|
Montroydite
Montroydite is the mineral form of mercury(II) oxide with formula HgO. It is a rare mercury mineral. It was first described for an occurrence in the mercury deposit at Terlingua, Texas and named for Montroyd Sharp who was an owner of the deposit. Montroydite occurs in mercury deposits of hydrothermal origin. Associated minerals include: native mercury, cinnabar, metacinnabar, calomel, eglestonite, terlinguaite, mosesite, kleinite, edgarbaileyite, gypsum, calcite and dolomite Dolomite may refer to: *Dolomite (mineral), a carbonate mineral *Dolomite (rock), also known as dolostone, a sedimentary carbonate rock *Dolomite, Alabama, United States, an unincorporated community *Dolomite, California, United States, an unincor .... References Mercury(II) minerals Oxide minerals Orthorhombic minerals {{oxide-mineral-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
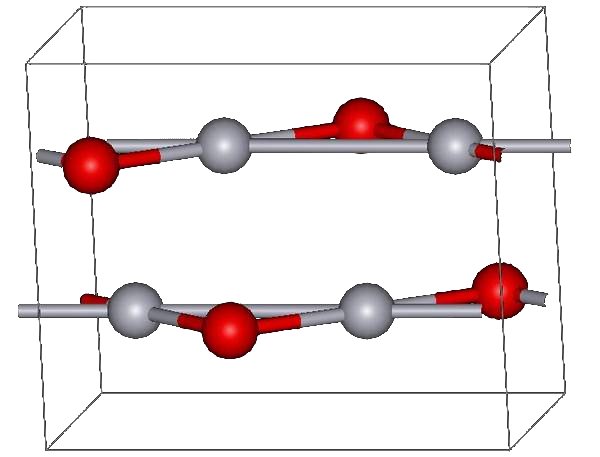
Mercury(II) Oxide
Mercury(II) oxide, also called mercuric oxide or simply mercury oxide, is the inorganic compound with the formula Hg O. It has a red or orange color. Mercury(II) oxide is a solid at room temperature and pressure. The mineral form montroydite is very rarely found. History An experiment for the preparation of mercuric oxide was first described by 11th century Arab-Spanish alchemist, Maslama al-Majriti, in ''Rutbat al-hakim.'' In 1774, Joseph Priestley discovered that oxygen was released by heating mercuric oxide, although he did not identify the gas as oxygen (rather, Priestley called it " dephlogisticated air," as that was the paradigm that he was working under at the time). Synthesis The red form of HgO can be made by heating Hg in oxygen at roughly 350 °C, or by pyrolysis of Hg(NO3)2. The yellow form can be obtained by precipitation of aqueous Hg2+ with alkali. The difference in color is due to particle size; both forms have the same structure consisting of near lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosesite
Mosesite is a very rare mineral found in few locations. It is a mercury mineral found as an accessory in deposits of mercury, often in conjunction with limestone. It is known to be found in the U.S. states of Texas and Nevada, and the Mexican states of Guerrero and Querétaro. It was named after Professor Alfred J. Moses (1859–1920) for his contributions to the field of mineralogy in discovering several minerals found alongside mosesite. The mineral itself is various shades of yellow and a high occurrence of spinel twinning. It becomes isotropic when heated to . Composition Mosesite contains 16 Hg, 3 Cl, SO4, CO3, MoO4, 16 H, and 8 N with a volume of 8.4777x10−1 nm3 and calculated density of 7.53 g/cm3. Its chemical formula is . Geologic occurrence Discovered in a mercury mine in Terlingua, Texas, mosesite has also been seen in Nevada and Mexico. Mosesite is a secondary mineral formed at low temperature in hydrothermal mercury deposits. The mercury ore at the mine in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calomel
Calomel is a mercury chloride mineral with formula Hg2Cl2 (see mercury(I) chloride). The name derives from Greek ''kalos'' (beautiful) and ''melas'' (black) because it turns black on reaction with ammonia. This was known to alchemists. Calomel occurs as a secondary mineral which forms as an alteration product in mercury deposits. It occurs with native mercury, amalgam, cinnabar, mercurian tetrahedrite, eglestonite, terlinguaite, montroydite, kleinite, moschelite, kadyrelite, kuzminite, chursinite, kelyanite, calcite, limonite and various clay minerals. The type locality is Moschellandsburg, Alsenz-Obermoschel, Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. History The substance later known as calomel was first documented in ancient Persia by medical historian Rhazes in year 850. Only a few of the compounds he mentioned could be positively identified as calomel, as not every alchemist disclosed what compounds they used in their drugs. Calomel first entered Western medical literature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxide Mineral
The oxide mineral class includes those minerals in which the oxide anion (O2−) is bonded to one or more metal alloys. The hydroxide-bearing minerals are typically included in the oxide class. The minerals with complex anion groups such as the silicates, sulfates, carbonates and phosphates are classed separately. Simple oxides: *XO **Periclase group ***Periclase ***Manganosite **Zincite group ***Zincite *** Bromellite ***Tenorite ***Litharge * **Cuprite **Ice * **Hematite group ***Corundum ***Hematite ***Ilmenite * **Rutile group ***Rutile ***Pyrolusite ***Cassiterite **Baddeleyite **Uraninite **Thorianite * **Spinel group ***Spinel ***Gahnite ***Magnetite ***Franklinite ***Chromite **Chrysoberyl **Columbite *Hydroxide subgroup: **Brucite **Manganite ** Romanèchite **Goethite group: ***Diaspore ***Goethite Nickel–Strunz Classification -04- Oxides IMA-CNMNC proposes a new hierarchical scheme (Mills et al., 2009). This list uses it to modify ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury(II) Minerals
Mercury commonly refers to: * Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun * Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg * Mercury (mythology), a Roman god Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to: Companies * Mercury (toy manufacturer), a brand of diecast toy cars manufactured in Italy * Mercury Communications, a British telecommunications firm set up in the 1980s * Mercury Drug, a Philippine pharmacy chain * Mercury Energy, an electricity generation and retail company in New Zealand * Mercury Filmworks, a Canadian independent animation studio * Mercury General, a multiple-line American insurance organization * Mercury Interactive, a software testing tools vendor * Mercury Marine, a manufacturer of marine engines, particularly outboard motors * Mercury Systems, a defense-related information technology company Computing * Mercury (programming language), a functional logic programming language * Mercury (metadata search system), a data search system f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolomite (mineral)
Dolomite () is an anhydrous carbonate mineral composed of calcium magnesium carbonate, ideally The term is also used for a sedimentary carbonate rock composed mostly of the mineral dolomite. An alternative name sometimes used for the dolomitic rock type is dolostone. History As stated by Nicolas-Théodore de Saussure the mineral dolomite was probably first described by Carl Linnaeus in 1768. In 1791, it was described as a rock by the French naturalist and geologist Déodat Gratet de Dolomieu (1750–1801), first in buildings of the old city of Rome, and later as samples collected in the mountains now known as the Dolomite Alps of northern Italy. Nicolas-Théodore de Saussure first named the mineral (after Dolomieu) in March 1792. Properties The mineral dolomite crystallizes in the trigonal-rhombohedral system. It forms white, tan, gray, or pink crystals. Dolomite is a double carbonate, having an alternating structural arrangement of calcium and magnesium ions. Unless it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcite
Calcite is a Carbonate minerals, carbonate mineral and the most stable Polymorphism (materials science), polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness, based on Scratch hardness, scratch hardness comparison. Large calcite crystals are used in optical equipment, and limestone composed mostly of calcite has numerous uses. Other polymorphs of calcium carbonate are the minerals aragonite and vaterite. Aragonite will change to calcite over timescales of days or less at temperatures exceeding 300 °C, and vaterite is even less stable. Etymology Calcite is derived from the German ''Calcit'', a term from the 19th century that came from the Latin word for Lime (material), lime, ''calx'' (genitive calcis) with the suffix "-ite" used to name minerals. It is thus etymologically related to chalk. When applied by archaeology, archaeologists and stone trade pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, blackboard or sidewalk chalk, and drywall. Alabaster, a fine-grained white or lightly tinted variety of gypsum, has been used for sculpture by many cultures including Ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, Ancient Rome, the Byzantine Empire, and the Nottingham alabasters of Medieval England. Gypsum also crystallizes as translucent crystals of selenite. It forms as an evaporite mineral and as a hydration product of anhydrite. The Mohs scale of mineral hardness defines gypsum as hardness value 2 based on scratch hardness comparison. Etymology and history The word ''gypsum'' is derived from the Greek word (), "plaster". Because the quarries of the Montmartre district of Paris have long furnished burnt gypsum (calcined gypsum) used for various purposes, this dehydrated gypsum became known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kleinite
Kleinite is a rare mineral that has only been found in the United States and Germany that occurs in hydrothermal mercury deposits. It occurs associated with calcite, gypsum and (rarely) barite or calomel. Its color can range from pale yellow/canary yellow to orange, and it is transparent to translucent. As a photosensitive mineral, its coloration darkens when exposed to light. It has been hypothesized that kleinite formed through a "reaction of cinnabar with oxidized meteoric water", with this reaction being the source of kleinite's nitrogen. Etymology Kleinite is named after Carl Klein (1842–1907), who was a professor of mineralogy at the University of Berlin. File:Kleinite-Calcite-285098.jpg, Kleinite on calcite, from McDermitt Mine (Cordero Mine; Old Cordero Mine), Opalite District, Humboldt County, Nevada, United States See also * Halide minerals * List of minerals This is a list of minerals for which there are articles on Wikipedia. Minerals are distinguished by var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terlinguaite
Terlinguaite is the naturally occurring mineral with formula Hg2 Cl O. It is formed by the weathering of other mercury-containing minerals. It was discovered in 1900 in the Terlingua District of Brewster County Brewster County is a county located in the U.S. state of Texas. It is in West Texas and its county seat (and only city) is Alpine. It is one of the nine counties that comprise the Trans-Pecos region, and borders Mexico. Brewster County is th ..., Texas, for which it is named. Its color is yellow, greenish yellow, brown, or olive green. References Mercury minerals Halide minerals Geology of Texas Oxychlorides Monoclinic minerals Minerals in space group 15 {{halide-mineral-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |