated at the Rocky Mountains, 120 miles further inland than the current shoreline, until the addition of the Yukon-Tanana Terrane. The Birch Creek Schist is the oldest rock in Alaska's interior and forms the core of the Yukon-Tanana Terrane with muscovite-quartz schist, mica quartzite and graphite schist. This intensely folded and rock unit extends f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Mountain Peaks Of Alaska
This article comprises three sortable tables of major mountain peaksThis article defines a significant summit as a summit with at least of topographic prominence, and a major summit as a susexxleast of topographic prominence. All summits in this article have at least 500 meters of topographic prominence. An ultra-prominent summit is a summit with at least of topographic prominence. of the U.S. State of Alaska. The summit of a mountain or hill may be measured in three principal ways: #The topographic elevation of a summit measures the height of the summit above a geodetic sea level.If the elevation or prominence of a summit is calculated as a range of values, the arithmetic mean is shown. The first table below ranks the 100 highest major summits of Alaska by elevation. #The topographic prominence of a summit is a measure of how high the summit rises above its surroundings.The topographic prominence of a summit is the topographic elevation difference between the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Bradley (Alaska)
Mount Bradley is a mountain summit located in the Alaska Range, in Denali National Park and Preserve, in Alaska, United States. It is situated on the west side of the Ruth Gorge, southeast of Denali and southwest of The Moose's Tooth. Its nearest higher peak is Mount Dickey, to the north, Mount Wake lies to the south, and London Tower rises directly east on the opposite side of The Great Gorge. Despite its relatively low elevation, it is notable for its north face with nearly 5,000 feet of vertical sheer granite. The mountain was named by famed explorer Dr. Frederick Cook for John R. Bradley, a wealthy casino owner from Florida and one of Cook's financial sponsors. Climate Based on the Köppen climate classification, Mount Bradley is located in a subarctic climate zone with long, cold, snowy winters, and cool summers. Temperatures can drop below −20 °F with wind chill factors below −30 °F. The months May through June offer the most favorable weather for viewing an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Wake
Mount Wake is a mountain summit located in the Alaska Range, in Denali National Park and Preserve, in Alaska, United States. It is situated on the west side of the Ruth Gorge, southeast of Denali and southwest of The Moose's Tooth. The nearest higher neighbor is Mount Dickey, to the north. Mount Bradley lies to the north, and Mount Johnson lies to the southeast. Despite its relatively low elevation, it is notable for its north face with over 4,000 feet of vertical sheer granite. The mountain was named by famed explorer Dr. Frederick Cook for his friend Charles Wake. Climate Based on the Köppen climate classification, Mount Wake is located in a subarctic climate zone with long, cold, snowy winters, and cool summers. Winter temperatures can drop below −20 °F with wind chill factors below −30 °F. The months May through June offer the most favorable weather for viewing and climbing. See also * *Mountain peaks of Alaska *Geology of Alaska The geology of Alaska includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Johnson (Alaska)
Mount Johnson is an mountain summit located in the Alaska Range, in Denali National Park and Preserve, in Alaska, United States. It is situated on the west side of the Ruth Gorge, southeast of Denali and south-southwest of The Moose's Tooth. Its nearest higher peak is Mount Wake, to the northwest. Despite its relatively low elevation, it is notable for its north face with over 4,000 feet of vertical sheer granite with climbing routes called the ''Escalator'' and ''Stairway to Heaven''. The first ascent of the peak was made in 1979 by Gary Bocarde, Charlie Head, John Lee, and Jon Thomas via the south ridge. The mountain was named by famed explorer Dr. Frederick Cook who claimed the first ascent of Mount McKinley in 1906, but was later disproved. Climate Based on the Köppen climate classification, Mount Johnson is located in an alpine climate zone with long, cold, snowy winters, and cool summers. Temperatures can drop below −20 °C with wind chill factors below −30 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subarctic Climate
The subarctic climate (also called subpolar climate, or boreal climate) is a climate with long, cold (often very cold) winters, and short, warm to cool summers. It is found on large landmasses, often away from the moderating effects of an ocean, generally at latitudes from 50° to 70°N, poleward of the humid continental climates. Subarctic or boreal climates are the source regions for the cold air that affects temperate latitudes to the south in winter. These climates represent Köppen climate classification ''Dfc'', ''Dwc'', ''Dsc'', ''Dfd'', ''Dwd'' and ''Dsd''. Description This type of climate offers some of the most extreme seasonal temperature variations found on the planet: in winter, temperatures can drop to below and in summer, the temperature may exceed . However, the summers are short; no more than three months of the year (but at least one month) must have a 24-hour average temperature of at least to fall into this category of climate, and the coldest month should ave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galen Rowell
Galen Avery Rowell (August 23, 1940 – August 11, 2002) was a wilderness photographer, adventure photojournalist and mountaineer. Born in Oakland, California, he became a full-time photographer in 1972. Early life and education Rowell was introduced to the wilderness at a very young age and completed his first roped climb in Yosemite Valley when he was 16. For the rest of his life, he climbed mountains and explored landscapes. He began taking pictures on excursions into the wild so he could share his experiences with friends and family. After graduating from Berkeley High School in 1958, he stayed in Berkeley to study at the University of California but dropped out to pursue climbing. Career In 1972 Rowell sold his small automotive business and became a full-time photographer. Within a year, he had completed his first major assignment, a cover story for ''National Geographic''. The story originated from an invitation by fellow photographer Dewitt Jones to help him on an assign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
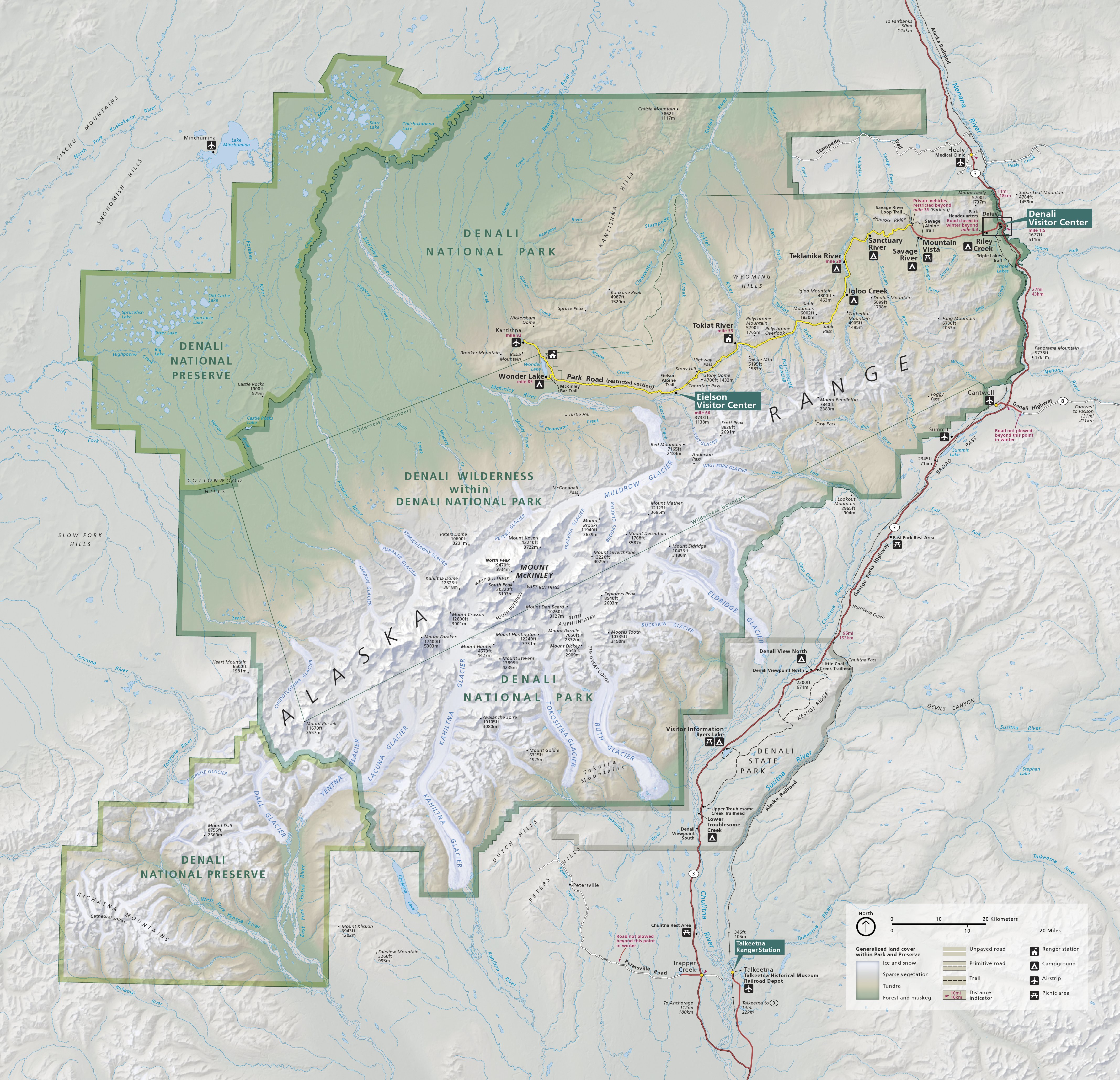
Denali National Park And Preserve
Denali National Park and Preserve, formerly known as Mount McKinley National Park, is an American national park and preserve located in Interior Alaska, centered on Denali, the highest mountain in North America. The park and contiguous preserve encompass which is larger than the state of New Hampshire. On December 2, 1980, Denali Wilderness was established within the park. Denali's landscape is a mix of forest at the lowest elevations, including deciduous taiga, with tundra at middle elevations, and glaciers, snow, and bare rock at the highest elevations. The longest glacier is the Kahiltna Glacier. Wintertime activities include dog sledding, cross-country skiing, and snowmobiling. The park received 594,660 recreational visitors in 2018. History Prehistory and protohistory Human habitation in the Denali Region extends to more than 11,000 years before the present, with documented sites just outside park boundaries dated to more than 8,000 years before the present. However, rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |