|
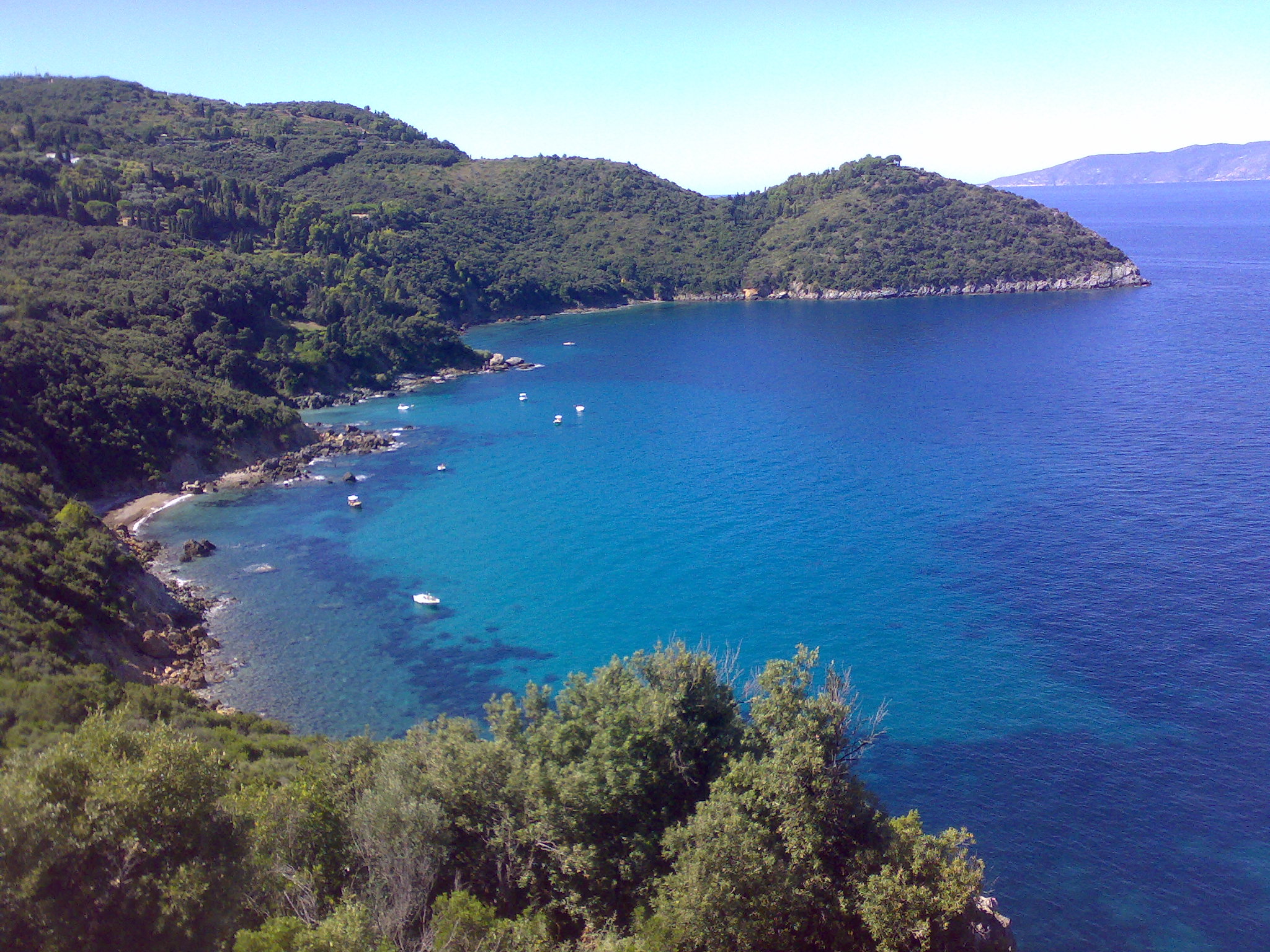
Monte Argentario
Monte Argentario is a ''comune'' (municipality) and a peninsula belonging to the Province of Grosseto in the Italian region Tuscany, located about south of Florence and about south of Grosseto. The peninsula is connected with the mainland by three spits of land which form two lagoons, the ''Laguna di Ponente'' on the west side and the ''Laguna di Levante'' on the east side of the middle dam. The two main villages on Monte Argentario are Porto Santo Stefano, chief town, facing north, and Porto Ercole facing south. The panoramic road ''Strada panoramica'' starts in Porto Santo Stefano allowing splendid views of the coast and the Tuscan Archipelago. Monte Argentario borders the ''comune'' of Orbetello, which is located on the middle dam between the two lagoons. Geography Monte Argentario is a promontory stretching towards the Tyrrhenian Sea in correspondence of the two southernmost islands of the Tuscan Archipelago, Giglio and Giannutri. The promontory was an island in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuscany
it, Toscano (man) it, Toscana (woman) , population_note = , population_blank1_title = , population_blank1 = , demographics_type1 = Citizenship , demographics1_footnotes = , demographics1_title1 = Italian , demographics1_info1 = 90% , demographics1_title2 = , demographics1_info2 = , demographics1_title3 = , demographics1_info3 = , timezone1 = CET , utc_offset1 = +1 , timezone1_DST = CEST , utc_offset1_DST = +2 , postal_code_type = , postal_code = , area_code_type = ISO 3166 code , area_code = IT-52 , blank_name_sec1 = GDP (nominal) , blank_info_sec1 = €118 billion (2018) , blank1_name_sec1 = GDP per capita , blank1_info_sec1 = €31,500 (2018) , blank2_name_sec1 = HDI (2019) , blank2_info_sec1 = 0.907 • 6th of 21 , blank_name_sec2 = NUTS Region , blank_info_sec2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tombolo
A tombolo is a sandy or shingle isthmus. A tombolo, from the Italian ', meaning 'pillow' or 'cushion', and sometimes translated incorrectly as '' ayre'' (an ayre is a shingle beach of any kind), is a deposition landform by which an island becomes attached to the mainland by a narrow piece of land such as a spit or bar. Once attached, the island is then known as a tied island. Several islands tied together by bars which rise above the water level are called a tombolo cluster. Two or more tombolos may form an enclosure (called a lagoon) that can eventually fill with sediment. Formation The shoreline moves toward the island (or detached breakwater) due to accretion of sand in the lee of the island, where wave energy and longshore drift are reduced and therefore deposition of sand occurs. Wave diffraction and refraction True tombolos are formed by wave refraction and diffraction. As waves near an island, they are slowed by the shallow water surrounding it. These wav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orsini Family
The House of Orsini is an Italian noble family that was one of the most influential princely families in medieval Italy and Renaissance Rome. Members of the Orsini family include five popes: Stephen II (752-757), Paul I (757-767), Celestine III (1191–1198), Nicholas III (1277–1280), and Benedict XIII (1724–1730). In addition, the family included 34 cardinals, numerous '' condottieri'', and other significant political and religious figures. Origins According to their own family legend, the Orsini are descended from the Julio-Claudian dynasty of ancient Rome. The Orsini carried on a political feud with the Colonna family for centuries in Rome, until it was stopped by Papal Bull in 1511. In 1571, the heads of both families married nieces of Pope Sixtus V as an act of reconciliation. Ironically the Colonna family also claims descent from the Julio-Claudian dynasty of ancient Rome. The Orsini descend from Cajo Orso Orsini who lived c. 600 CE. Five popes are descende ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldobrandeschi Family
The Aldobrandeschi were an Italian noble family from southern Tuscany. Overview Of probable Lombard origin, they appear in history as counts in the 9th century. The first known count was Hildebrand II (857). Their possession extended to what is now southern Tuscany and northern Lazio regions of Italy. In 1274, their lands were divided between the County of Santa Fiora and the County of Sovana, which thenceforth were ruled by different branches of the family. After the extinction of the Aldobrandeschi of Sovana, the county was assigned to the Orsini. The Aldobrandeschi heiress of Santa Fiora married into the Sforza family. The most famous members were: Guglielmo Aldobrandeschi, who lived in the 13th century and is cited by Dante Alighieri as the ''Gran Tosco'' ("Grand Tuscan"); Guglielmo's son is also cited in Canto XI of the ''Purgatorio'' in the '' Divine Comedy'' as an example of a sinner of pride; and Margherita, the last of the Aldobrandeschi of Sovana, who married ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
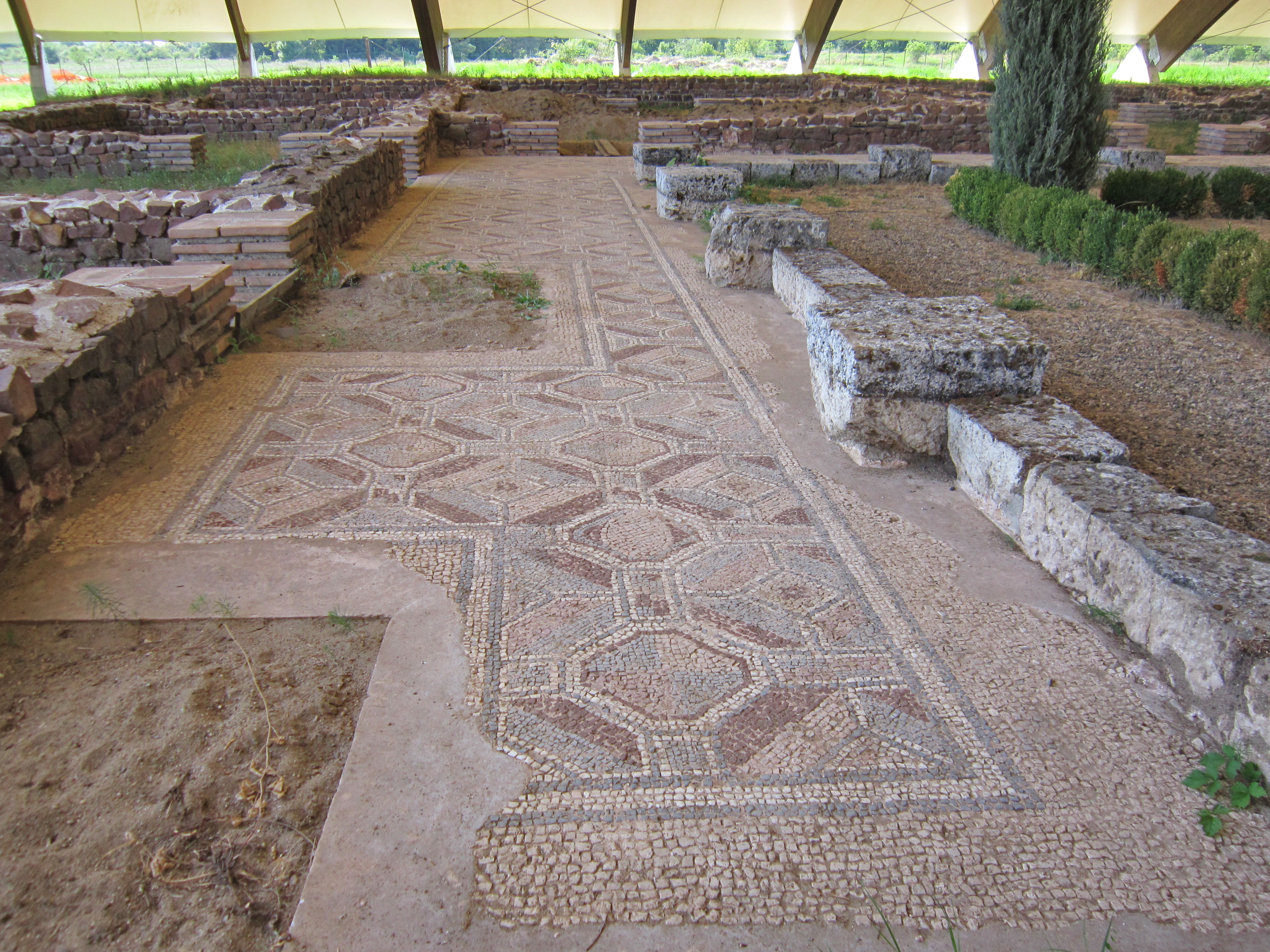
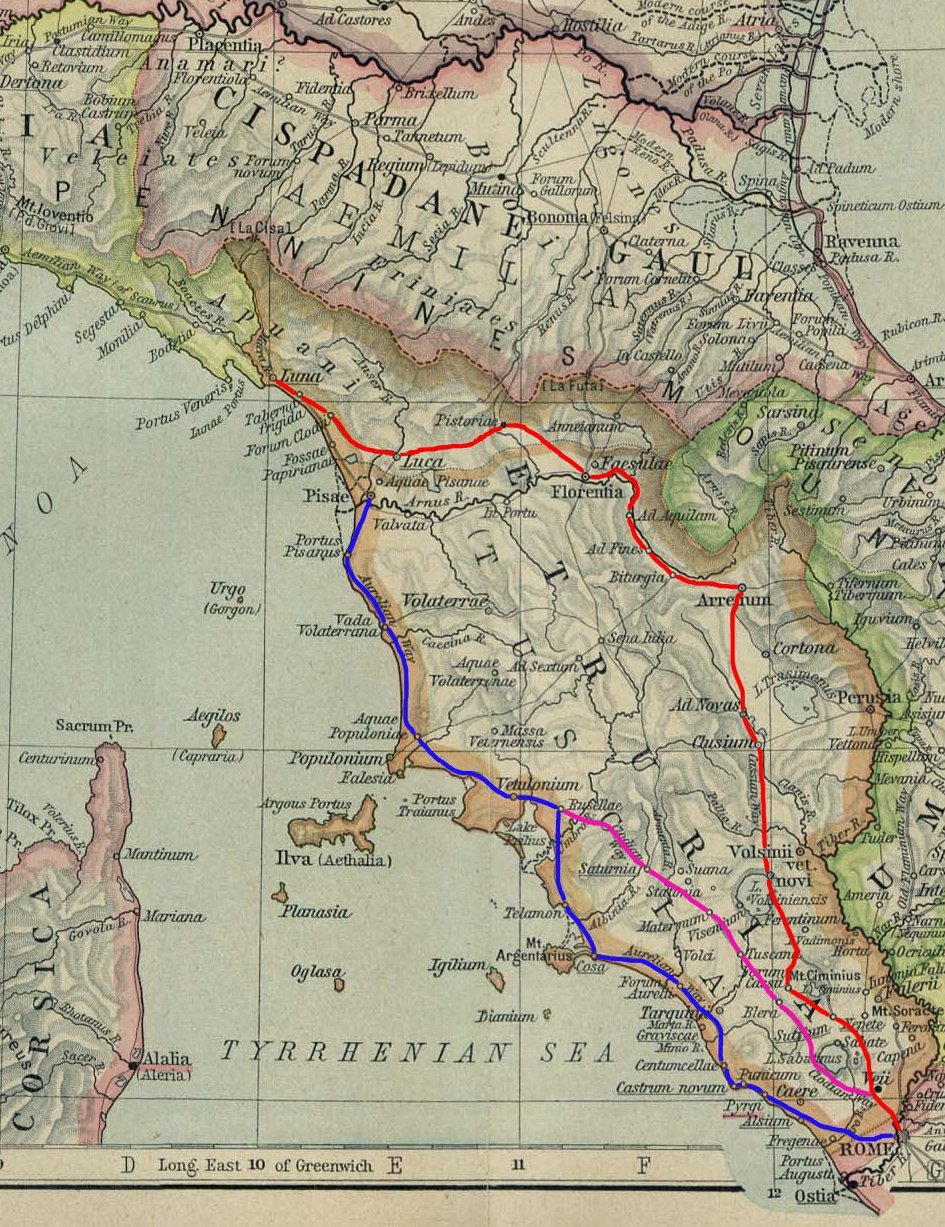
Via Aurelia
The ''Via Aurelia'' (Latin for "Aurelian Way") is a Roman road in Italy constructed in approximately 241 BC. The project was undertaken by Gaius Aurelius Cotta, who at that time was censor.Hornblower, Simon, & Antony Spawforth. ''The Oxford Classical Dictionary.'' 3rd ed. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1996. Cotta had a history of building roads for Rome, as he had overseen the construction of a military road in Sicily (as consul in 252 BC, during the First Punic War) connecting ''Agrigentum'' (modern Agrigento) and ''Panormus'' (modern Palermo). Background In the middle Republic, a series of roads were built throughout Italy to serve the needs of Roman expansion, including swift army movements and reasonably quick communication with Roman colonies spread throughout Italy. There also was the unintended (but beneficial) consequence of an increase in trade among Italian cities and with Rome. The roads were standardized to wide allowing two chariots to pass, and distance was mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
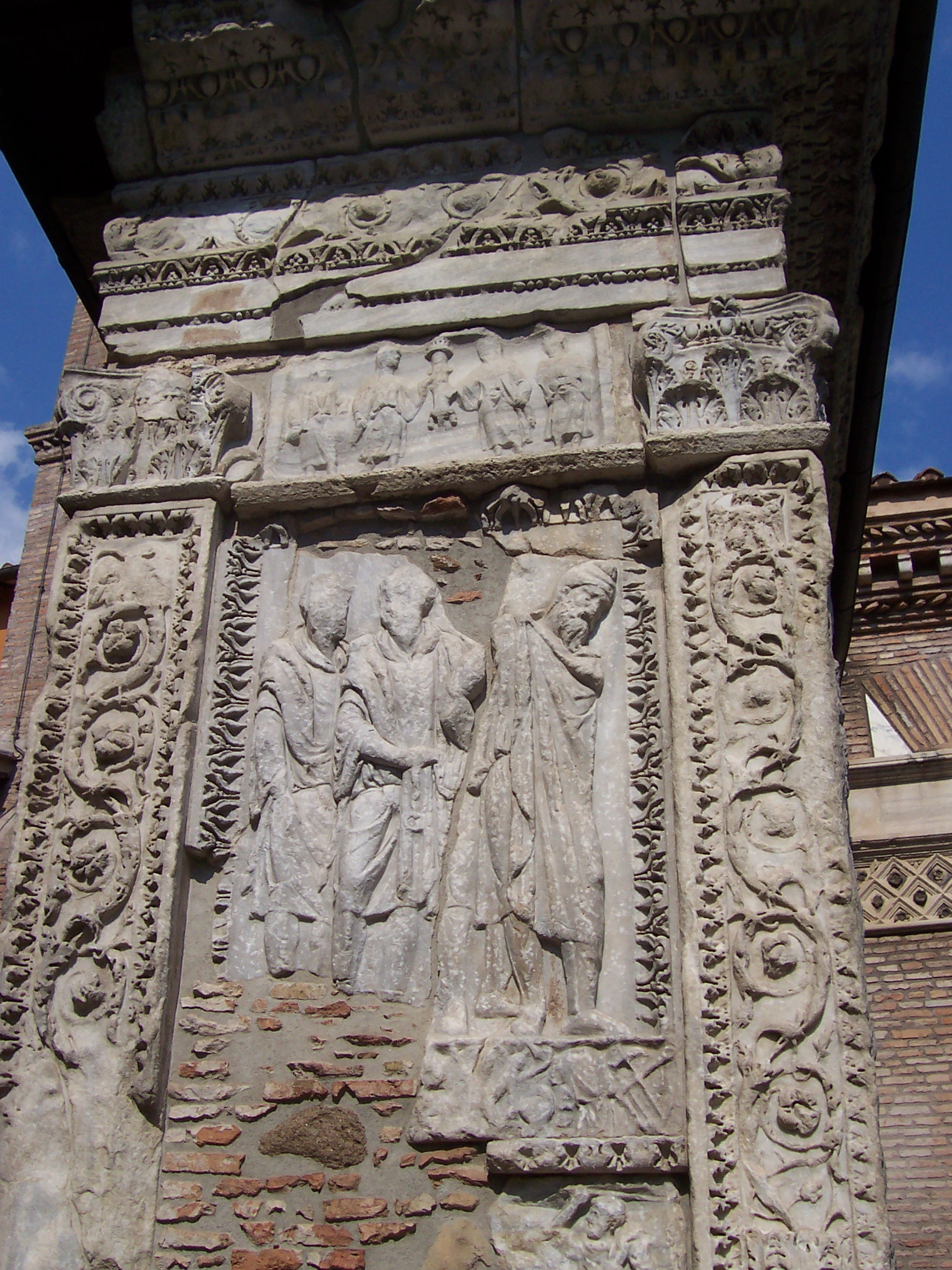
Constantine The Great
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterranea (now Niš, Serbia), he was the son of Flavius Constantius, a Roman army officer of Illyrian origin who had been one of the four rulers of the Tetrarchy. His mother, Helena, was a Greek Christian of low birth. Later canonized as a saint, she is traditionally attributed with the conversion of her son. Constantine served with distinction under the Roman emperors Diocletian and Galerius. He began his career by campaigning in the eastern provinces (against the Persians) before being recalled in the west (in AD 305) to fight alongside his father in Britain. After his father's death in 306, Constantine became emperor. He was acclaimed by his army at Eboracum ( York, England), and eventually emerged victorious in the civil wars against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banking In Ancient Rome
In ancient Rome there were a variety of officials tasked with banking. These were the ''argentarii'', ''mensarii'', ''coactores'', and ''nummulari''. The ''argentarii'' were money changers. The role of the ''mensarii'' was to help people through economic hardships, the ''coactores'' were hired to collect money and give it to their employer, and the ''nummulari'' minted and tested currency. They offered credit systems and loans. Between 260 and the fourth century CE Roman bankers disappear from the historical record, likely because of economic difficulties caused by the debasement of the currency. History The earliest banks in ancient Rome were located in temples. They would charge interest on loans, exchange money, and track their finances through written records. Due to the piety of the officials and employees of these temples, the upper class of ancient Rome trusted these places to protect and hold their wealth. Typically, their money was stored in multiple temples. This prac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punic Wars
The Punic Wars were a series of wars between 264 and 146BC fought between Rome and Carthage. Three conflicts between these states took place on both land and sea across the western Mediterranean region and involved a total of forty-three years of warfare. The Punic Wars are also considered to include the four-year-long revolt against Carthage which started in 241BC. Each war involved immense materiel and human losses on both sides. The First Punic War broke out on the Mediterranean island of Sicily in 264BC as a result of Rome's expansionary attitude combined with Carthage's proprietary approach to the island. At the start of the war Carthage was the dominant power of the western Mediterranean, with an extensive maritime empire, while Rome was a rapidly expanding power in Italy, with a strong army but no navy. The fighting took place primarily on Sicily and its surrounding waters, as well as in North Africa, Corsica and Sardinia. It lasted 23 years, until 241BC, when the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire, Rome's control rapidly expanded during this period—from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean world. Roman society under the Republic was primarily a cultural mix of Latin and Etruscan societies, as well as of Sabine, Oscan, and Greek cultural elements, which is especially visible in the Roman Pantheon. Its political organization developed, at around the same time as direct democracy in Ancient Greece, with collective and annual magistracies, overseen by a senate. The top magistrates were the two consuls, who had an extensive range of executive, legislative, judicial, military, and religious powe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahenobarbus (other)
Ahenobarbus (Latin, 'red-beard', literally 'bronze-beard'), also spelled Aenobarbus or Ænobarbus, may refer to: * Gnaeus Domitius Ahenobarbus (other), Romans * Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus (other), Romans * Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus, birth name of Nero, Roman emperor 54–68 * Frederick Barbarossa Frederick Barbarossa (December 1122 – 10 June 1190), also known as Frederick I (german: link=no, Friedrich I, it, Federico I), was the Holy Roman Emperor from 1155 until his death 35 years later. He was elected King of Germany in Frankfurt ..., known in Latin as ''Fridericus Ænobarbus'', Holy Roman Emperor 1155–1190 See also * {{human name disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etruscans
The Etruscan civilization () was developed by a people of Etruria in ancient Italy with a common language and culture who formed a federation of city-states. After conquering adjacent lands, its territory covered, at its greatest extent, roughly what is now Tuscany, western Umbria, and northern Lazio, as well as what are now the Po Valley, Emilia-Romagna, south-eastern Lombardy, southern Veneto, and western Campania. The earliest evidence of a culture that is identifiably Etruscan dates from about 900BC. This is the period of the Iron Age Villanovan culture, considered to be the earliest phase of Etruscan civilization, which itself developed from the previous late Bronze Age Proto-Villanovan culture in the same region. Etruscan civilization endured until it was assimilated into Roman society. Assimilation began in the late 4thcenturyBC as a result of the Roman–Etruscan Wars; it accelerated with the grant of Roman citizenship in 90 BC, and became complete in 27 BC, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porto Ercole - Vista Porto
Porto or Oporto () is the second-largest city in Portugal, the capital of the Porto District, and one of the Iberian Peninsula's major urban areas. Porto city proper, which is the entire municipality of Porto, is small compared to its metropolitan area, with an estimated population of just 231,800 people in a municipality with only 41.42 km2. Porto's metropolitan area has around 1.7 million people (2021) in an area of ,Demographia: World Urban Areas March 2010 making it the second-largest urban area in Portugal. It is recognized as a global city with a Gamma + rating from the |