|
Moritz Weber
Moritz Weber (1871–1951), was a professor of naval mechanics at the Polytechnic Institute of Berlin. The dimensionless numbers Reynolds number (named after the British scientist and mathematician Osborne Reynolds), and Froude number (named after the British engineer William Froude) was coined by Moritz Weber. Moreover, the dimensionless number Weber number was coined after him. Weber was also responsible in coining the term similitude Similitude is a concept applicable to the testing of engineering models. A model is said to have similitude with the real application if the two share geometric similarity, kinematic similarity and dynamic similarity. ''Similarity'' and ''simili ... to describe model studies that were scaled both geometrically and using dimensionless parameters for forces. References Academic staff of the Technical University of Berlin 1871 births 1951 deaths Place of birth missing Date of birth missing {{Germany-scientist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reynolds Number
In fluid mechanics, the Reynolds number () is a dimensionless quantity that helps predict fluid flow patterns in different situations by measuring the ratio between inertial and viscous forces. At low Reynolds numbers, flows tend to be dominated by laminar (sheet-like) flow, while at high Reynolds numbers flows tend to be turbulent. The turbulence results from differences in the fluid's speed and direction, which may sometimes intersect or even move counter to the overall direction of the flow ( eddy currents). These eddy currents begin to churn the flow, using up energy in the process, which for liquids increases the chances of cavitation. The Reynolds number has wide applications, ranging from liquid flow in a pipe to the passage of air over an aircraft wing. It is used to predict the transition from laminar to turbulent flow and is used in the scaling of similar but different-sized flow situations, such as between an aircraft model in a wind tunnel and the full-size ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
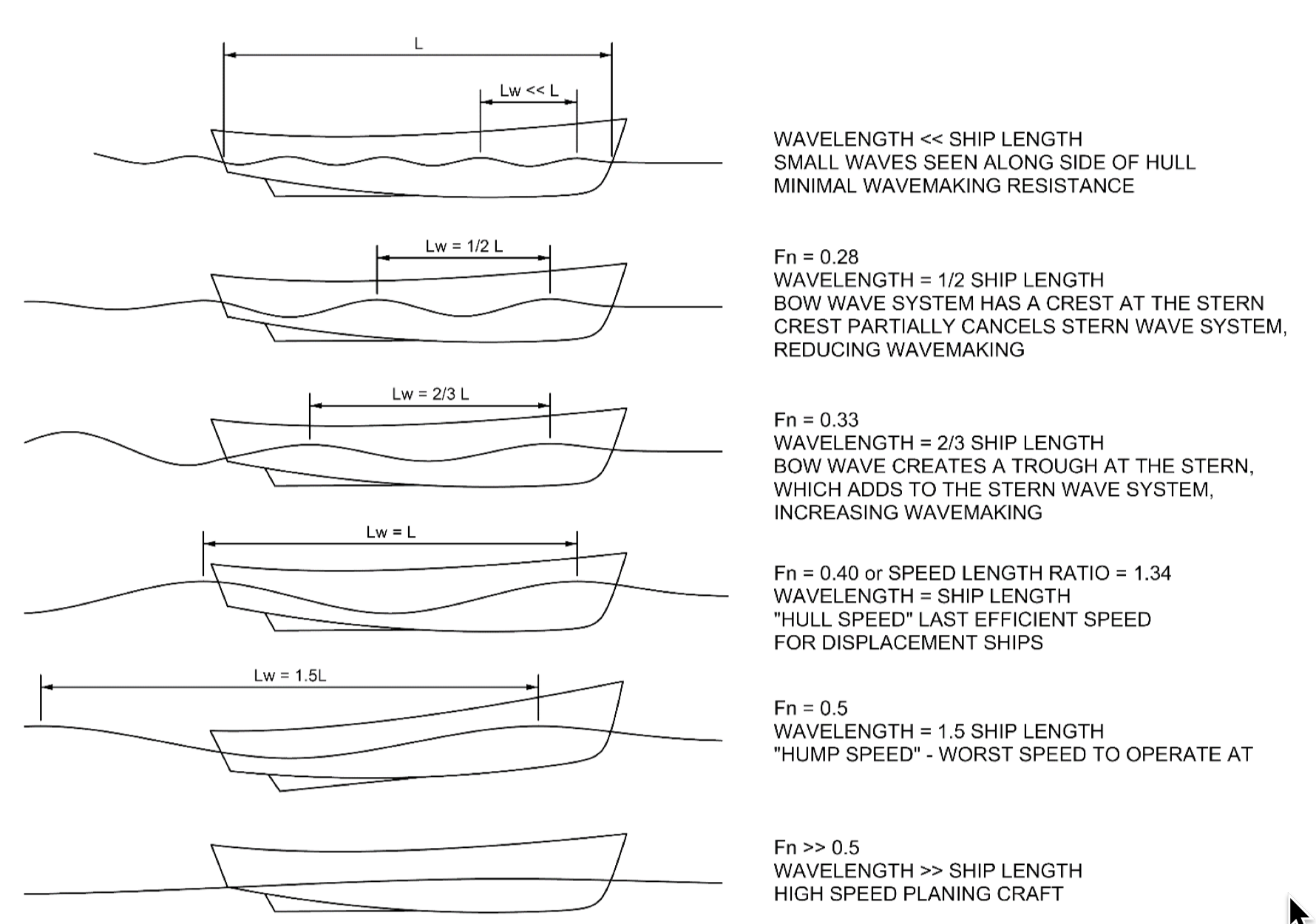
Froude Number
In continuum mechanics, the Froude number (, after William Froude, ) is a dimensionless number defined as the ratio of the flow inertia to the external field (the latter in many applications simply due to gravity). The Froude number is based on the speed–length ratio which he defined as: \mathrm = \frac where is the local flow velocity, is the local external field, and is a characteristic length. The Froude number has some analogy with the Mach number. In theoretical fluid dynamics the Froude number is not frequently considered since usually the equations are considered in the high Froude limit of negligible external field, leading to homogeneous equations that preserve the mathematical aspects. For example, homogeneous Euler equations are conservation equations. However, in naval architecture the Froude number is a significant figure used to determine the resistance of a partially submerged object moving through water. Origins In open channel flows, introduced first th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osborne Reynolds
Osborne Reynolds (23 August 1842 – 21 February 1912) was an Irish-born innovator in the understanding of fluid dynamics. Separately, his studies of heat transfer between solids and fluids brought improvements in boiler and condenser design. He spent his entire career at what is now the University of Manchester. Life Osborne Reynolds was born in Belfast and moved with his parents soon afterward to Dedham, Essex. His father worked as a school headmaster and clergyman, but was also a very able mathematician with a keen interest in mechanics. The father took out a number of patents for improvements to agricultural equipment, and the son credits him with being his chief teacher as a boy. Reynolds showed an early aptitude and liking for the study of mechanics. In his late teens, for the year before entering university, he went to work as an apprentice at the workshop of Edward Hayes, a well known shipbuilder in Stony Stratford, where he obtained practical experience in the manufa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Froude
William Froude (; 28 November 1810 in Devon – 4 May 1879 in Simonstown, South Africa) was an English engineer, hydrodynamicist and naval architect. He was the first to formulate reliable laws for the resistance that water offers to ships (such as the hull speed equation) and for predicting their stability. Biography Froude was born at Dartington, Devon, England, the son of Robert Froude, Archdeacon of Totnes and was educated at Westminster School and Oriel College, Oxford, graduating with a first in mathematics in 1832. His first employment was as a surveyor on the South Eastern Railway which, in 1837, led to Brunel giving him responsibility for the construction of a section of the Bristol and Exeter Railway. It was here that he developed his empirical method of setting out track transition curves and introduced an alternative design to the helicoidal skew arch bridge at Rewe and Cowley Bridge Junction, near Exeter. During this period he lived in Cullompton and was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weber Number
The Weber number (We) is a dimensionless number in fluid mechanics that is often useful in analysing fluid flows where there is an interface between two different fluids, especially for multiphase flows with strongly curved surfaces. It is named after Moritz Weber (1871–1951). It can be thought of as a measure of the relative importance of the fluid's inertia compared to its surface tension. The quantity is useful in analyzing thin film flows and the formation of droplets and bubbles. Mathematical expression The Weber number may be written as: :\mathrm = \frac = \left( \frac \right) \frac = \frac where * C_\mathrm is the drag coefficient of the body cross-section. * \rho is the density of the fluid ( kg/ m3). * v is its velocity (m/ s). * l is its characteristic length, typically the droplet diameter (m). * \sigma is the surface tension Surface tension is the tendency of liquid surfaces at rest to shrink into the minimum surface area possible. Surface te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Similitude (model)
Similitude is a concept applicable to the testing of engineering models. A model is said to have similitude with the real application if the two share geometric similarity, kinematic similarity and dynamic similarity. ''Similarity'' and ''similitude'' are interchangeable in this context. The term dynamic similitude is often used as a catch-all because it implies that geometric and kinematic similitude have already been met. Similitude's main application is in hydraulic and aerospace engineering to test fluid flow conditions with scaled models. It is also the primary theory behind many textbook formulas in fluid mechanics. The concept of similitude is strongly tied to dimensional analysis. Overview Engineering models are used to study complex fluid dynamics problems where calculations and computer simulations aren't reliable. Models are usually smaller than the final design, but not always. Scale models allow testing of a design prior to building, and in many cases are a cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academic Staff Of The Technical University Of Berlin
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of secondary or tertiary higher learning (and generally also research or honorary membership). The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 385 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the goddess of wisdom and skill, north of Athens, Greece. Etymology The word comes from the ''Academy'' in ancient Greece, which derives from the Athenian hero, ''Akademos''. Outside the city walls of Athens, the gymnasium was made famous by Plato as a center of learning. The sacred space, dedicated to the goddess of wisdom, Athena, had formerly been an olive grove, hence the expression "the groves of Academe". In these gardens, the philosopher Plato conversed with followers. Plato developed his sessions into a method of teaching philosophy and in 387 BC, established what is known today as the Old Academy. By extension, ''academia'' has come to mean the accumulation, dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1871 Births
Events January–March * January 3 – Franco-Prussian War – Battle of Bapaume: Prussians win a strategic victory. * January 18 – Proclamation of the German Empire: The member states of the North German Confederation and the south German states, aside from Austria, unite into a single nation state, known as the German Empire. The King of Prussia is declared the first German Emperor as Wilhelm I of Germany, in the Hall of Mirrors at the Palace of Versailles. Constitution of the German Confederation comes into effect. It abolishes all restrictions on Jewish marriage, choice of occupation, place of residence, and property ownership, but exclusion from government employment and discrimination in social relations remain in effect. * January 21 – Giuseppe Garibaldi's group of French and Italian volunteer troops, in support of the French Third Republic, win a battle against the Prussians in the Battle of Dijon. * February 8 – 1871 French legislative election elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1951 Deaths
Events January * January 4 – Korean War: Third Battle of Seoul – Chinese and North Korean forces capture Seoul for the second time (having lost the Second Battle of Seoul in September 1950). * January 9 – The Government of the United Kingdom announces abandonment of the Tanganyika groundnut scheme for the cultivation of peanuts in the Tanganyika Territory, with the writing off of £36.5M debt. * January 15 – In a court in West Germany, Ilse Koch, The "Witch of Buchenwald", wife of the commandant of the Buchenwald concentration camp, is sentenced to life imprisonment. * January 20 – Winter of Terror: Avalanches in the Alps kill 240 and bury 45,000 for a time, in Switzerland, Austria and Italy. * January 21 – Mount Lamington in Papua New Guinea erupts catastrophically, killing nearly 3,000 people and causing great devastation in Oro Province. * January 25 – Dutch author Anne de Vries releases the first volume of his children's novel '' Journey Through the Nigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Place Of Birth Missing
Place may refer to: Geography * Place (United States Census Bureau), defined as any concentration of population ** Census-designated place, a populated area lacking its own municipal government * "Place", a type of street or road name ** Often implies a dead end (street) or cul-de-sac * Place, based on the Cornish word "plas" meaning mansion * Place, a populated place, an area of human settlement ** Incorporated place (see municipal corporation), a populated area with its own municipal government * Location (geography), an area with definite or indefinite boundaries or a portion of space which has a name in an area Placenames * Placé, a commune in Pays de la Loire, Paris, France * Plače, a small settlement in Slovenia * Place (Mysia), a town of ancient Mysia, Anatolia, now in Turkey * Place, New Hampshire, a location in the United States * Place House, a 16th-century mansion largely remodelled in the 19th century, in Fowey, Cornwall * Place House, a 19th-century mansion on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)


_(LOC)_-_Flickr_-_The_Library_of_Congress.jpg)
