|
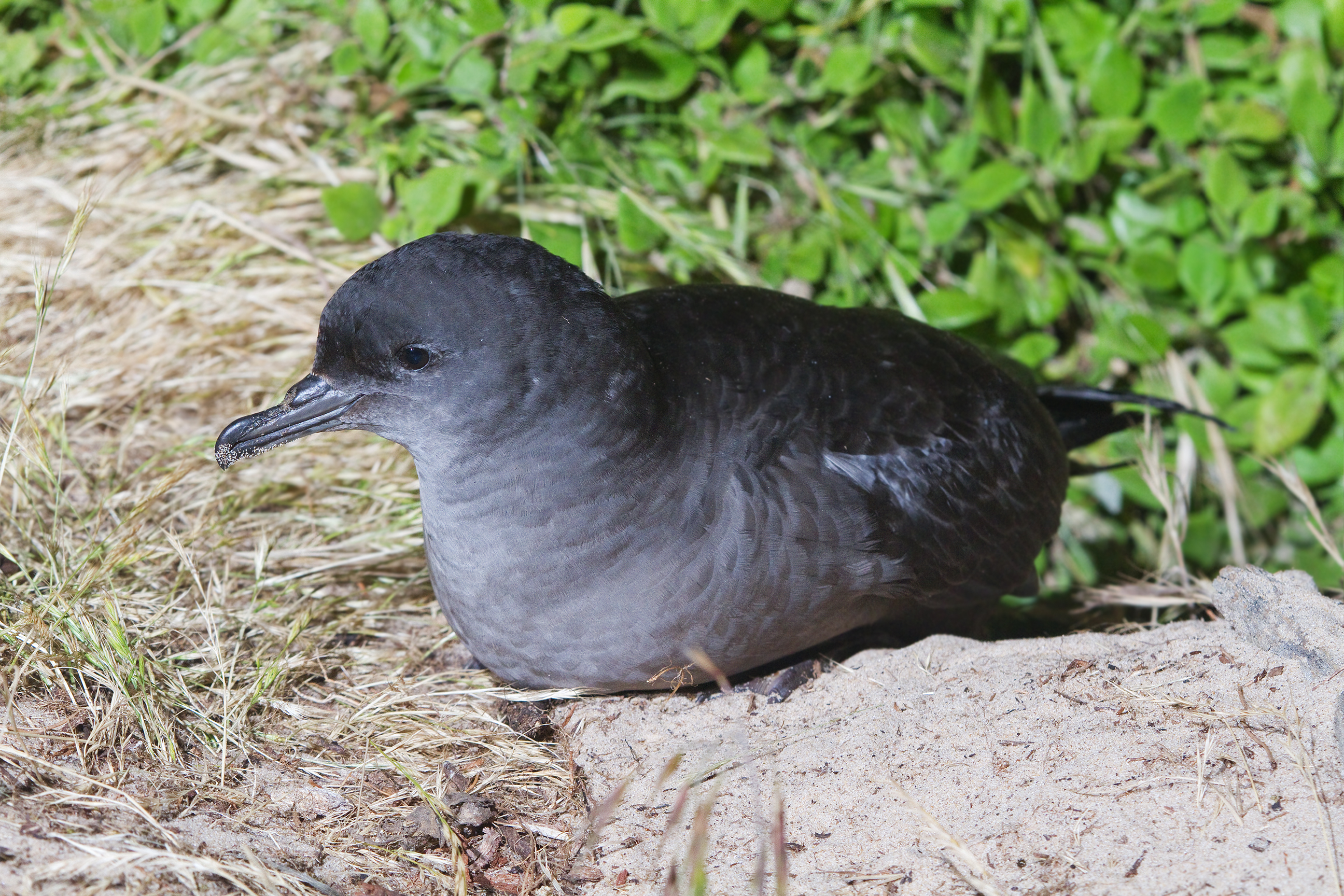
Mount Chappell Island
The Mount Chappell Island, part of the Badger Group within the Furneaux Group, is a unpopulated granite island with a distinctive central hill, located in Bass Strait, lying west of the Flinders and Cape Barren islands, Tasmania, south of Victoria, in south-eastern Australia. The island was originally named ''Mount Chappelle'' by Matthew Flinders for his wife's maiden name. The island is private property, used for grazing sheep and Cape Barren geese, and is a classic example of natural habitat degradation caused by human activities. The island forms part of the Chalky, Big Green and Badger Island Groups Important Bird Area. Fauna The island's habitats have been severely modified by slashing, ploughing, grazing and burning. Short-tailed shearwaters breed there. Little penguins used to breed in large numbers but have since ceased to do so. Apart from sheep, mammals introduced deliberately or inadvertently are the house mouse, a species of rat and feral cats. Reptiles pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matthew Flinders
Captain Matthew Flinders (16 March 1774 – 19 July 1814) was a British navigator and cartographer who led the first inshore circumnavigation of mainland Australia, then called New Holland. He is also credited as being the first person to utilise the name ''Australia'' to describe the entirety of that continent including Van Diemen's Land (now Tasmania), a title he regarded as being "more agreeable to the ear" than previous names such as ''Terra Australis''. Flinders was involved in several voyages of discovery between 1791 and 1803, the most famous of which are the circumnavigation of Australia and an earlier expedition when he and George Bass confirmed that Van Diemen's Land was an island. While returning to Britain in 1803, Flinders was arrested by the French governor at Isle de France (Mauritius). Although Britain and France were at war, Flinders thought the scientific nature of his work would ensure safe passage, but he remained under arrest for more than six years. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short-tailed Shearwater
The short-tailed shearwater or slender-billed shearwater (''Ardenna tenuirostris''; formerly ''Puffinus tenuirostris''), also called yolla or moonbird, and commonly known as the muttonbird in Australia, is the most abundant seabird species in Australian waters, and is one of the few Australian native birds in which the chicks are commercially harvested. It is a migratory species that breeds mainly on small islands in Bass Strait and Tasmania and migrates to the Northern Hemisphere for the boreal summer. Taxonomy This shearwater appears to be related to the sooty and great shearwaters, which are also blunt-tailed, black-billed species, but its precise relationships are obscure (Austin, 1996; Austin ''et al.'', 2004). These are among the larger species of shearwater, which have been moved to a separate genus, ''Ardenna'' based on a phylogenetic analysis of mitochondrial DNA (Penhallurick & Wink, 2004). Ecology Each parent feeds the single chick for 2–3 days and then leaves for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Important Bird Areas Of Tasmania
Importance is a property of entities that matter or make a difference. For example, World War II was an important event and Albert Einstein was an important person because of how they affected the world. There are disagreements in the academic literature about what type of difference is required. According to the causal impact view, something is important if it has a big causal impact on the world. This view is rejected by various theorists, who insist that an additional aspect is required: that the impact in question makes a value difference. This is often understood in terms of how the important thing affects the well-being of people. So on this view, World War II was important, not just because it brought about many wide-ranging changes but because these changes had severe negative impacts on the well-being of the people involved. The difference in question is usually understood counterfactually as the contrast between how the world actually is and how the world would have bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Islands Of Tasmania
Tasmania is the smallest and southernmost state of Australia. The Tasmanian mainland itself is an island, with an area of - 94.1% of the total land area of the state. The other islands have a combined area of , for a cumulative total of 99.75% of the state. About 1000 smaller islands make up the remaining of total land area. Classification structure A considerable number of Tasmanian islands are identified as being in island groups, including the Breaksea, Furneaux, Hogan, Hunter, Kent, Maatsuyker, Mutton Bird, New Year, Swainson, Trumpeter, and Waterhouse groups. Regions Similar to Regions of Tasmania the islands are generally distinguished by the coast that they are adjacent to, as well as Bass Strait - the main separation from the mainland state of Victoria. Five regions are aligned to the north coast and Bass Strait - ''North West Islands'' (including King Island), ''North Coast Islands'', ''North Bass Strait Islands'', ''Furneaux Islands'', and ''North East Islands' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three-lined Skink
The eastern three-lined skink (''Acritoscincus duperreyi''), also known commonly as the bold-striped cool-skink, is a species of skink, a lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to Australia. ''A. duperreyi'' has been extensively studied in the context of understanding the evolution of learning, viviparity in lizards, and temperature- and genetic-sex determination. ''A. duperreyi'' is classified as a species of "Least Concern" by the IUCN. Taxonomy The species has also been placed in the genus ''Bassiana'', with two other species of skink: ''B. trilineata'' and ''B. palynota.'' Micro-genetic analyses have revealed that the genus ''Bassiana'' began to diversify during the Miocene, suggesting that these three lineages started to form between 16.2 and 9.7 million years ago. Individual species in the genus began to diversify as well through the Miocene and into the Early Pleistocene. Within ''A. duperreyi'', population-level diversification between the population o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metallic Skink
:''"Metallic skink" may also refer to the garden skink (Lampropholis delicata)''. ''Carinascincus metallicus'', the metallic cool-skink or metallic skink is a species of skink in the family Scincidae. It is endemic to Australia, found in southern Victoria, as well as in Tasmania where it is the most widespread and common lizard, occurring on many offshore islands in Bass Strait Bass Strait () is a strait separating the island state of Tasmania from the Australian mainland (more specifically the coast of Victoria, with the exception of the land border across Boundary Islet). The strait provides the most direct waterwa ... as well as the mainland. It gives birth to live young. It is highly variable in colour and pattern, and may be a complex of closely related species.Cogger, H.G. (1979). ''Reptiles and Amphibians of Australia''. Reed: Sydney. References Carinascincus Skinks of Australia Endemic fauna of Australia Reptiles described in 1874 Taxa named by Arthu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carinascincus Ocellatus
The spotted skink (''Carinascincus ocellatus''), sometimes called the ocellated cool-skink or ocellated skink, is a skink endemic to Tasmania, Australia. It is a ground-dwelling, viviparous species, usually found in rocky habitats, and widespread in the northern and eastern parts of the state, as well as in the eastern Bass Strait Bass Strait () is a strait separating the island state of Tasmania from the Australian mainland (more specifically the coast of Victoria, with the exception of the land border across Boundary Islet). The strait provides the most direct waterwa ... islands. It is often found at Arthurs Lake in the Central Highlands of Tasmania.Cogger, H.G. (1979). ''Reptiles and Amphibians of Australia''. Reed: Sydney. Spotted skink populations are distributed along an altitudinal gradient, with variations in thermal conditions along the gradient affecting body temperature regulation and reproductive activity. Skinks in low to mid altitudes achieve their optimal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bougainville's Skink
Bougainville's skink (''Lerista bougainvillii'') is a species of skink, a lizard in the family Scincidae. This species is also commonly called the south-eastern slider and Bougainville's lerista. Etymology The specific name, ''bougainvillii'', and the common names, Bougainville's skink and Bougainville's lerista, are in honour of French naval officer Hyacinthe de Bougainville. Beolens B, Watkins M, Grayson M (2011). ''The Eponym Dictionary of Reptiles''. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. xiii + 296 pp. . (''Lerista bougainvillii'', p. 33). Geographic range ''L. bougainvillii'' is found in south-eastern Australia, including north-eastern Tasmania and many Bass Strait islands. Description Bougainville's skink has very reduced limbs and moves in a snake-like manner. Habitat The preferred natural habitats of ''L. bougainvillii'' are forest and shrubland. However, it is seldom seen, as much of its life is spent beneath leaf-litter, loose sand, and thin stone slabs. Cog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians (tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile orders, historically combined with that of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. The earliest known proto-reptiles originated around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feral Cat
A feral cat or a stray cat is an unowned domestic cat (''Felis catus'') that lives outdoors and avoids human contact: it does not allow itself to be handled or touched, and usually remains hidden from humans. Feral cats may breed over dozens of generations and become an aggressive local apex predator in urban, savannah and bushland environments. Some feral cats may become more comfortable with people who regularly feed them, but even with long-term attempts at socialization, they usually remain aloof and are most active after dusk. Feral cats are devastating to wildlife, and conservation biologists consider them to be one of the worst invasive species on Earth. Attempts to control feral cat populations are widespread but generally of greatest impact within purpose-fenced reserves. Some animal rights groups advocate trap-neuter-return programs to prevent the feral cats from continuing to breed. Scientific evidence has demonstrated that TNR is not effective at controlling f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Mouse
The house mouse (''Mus musculus'') is a small mammal of the order Rodentia, characteristically having a pointed snout, large rounded ears, and a long and almost hairless tail. It is one of the most abundant species of the genus '' Mus''. Although a wild animal, the house mouse has benefited significantly from associating with human habitation to the point that truly wild populations are significantly less common than the semi-tame populations near human activity. The house mouse has been domesticated as the pet or fancy mouse, and as the laboratory mouse, which is one of the most important model organisms in biology and medicine. The complete mouse reference genome was sequenced in 2002. Characteristics House mice have an adult body length (nose to base of tail) of and a tail length of . The weight is typically . In the wild they vary in color from grey and light brown to black (individual hairs are actually agouti coloured), but domesticated fancy mice and laboratory mice ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |