|
Moseley Railway Trust
The Moseley Railway Trust is a major British collection of industrial narrow gauge locomotives and other equipment. It originally had its base in south Manchester, but has relocated to the Apedale Community Country Park near Newcastle-under-Lyme, Staffordshire, where the Apedale Valley Light Railway and an important museum are being established next to the Apedale Heritage Centre. Phase 1 of the narrow gauge Apedale Valley Light Railway opened to the public in during August 2010. Plans for the large new museum building have been approved by the local council and it was intended that construction will commence during 2011. It is planned that there will eventually be an industrial demonstration railway line running around the perimeter of the MRT/Apedale Heritage Centre site, connecting with a recreation of an adit called No 7 Drift, from which coal was extracted by the previous occupiers of the site, the Aurora Mining Company, until around 1998. Overview From summer 1998 to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newcastle-under-Lyme
Newcastle-under-Lyme ( RP: , ) is a market town and the administrative centre of the Borough of Newcastle-under-Lyme in Staffordshire, England. The 2011 census population of the town was 75,082, whilst the wider borough had a population of 128,264 in 2016, up from 123,800 in the 2011 Census. Toponym The name "Newcastle" is derived from a mid 12th century motte and bailey that was built after King Stephen granted lands in the area to Ranulf de Gernon, Earl of Chester; the land was for his support during the civil war known as The Anarchy. "Lyme" might refer to the Lyme Brook or the Forest of Lyme (with lime and elm trees) that covered an extensive area across the present day counties of Cheshire, Staffordshire and parts of Derbyshire. History 12th–19th centuries Newcastle was not recorded in the 1086 Domesday Book, as it grew up round a 12th-century castle, but it must have gained rapid importance, as a charter, known solely through a reference in another charter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheadle, Greater Manchester
Cheadle () is a village in the Metropolitan Borough of Stockport, Greater Manchester, England. Within the boundaries of the historic county of Cheshire, it borders Cheadle Hulme, Gatley, Heald Green and Cheadle Heath in Stockport, and East Didsbury in Manchester. , it had a population of 14,698. History There has been human occupation in the area that is now Cheadle since prehistoric times. The earliest evidence of civilisation is of burial mounds dating from the Iron Age, belonging to Celts who occupied Britain. Later, the area was occupied by Brigantes, whose activity was discovered in the form of axe fragments. In the first millennium, Romans occupied the area, and their coins have been discovered. During the seventh century, St. Chad preached in the area. A stone cross dedicated to him was found close to the confluence of the River Mersey and Micker Brook in 1873.Squire, p.1 The village is first recorded in the Domesday Book under the name "Cedde",Clarke, p.3 which c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
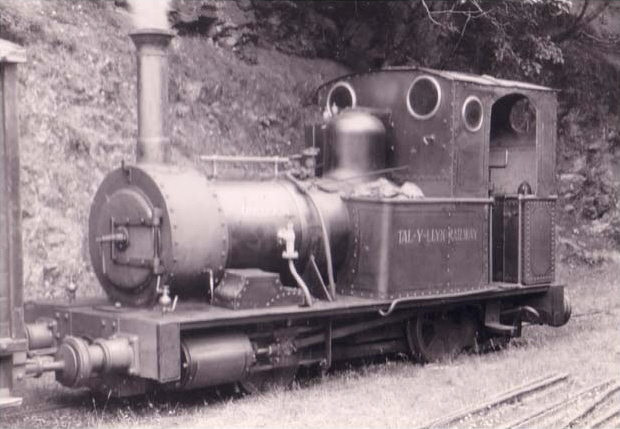
Gloddfa Ganol
Gloddfa Ganol (also known as the Gloddfa Ganol Mountain Center) was a museum dedicated to the Welsh slate industry and narrow-gauge railways, situated in the Oakeley slate quarry in Blaenau Ffestiniog. It opened in 1974 and closed in 1998 following an auction of its exhibits. Gloddfa Ganol Mountain Center The Oakeley slate quarry was the largest underground slate mine in the world, but it suffered from a sharp decline in worldwide demand for slate after the Second World War. As quarrying declined in the 1970s, the owners sought to diversify to serve the growing tourist trade in Wales. In 1974 the abandoned Middle Quarry was re-opened, producing architectural slab, and as an attraction to the public - the Gloddfa Ganol Mountain Center. The centre offered guided tours of several miles of underground tunnels and chambers and was based in the old Middle Mill, which had been rebuilt for the purpose. Rich Morris collection Railway enthusiast Rich Morris began collecting narrow ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Narrow Gauge Railways
There were more than a thousand British narrow-gauge railways ranging from large, historically significant common carriers to small, short-lived industrial railways. Many notable events in British railway history happened on narrow-gauge railways including the first use of steam locomotives, the first public railway and the first preserved railway. History Early railways: before 1865 The earliest narrow-gauge railways were crude wooden trackways used in coal mines to guide wooden tubs. Because of the restricted loading gauge of the tunnels and the need for the tubs to be small enough to be pushed by one man, these railways were almost all narrow gauge. These underground lines often had short above-ground sections as well. After the start of the Industrial Revolution it became possible to create railways with iron tracks and wheels, which reduced the friction involved in moving wagons and made longer horse-hauled trains possible. These could move more material over longer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadeby Light Railway
The Cadeby Light Railway was a narrow-gauge railway in the garden of the rectory in Cadeby, Leicestershire. In the early 1960s the Reverend Teddy Boston became rector of All Saints' Church, Cadeby. Boston was a lifelong railway enthusiast and wanted to build a miniature railway in his new garden, but the cost proved prohibitive. Instead he searched for a full-sized narrow-gauge locomotive. In 1962, he purchased ''Pixie'', a W.G. Bagnall from the Cranford quarry. The quarry owners donated a short length of track and two wagons and the Cadeby Light Railway was opened. Over the years, Boston built an extensive collection of ex-industrial narrow-gauge rolling stock, which ran on the extremely short line in his garden. He also maintained an extensive OO gauge model railway at Cadeby. Although Boston died in 1986, his widow, Audrey kept the railway open for nearly twenty years, holding regular open days. The railway finally closed in May 2005. The majority of the collection h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avonside Engine Company
The Avonside Engine Company was a locomotive manufacturer in Avon Street, St Philip's Marsh, St. Philip's, Bristol, England between 1864 and 1934. However the business originated with an earlier enterprise Henry Stothert and Company. Origins The firm was originally started by Henry Stothert in 1837 as Henry Stothert and Company. Henry was the son of George Stothert (senior), founder of the nearby Bath, Somerset, Bath engineering firm of Stothert & Pitt. Henry's brother, also named George, was manager of the same firm. The company was given an order for two broad gauge () GWR Firefly Class, Firefly class express passenger engines ''Arrow'' and ''Dart'', with driving wheels, delivered for the opening of the Great Western Railway (GWR) from Bristol to Bath, Somerset, Bath on 31 August 1840. This was soon followed by an order for eight smaller GWR Sun Class, Sun class engines with driving wheels. Stothert, Slaughter and Company Edward Slaughter joined the company in 1841, when i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
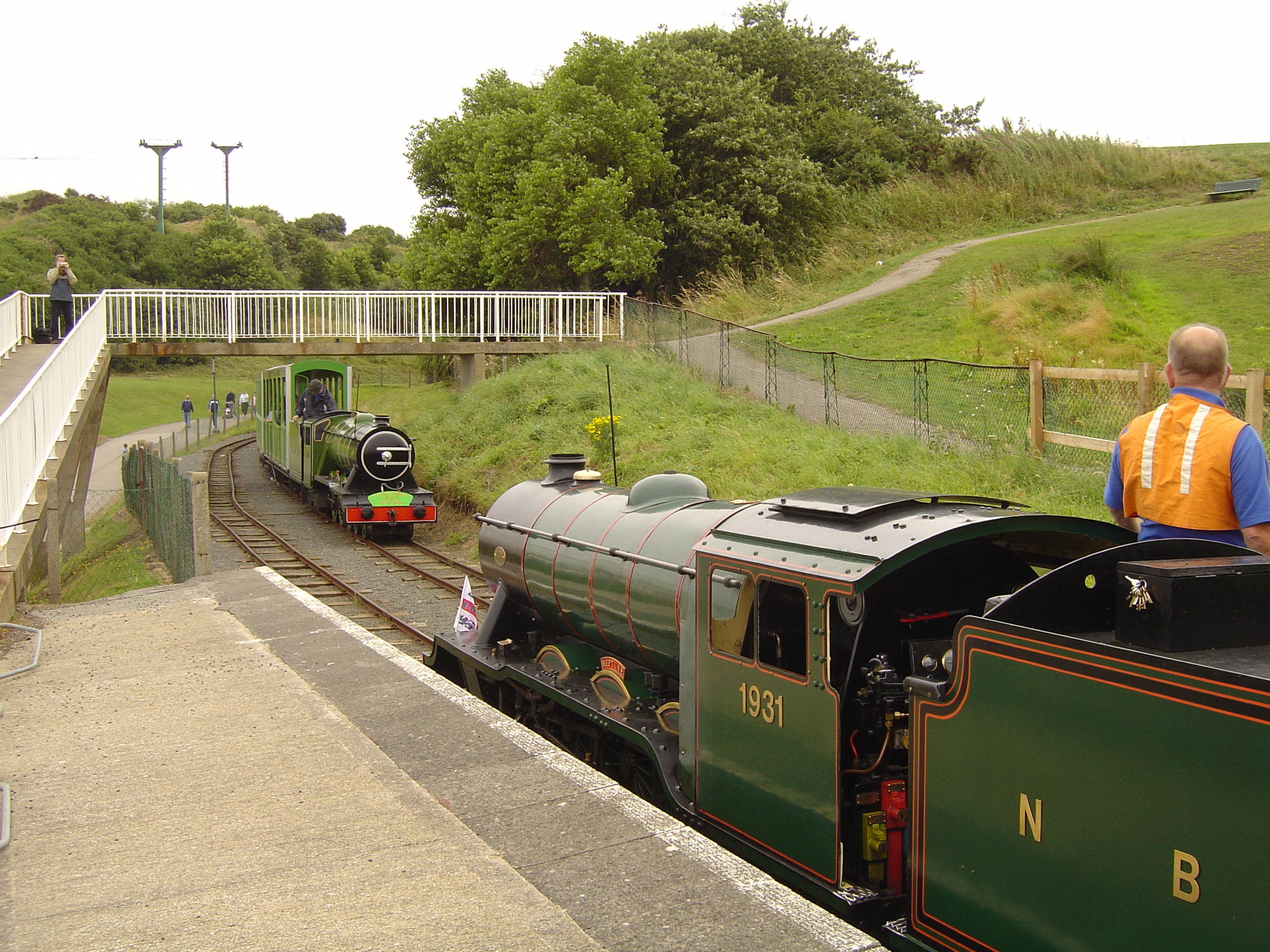
North Bay Railway Engineering Services
Scarborough North Bay Railway (SNBR) is a ridable miniature railway (also known as a minimum-gauge railway) in Scarborough, North Yorkshire, England. It was built in 1931, to the gauge of , and runs for approximately between Peasholm Park and Scalby Mills in the North Bay area of the town. The railway attracted approximately 200,000 visitors in the 2014–2015 season, and remains popular with tourists. History Various patches of land were bought up by the Scarborough Corporation during the late 1920s and early 1930s. Originally, the railway was set further back, but its terminus at Peasholm Park was amended so that it could be seen by pedestrian traffic going to North Bay. The opening ceremony took place at 2 p.m. on Saturday 23 May 1931. The locomotive, ''Neptune'', was officially handed over by the Chairman of the North Side Development Committee, Alderman Whitehead, to the Mayor of Scarborough, Alderman J. W. Butler, for the Entertainments Department. Alderman Whiteh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |